Abstract
We recently encountered a very rare case of torsion of an intrascrotal testicular tumor in a 26-year-old male. Unlike the intra-abdominal undescended testis, intrascrotal spermatic cord torsion associated with a testicular tumor has rarely been reported. We write to report a case of intrascrotal spermatic cord torsion accompanied by a testicular tumor that had been overlooked preoperatively.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Nöske HD, Kraus SW, Altinkilic BM, Weidner W. Historical milestones regarding torsion of the scrotal organs. J Urol. 1998; 159:13–6.
2). Arce JD, Cortés M, Vargas JC. Sonographic diagnosis of acute spermatic cord torsion. Rotation of the cord: a key to the diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol. 2002; 32:485–91.
3). Shirakawa H, Kozakai N, Sugiura H, Hara S. Torsion of a testicular cancer in cryptorchidism prolapsing out of the inguinal canal: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2009; 55:783–5.
4). Takeshita H, Chiba K, Kitayama S, Noro A. Two cases of intrascrotal tumors complicated acute scrotum. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2008; 99:698–702.

5). Prando D. Torsion of the spermatic cord: the main gray-scale and doppler sonographic signs. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:648–61.

6). Vaidyanathan S, Hughes PL, Mansour P, Soni BM. Seminoma of testis masquerading as orchitis in an adult with paraplegia: proposed measures to avoid delay in diagnosing testicular tumours in spinal cord injury patients. Scientific World Journal. 2008; 8:149–56.

