Abstract
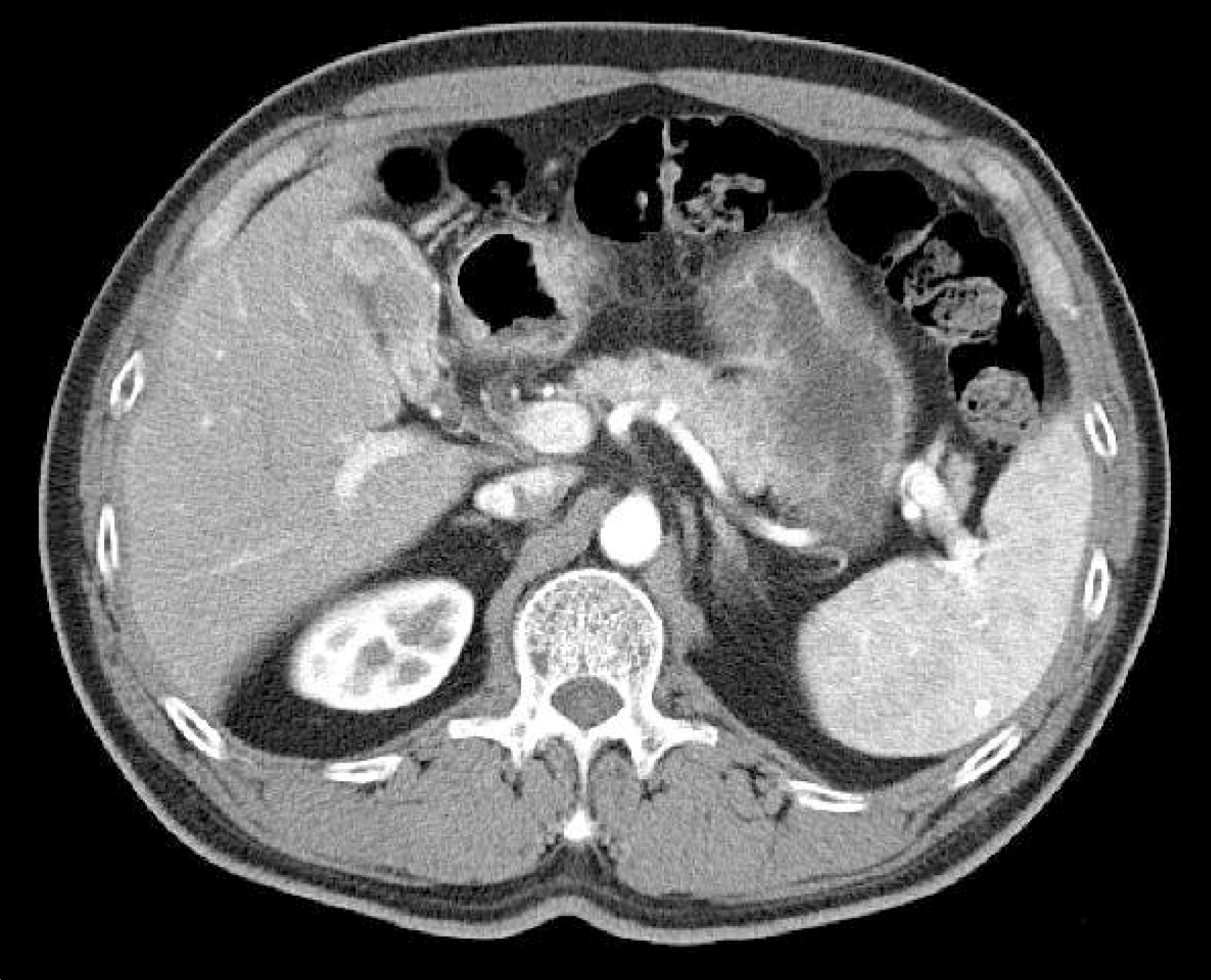
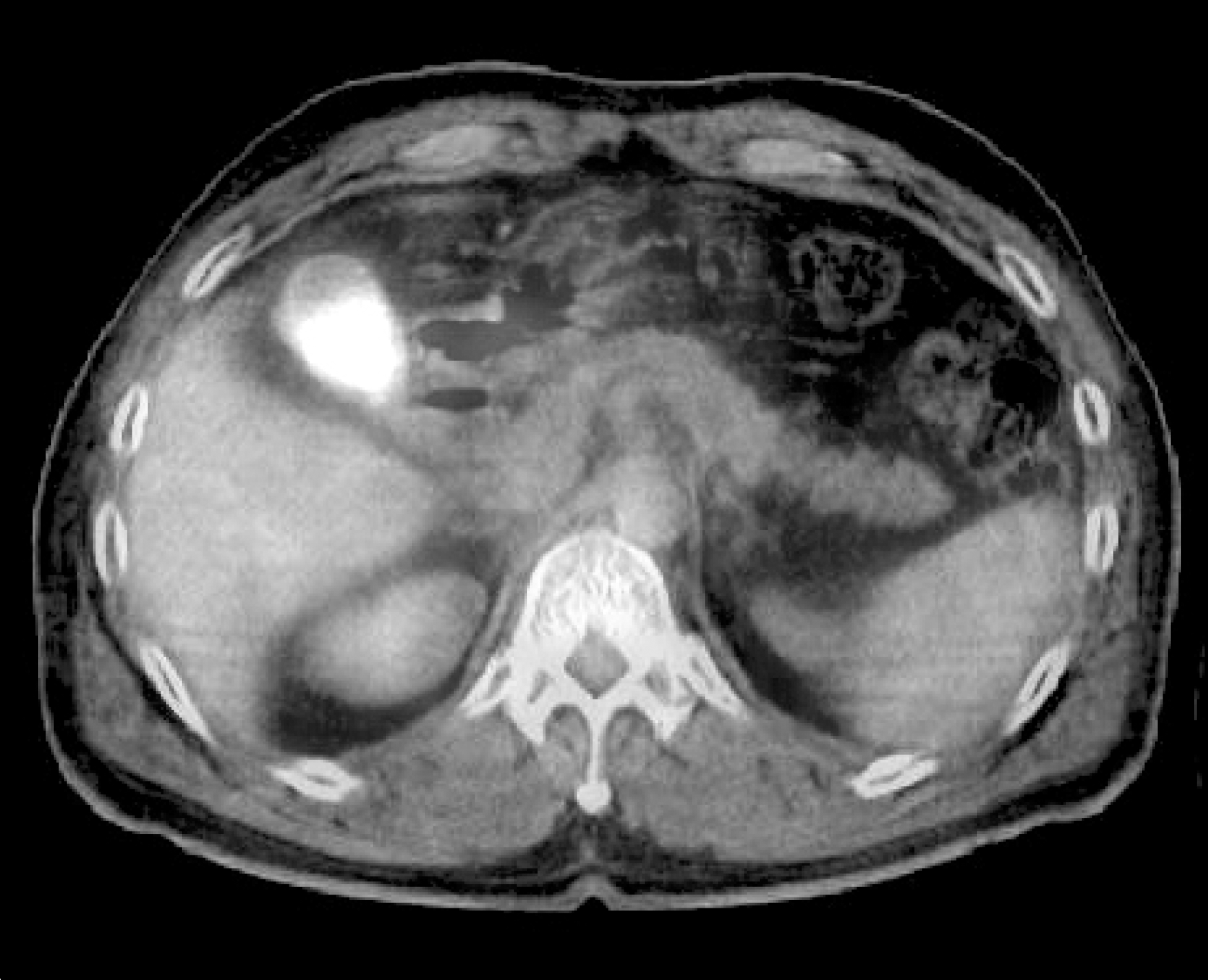
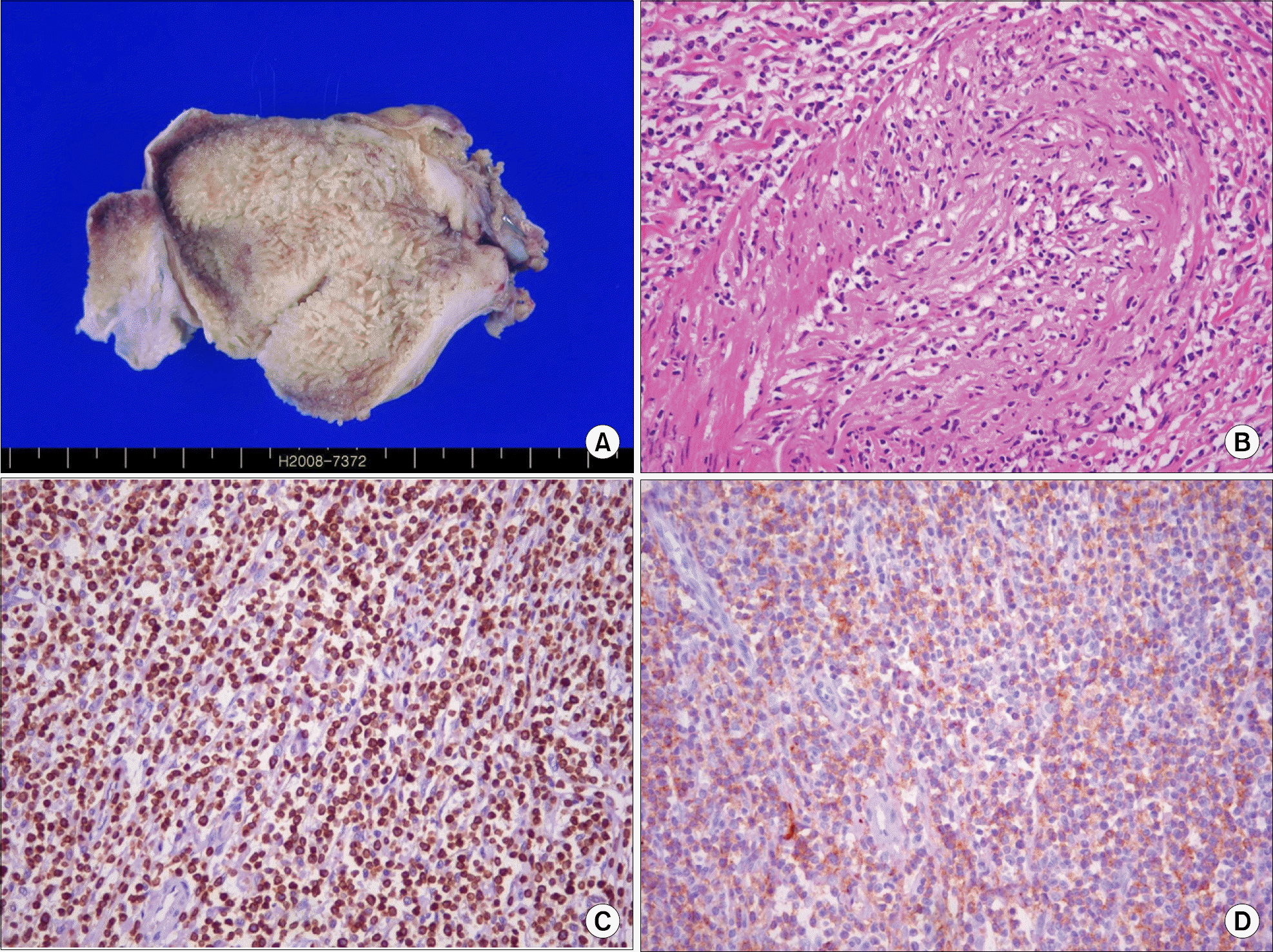
Extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma is a subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and this most commonly affects the nasal and paranasal cavities. Primary lymphoma of the gallbladder is extremely rare and solitary relapsed extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma of the gallbladder has not yet been reported in Korea. We experienced a case of a solitary relapsed extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma of the gallbladder. One year earlier, a 55-year-old man was diagnosed with extranodal NK-T cell lymphoma of the anus, and he underwent six cycles of chemotherapy with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine and prednisone), and he achieved complete remission. The patient was admitted for right upper quadrant pain. Computed tomography (CT) performed on readmission revealed gallbladder wall thickening. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) showed hypermetabolic lesions along the gallbladder wall. The specimen obtained at cholecystectomy revealed CD3(+) and CD56(+) lymphoma, which is characteristic of NK-T cell lymphoma.
References
1. Ko YH, Kim CW, Park CS, et al. REAL classification of malignant lymphomas in the Republic of Korea: incidence of recently recognized entities and changes in clinicopathologic features. Hematolymphoreticular Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. Revised European-American lymphoma. Cancer. 1998; 83:806–12.
2. AU WY, Pang A, Choy C, Chim CS, Kwong YL. Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in the diagnosis and monitoring of natural killer cell and EBV-positive lymphomas in immunocompetent patients. Blood. 2004; 104:243–9.

