Abstract
Acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which reduce the production of prostaglandin by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX), are widely used in children as antipyretic, analgesic, or anti-inflammatory drugs. They are known to be a major cause of pediatric drug allergies, which are diagnosed by a drug provocation test. The mechanism comprises an immunoglobulin E- or T cell-mediated immune reaction or pseudoallergy caused by the inhibition of COX-1. The diagnosis of NSAIDs drug allergy requires a differential, because there is a high cross-reactivity between NSAIDs. In this study, oral provocation tests with ibuprofen, acetaminophen, diclofenac and celecoxib were carried out, and various types of NSAIDs and acetaminophen allergies were observed. Safe drugs were recommended for each patient according to the test results. We report four cases of NSAIDs and acetaminophen allergy and include the results of oral provocation tests.
Go to : 
References
1. Orhan F, Karakas T, Cakir M, Akkol N, Bahat E, Sonmez FM, et al. Parental-reported drug allergy in 6-to 9-yr-old urban schoolchildren. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:82–5.
2. Rebelo Gomes E, Fonseca J, Araujo L, Demoly P. Drug allergy claims in children: from self-reporting to confirmed diagnosis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:191–8.

3. Kim SH. The current state of drug allergy test. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:630–42.
5. Stevenson DD, Szczeklik A. Clinical and pathologic perspectives on aspirin sensitivity and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:773–86.

6. Sánchez-Borges M, Capriles-Behrens E, Caballero-Fonseca F. Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:376–80.

7. Aberer W, Krä nke B. Provocation tests in drug hypersensitivity. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:567–84.

8. Aberer W, Bircher A, Romano A, Blanca M, Campi P, Fernandez J, et al. Drug provocation testing in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions: general considerations. Allergy. 2003; 58:854–63.

9. Romano A, Blanca M, Torres MJ, Bircher A, Aberer W, Brockow K, et al. Diagnosis of noni-mmediate reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Allergy. 2004; 59:1153–60.

10. Kvedariene V, Bencherioua AM, Messaad D, Godard P, Bousquet J, Demoly P. The accuracy of the diagnosis of suspected paracetamol (acetaminophen) hypersensitivity: results of a single-blinded trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1366–9.

11. Boussetta K, Ponvert C, Karila C, Bourgeois ML, Blic J, Scheinmann P. Hypersensitivity reactions to paracetamol in children: a study of 25 cases. Allergy. 2005; 60:1174–7.

