Abstract
Background
Etanercept is a recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) receptor fusion protein that inhibits TNF-α, a major mediator in the pathogenesis of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The purpose of our study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of etanercept therapy in children with steroid-refractory acute GVHD (aGVHD) (n=5) and chronic GVHD (cGVHD) (n=3).
Methods
Five males and 3 females were enrolled and their median age was 14.4 years (range, 2.1∼18.8). Etanercept 0.4 mg/kg per dose (maximum dose, 25 mg) was given subcutaneously twice weekly for 4 weeks followed by 0.4 mg/kg per dose (maximum dose, 25 mg) weekly for 4 weeks. At the time of initiation of etanercept, 5 patients had aGVHD grade III to IV (III=4, IV=1) and 3 patients had moderate to severe cGVHD (moderate=1, severe=2).
Results
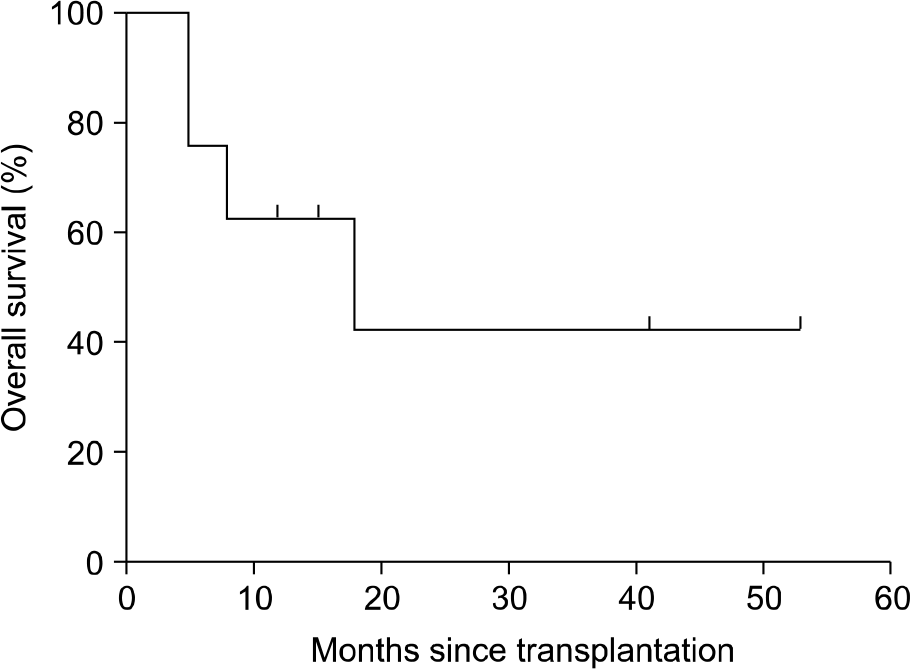
Overall, 6 of 8 patients (75%) responded to the treatment with etanercept, including 5 patients with aGVHD [n=3 complete response (CR), n=2 partial response (PR)] and 1 patient with cGVHD [n=1 PR, n=2 no response (NR)]. Clinical responses were most commonly seen in patients with refractory gut aGVHD. CMV reactivation occurred in 2 patients, bacterial infection in 1 patient, and fungal infection in 1 patient.
References
2. Kim SS. Treatment options in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41:1436–44.

3. Nogueira MC, Azevedo AM, Pereira SC, et al. Antitumor necrosis factor-α for the treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007; 40:1623–9.
4. Ritchie D, Seconi J, Wood C, Walton J, Watt V. Prospective monitoring of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma to predict the onset of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:706–12.
5. Uberti JP, Ayash L, Ratanatharathorn V, et al. Pilot trial on the use of etanercept and methylprednisolone as primary treatment for acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:680–7.

6. Wolff D, Roessler V, Steiner B, et al. Treatment of steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease with daclizumab and etanercept. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:1003–10.

7. Chiang KY, Abhyankar S, Bridges K, Godder K, Henslee-Downey JP. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor fusion protein as complementary treatment for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 2002; 73:665–7.
8. Busca A, Locatelli F, Marmont F, Ceretto C, Falda H. Recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor fusion protein as treatment for steroid refractory graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2007; 82:45–52.

9. Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15:825–8.
10. Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:945–56.
11. Urabe A. Clinical features of the neutropenic host: definitions and initial evaluation. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39(Suppl 1):S53–5.

12. Martin PJ, Schoch G, Fisher L, et al. A retrospective analysis of therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease: initial treatment. Blood. 1990; 76:1464–72.

13. MacMillan ML, Weisdorf DJ, Wagner JE, et al. Response of 443 patients to steroids as primary therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease: comparison of grading systems. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002; 8:387–94.

14. Kobbe G, Schneider P, Rohr U, et al. Treatment of severe steroid refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with infliximab, a chimeric human/mouse anti-TNFalpha antibody. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001; 28:47–9.
15. Couriel D, Saliba R, Hicks K, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade for the treatment of acute GVHD. Blood. 2004; 104:649–54.
16. Brown GR, Lindberg G, Meddings J, Silva M, Beutler B, Thiele D. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor ameliorates murine intestinal graft-versus-host disease. Gastroenterology. 1999; 116:593–601.

17. Andolina M, Rabusin M, Maximova N, Di Leo G. Etanercept in graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000; 26:929.

18. Coriel D, Saliba R, Hicks K, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α blockade for the treatment of acute GVHD. Blood. 2004; 104:649–54.
19. Patriarca F, Sperotto A, Damiani D, et al. Infliximab treatment for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Haematologica. 2004; 89:1352–9.
20. Holler E, Kolb HJ, Möller A, et al. Increased serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha precede major complications of bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990; 75:1011–6.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the patients and donors
Abbreviations: P, patient; D, donor; M, male; F, female; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; SAA, severe aplastic anemia; WAS, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; DLBL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; U, unrelated; R, related; BM, bone marrow; CB, cord blood; PB, pheripheral blood; Bu, busulfan; Flu, fludarabine; Cy, cyclophosphamide; ATG, anti-thymocyte globulin g; CsA, cyclosporine A; MTX, methotrexate; PD, prednisolone; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil.
Table 2.
Days of immunosuppressive treatments
Table 3.
Treatment with etanercept in patients with aGVHD
Table 4.
Treatment with etanercept in patients with cGVHD
Table 5.
Clinical outcomes of the patients treated with etanercept




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download