3. Suzuki R, Takeuchi K, Ohsima K, Nakamura S. Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma: diagnosis and treatment cues. Hematol Oncol. 2008; 26:66–72.
4. Takakuwa T, Dong Z, Nakatsuka S, et al. Frequent mutations of Fas gene in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma. Oncogene. 2002; 21:4702–5.

5. Jaffe ES, Chan JK, Su IJ, et al. Report of the workshop on nasal and related extranodal angiocentric T/natural killer cell lymphomas. Definitions, differential diagnosis, and epidemiology. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996; 20:103–11.
6. Sumi M, Tauchi T, Sashida G. et al. Natural killer cell lymphoma in the duodenum. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003; 44:201–4.
7. Ko YH, Ree HJ, Kim WS, Choi WH, Moon WS, Kim SW. Clinicopathologic and genotypic study of extranodal nasal type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and natural killer precursor lymphoma among Koreans. Cancer. 2000; 89:2106–16.
8. Mitropoulos FA, Angelopoulou MK, Siakantiris MP, et al. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the gall bladder. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000; 40:123–31.

9. Rosenberg SA, Diamond HD, Jaslowitz B, Craver LF. Lymphosarcoma: a review of 1269 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1961; 40:31–84.

10. Angelopoulou MK, Kontopidou FN, Pangalis GA. Adhesion molecules in B-chronic lymphoproliferative disorders. Semin Hematol. 1999; 36:178–97.
11. Tartar VM, Balfe DM. Lymphoma in the wall of the bile ducts: radiologic imaging. Gastrointest Radiol. 1990; 15:53–7.

12. Ono A, Tanoue S, Yamada Y, et al. Primary malignant lymphoma of the gallbladder: a case report and literature review. Br J Radiol. 2009; 82:e15–9.

13. Kim GE, Cho JH, Yang Wl, et al. Angiocentric lymphoma of the head and neck: patterns of systemic failure after radiation treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:54–63.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download