12. Liccardi G, Cazzola M, De Giglio C, Manfredi D, Piscitelli E, D'Amato M, et al. Safety of celecoxib in patients with adverse skin reactions to acetaminophen (paracetamol) and other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2005; 15:249–53.
Go to : 
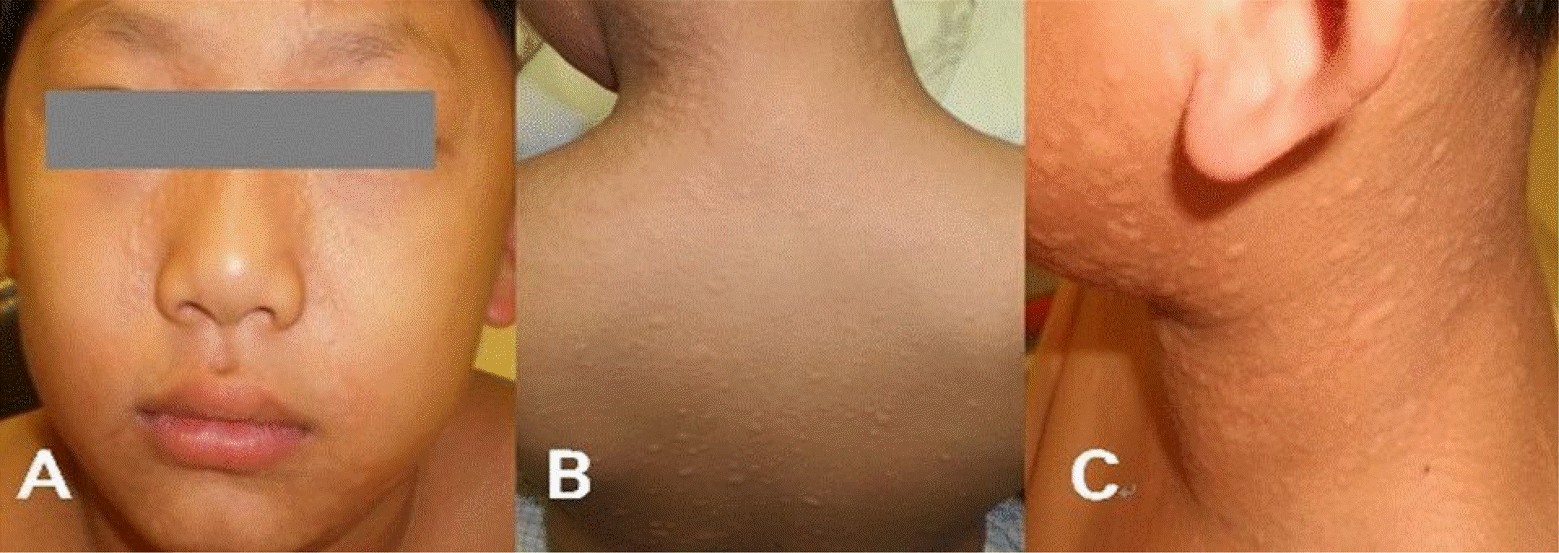 | Fig. 1.The figures show urticaria after oral provocation test of acetaminophen on the face (A), back (B) and neck (C). |
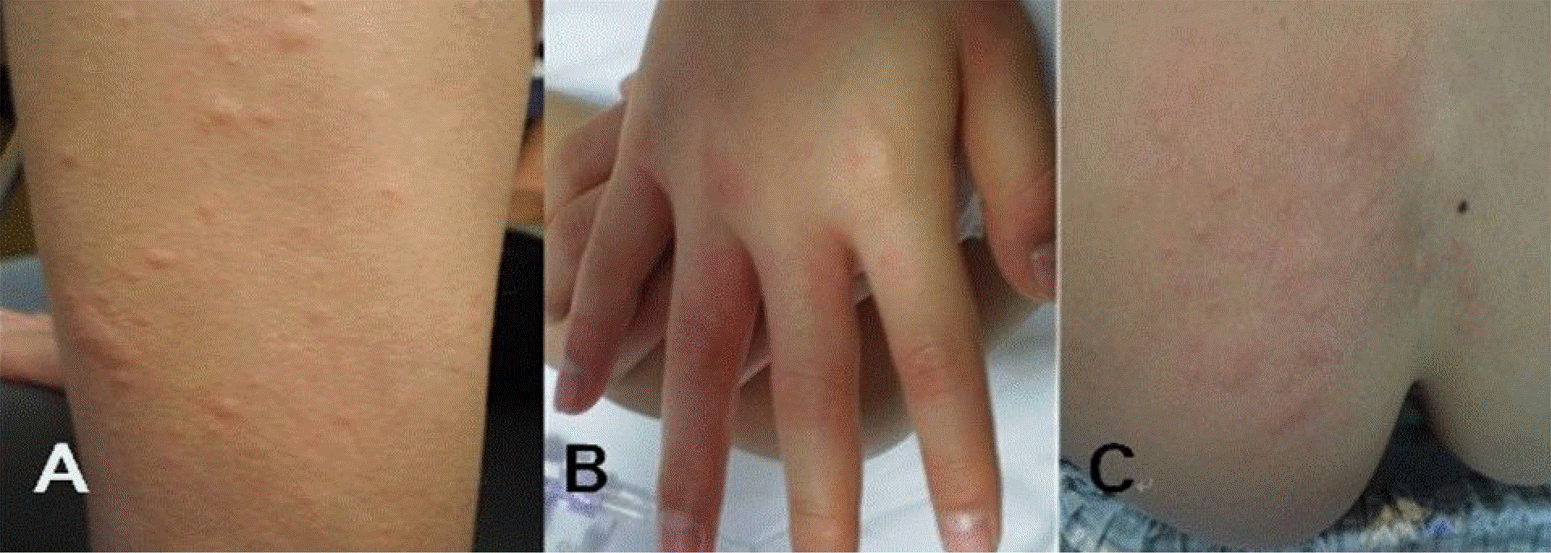 | Fig. 2.Urticaria on the leg (A) and swollen fingers (B) after acetaminophen provocation test, urticaria on bottom after ibuprofen provocation test (C). |
Table 1.
Results of Drug Allergy Tests in Four Cases




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download