7). Ringdahl E, Teague L. Testicular torsion. Am Fam Physician. 2006; 74:1739–43.
Go to : 
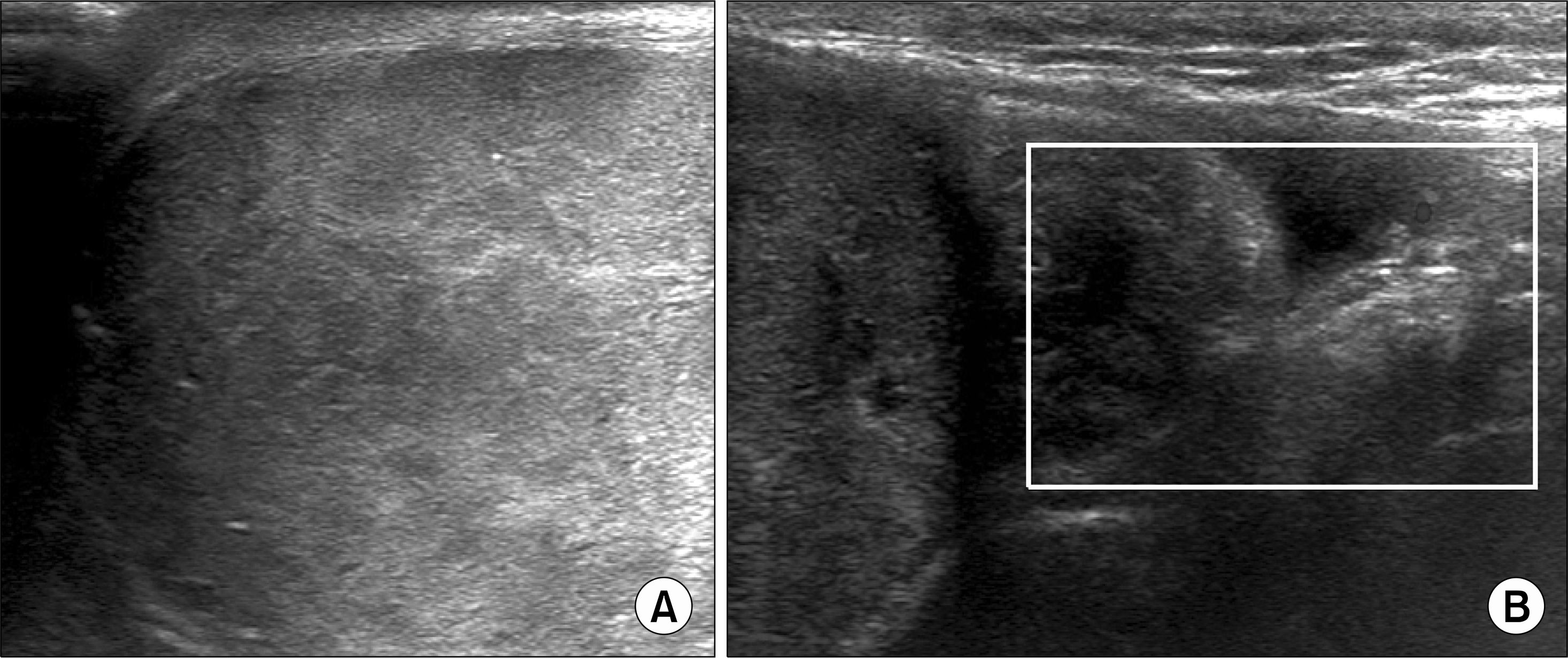 | Fig. 1.(A) Gray-scale sonography showing heterogenous echogenicity combined with hypoechoic lesions within the parenchyma. (B) Round shape epididymis without blood flow on Doppler sonography. |
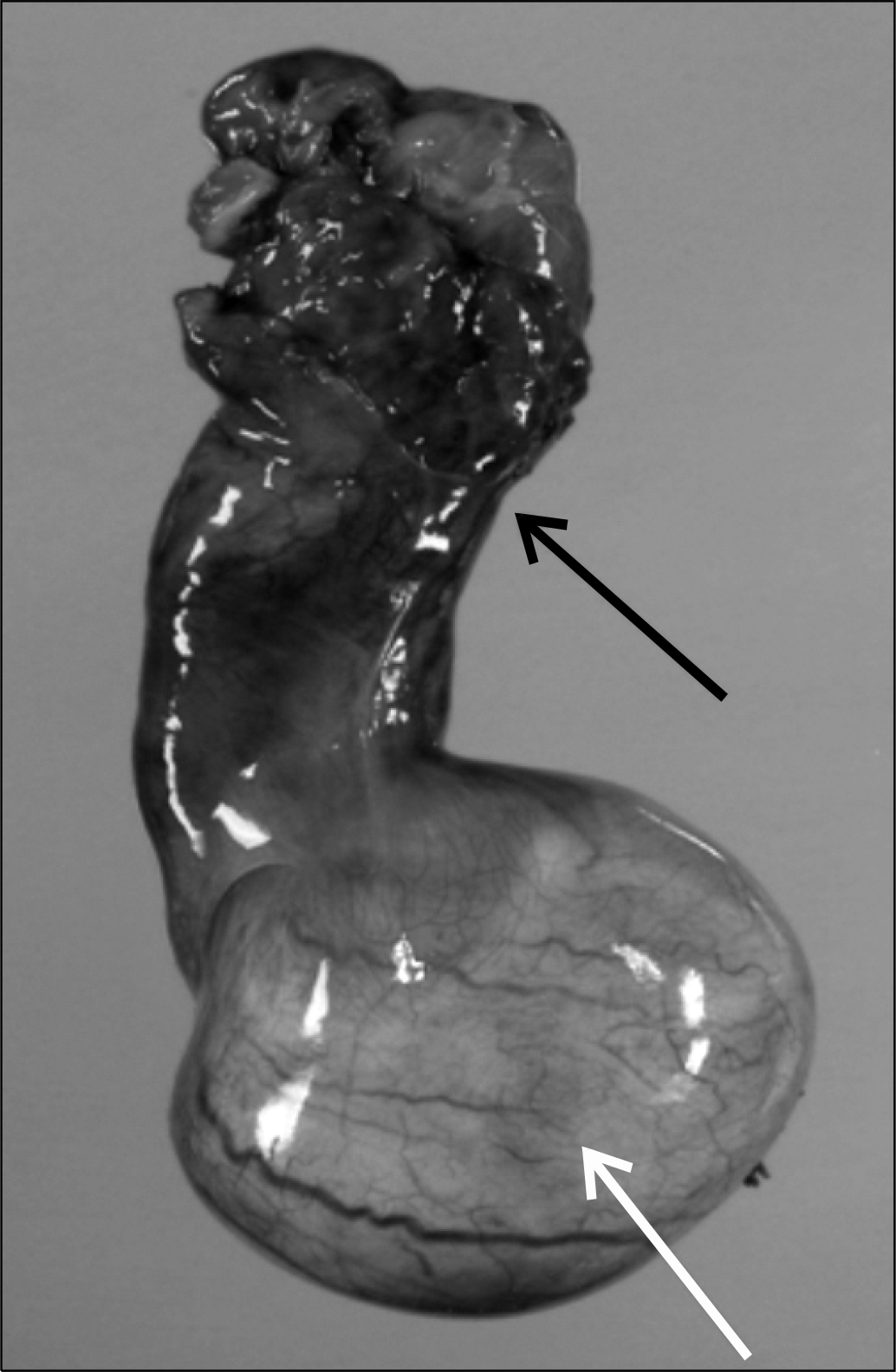 | Fig. 2.Bluish mass like lesions in seminiferous tubules transparently (white arrow) shown through albuginea with enlarged and congested epididymis (black arrow). |
 | Fig. 3.(A) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain revealed tumour cells with abundant clear to pale pink cytoplasm containing abundant glycogen with fibrous stromal network consistent with seminoma (×400). (B) Histopathology with H&E stain showing interstitial edema and hemorrhage at epididymis due to prolonged torsion (×100). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download