Abstract
Kikuchi's disease and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) present different clinical characteristics, especially in prognosis, although both diseases have the clinical similarity in initial presentations. Kikuchi's disease usually has a self-limiting clinical course, but HLH can be fatal. Accordingly, it is important that the differential diagnoses and decision as to initial treatment be made as soon as possible, at the time of clinical presentation. In the case of Kikuchi's disease accompanied with HLH, the decision concerning initial treatment can be very difficult, because these cases have been rarely reported and the prognosis is unpredictable. We report a case of a 21-year-old female diagnosed with Kikuchi's disease accompanied with HLH. Treatment involved steroid therapy, as for treatment of HLH. Recovery was complete. Kikuchi's disease with HLH can be completely treated with more aggressive therapy than used for Kikuchi's disease alone.
References
1. Bosch X, Guilabert A, Miquel R, Campo E. Enigmatic Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a comprehensive review. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004; 122:141–52.
2. Cho KJ, Lee SS, Khang SK. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis: a clinicopathologic study of 45 cases with in situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus and hepatitis B virus. J Korean Med Sci. 1996; 11:409–14.

4. Henter J, Horne A, AricóM , et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatric Blood Cancer. 2007; 48:124–31.

5. Imashuku S, Kuriyama K, Sakai R, et al. Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (EBV-HLH) in young adults: a report from the HLH study center. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003; 41:103–9.
6. Kim JW. Two cases of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following Kikuchi's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2007; 45:471–6.
7. Oh JH, Park JH, Hwang SY, et al. A case of Kikuchi's disease accompanied by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Infect Chemother. 2004; 36:185–8.
8. Lim GY, Cho B, Chung NG. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis preceded by Kikuchi disease in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2008; 38:756–61.

9. Kim YM, Lee YJ, Nam SO, Park SE, Kim JY, Lee EY. Hemophagocytic syndrome associated with Kikuchi's disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2003; 18:592–4.

10. Mahadeva U, Allport T, Bain B, Chan WK. Haemophagocytic syndrome and histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease). J Clin Pathol. 2000; 53:636–8.

11. Yilmaz M, Camci C, Sari I, et al. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease) mimicking systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of two cases. Lupus. 2006; 15:384–7.
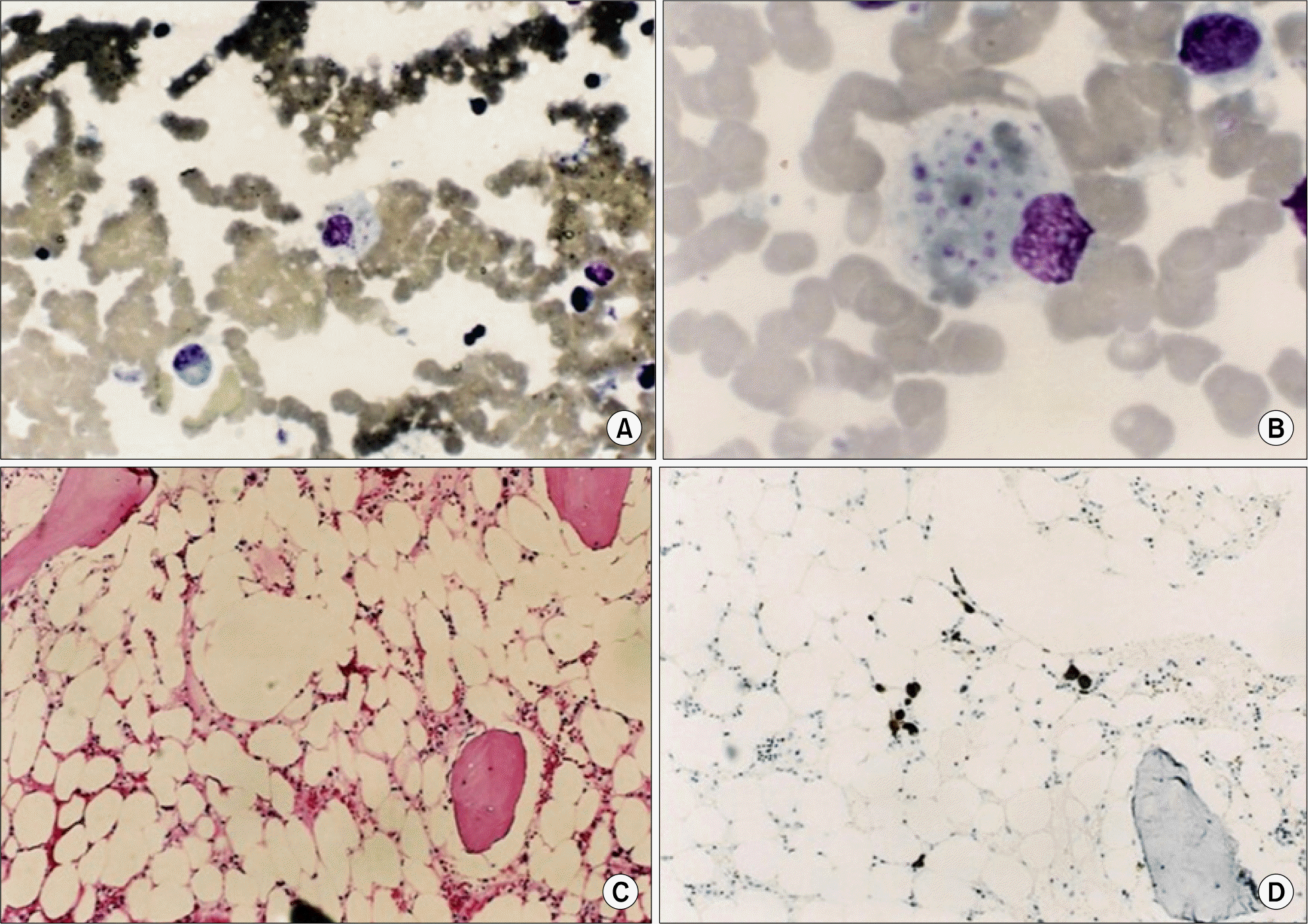
Fig. 1.
(A,B) BM aspiration: the monohistiocytes are increased in number, and some of them phagocytize RBC and platelet. (×400/×1,000, Wright-Giemsa stain) (C) BM section: the BM section is hypocellular (<10%) (×100, H&E stain) (D) BM section: EBV-LMP immunohistochemical staining result as positive in BM (×100, BM immunohistochemical stain).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download