Abstract
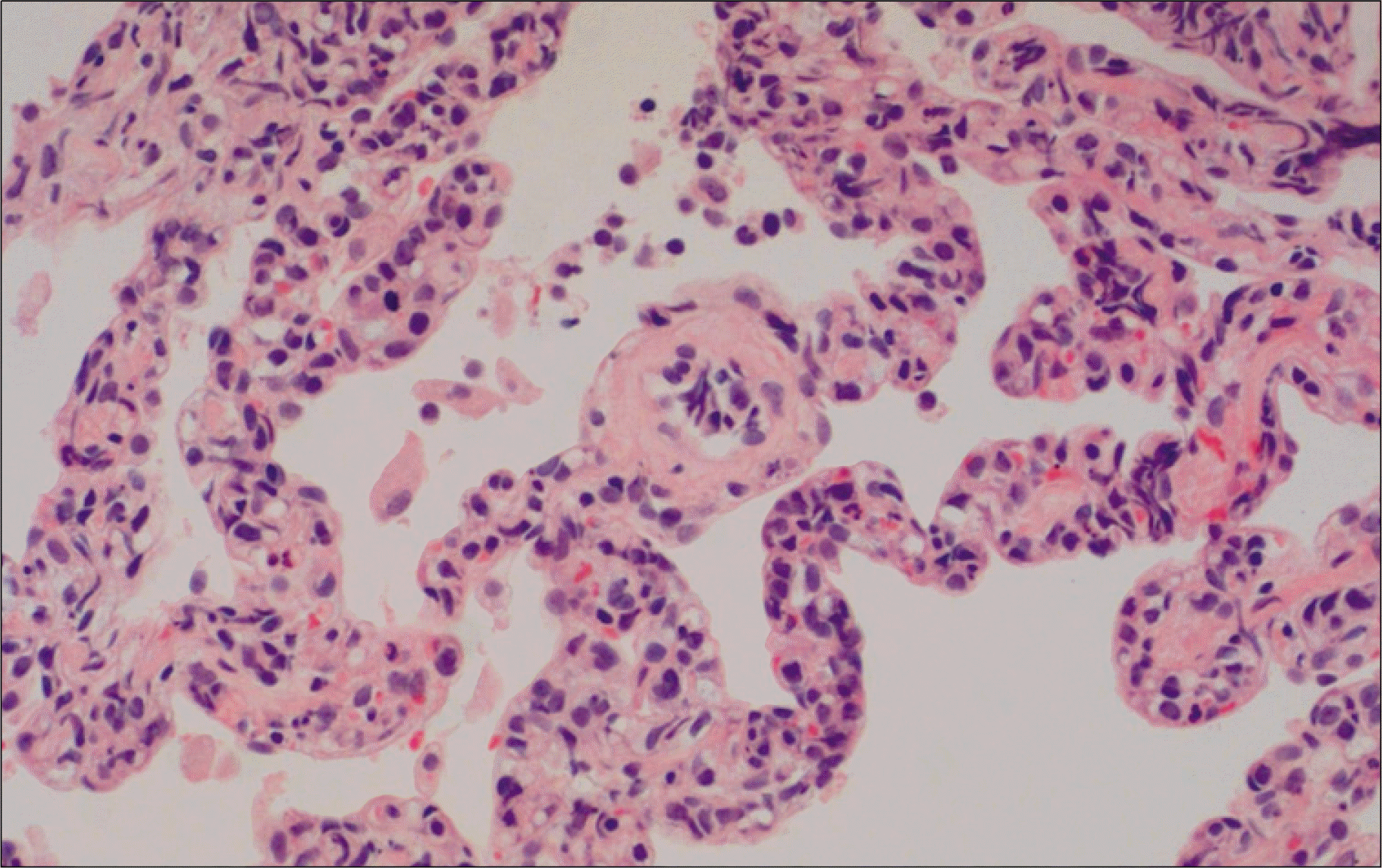
Intravascular lymphoma (IVL) is a rare form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that is characterized by the preferential growth of malignant lymphocytes within blood vessels. Pulmonary presentation of IVL is uncommon, and only a few cases have been reported in Korea. Here, we report on a 59-year-old woman with relapsed intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in the lungs. She had been treated with 6 cycles of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, and prednisolone (R-CHOP) combination chemotherapy for intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in the nasal cavity, and was followed up regularly with no evidence of disease recurrence. About 1 year later, her chest computed tomography showed extensive ground-glass opacity, suggesting interstitial lung disease and, interestingly, diffuse pulmonary fluorodeox-yglucose (FDG) uptake was observed in positron emission tomography (PET). We performed bronchoscopy, bronchoalveolar lavage, and transbronchial lung biopsy. Pathology revealed relapsed intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in the lungs, and she commenced ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, prednisolone (IMVP-16/PD) salvage chemotherapy. After 3 cycles of chemotherapy, PET showed no abnormal FDG uptake. We suggest that a primary or relapsed pulmonary IVL should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unexplained interstitial lung disease and that PET appears be useful in evaluating pulmonary IVL.
REFERENCES
1). Ponzoni M., Ferreri AJ., Campo E, et al. Definition, diagnosis, and management of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: proposals and perspectives from an international consensus meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:3168–73.

2). Ferreri AJ., Campo E., Seymour JF, et al. Intravascular lymphoma: clinical presentation, natural history, management and prognostic factors in a series of 38 cases, with special emphasis on the 'cutaneous variant'. Br J Haematol. 2004. 127:173–83.
3). Murase T., Nakamura S., Kawauchi K, et al. An Asian variant of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: clinical, pathological and cytogenetic approaches to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with haemo-phagocytic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2000. 111:826–34.

4). Aouba A., Diop S., Saadoun D, et al. Severe pulmonary arterial hypertension as initial manifestation of intravascular lymphoma: case report. Am J Hematol. 2005. 79:46–9.

5). Chan VL., Lee CK., Leung WS., Lin SY., Chu CM. A 57-year-old woman with fever and abnormal chest CT findings. Chest. 2006. 130:924–7.

6). Gabor EP., Sherwood T., Mercola KE. Intravascular lymphomatosis presenting as adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Hematol. 1997. 56:155–60.

7). Ko YH., Han JH., Go JH, et al. Intravascular lymphomatosis: a clinicopathological study of two cases presenting as an interstitial lung disease. Histopathology. 1997. 31:555–62.

8). Yousem SA., Colby TV. Intravascular lymphomatosis presenting in the lung. Cancer. 1990. 65:349–53.

9). Odawara J., Asada N., Aoki T, et al. 18F-Fluorodeoxy-glucose positron emission tomography for evaluation of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2007. 136:684.

10). Hofman MS., Fields P., Yung L., Mikhaeel NG., Ireland R., Nunan T. Meningeal recurrence of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: early diagnosis with PET-CT. Br J Haematol. 2007. 137:386.

11). Bouzani M., Karmiris T., Rontogianni D, et al. Disseminated intravascular B-cell lymphoma: clinicopathological features and outcome of three cases treated with anthracycline-based immunochemotherapy. Oncologist. 2006. 11:923–8.

12). Ferreri AJ., Campo E., Ambrosetti A, et al. Anthracycline-based chemotherapy as primary treatment for intravascular lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2004. 15:1215–21.

13). Mori S., Itoyama S., Mohri N, et al. Cellular characteristics of neoplastic angioendotheliosis. An immunohistological marker study of 6 cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985. 407:167–75.
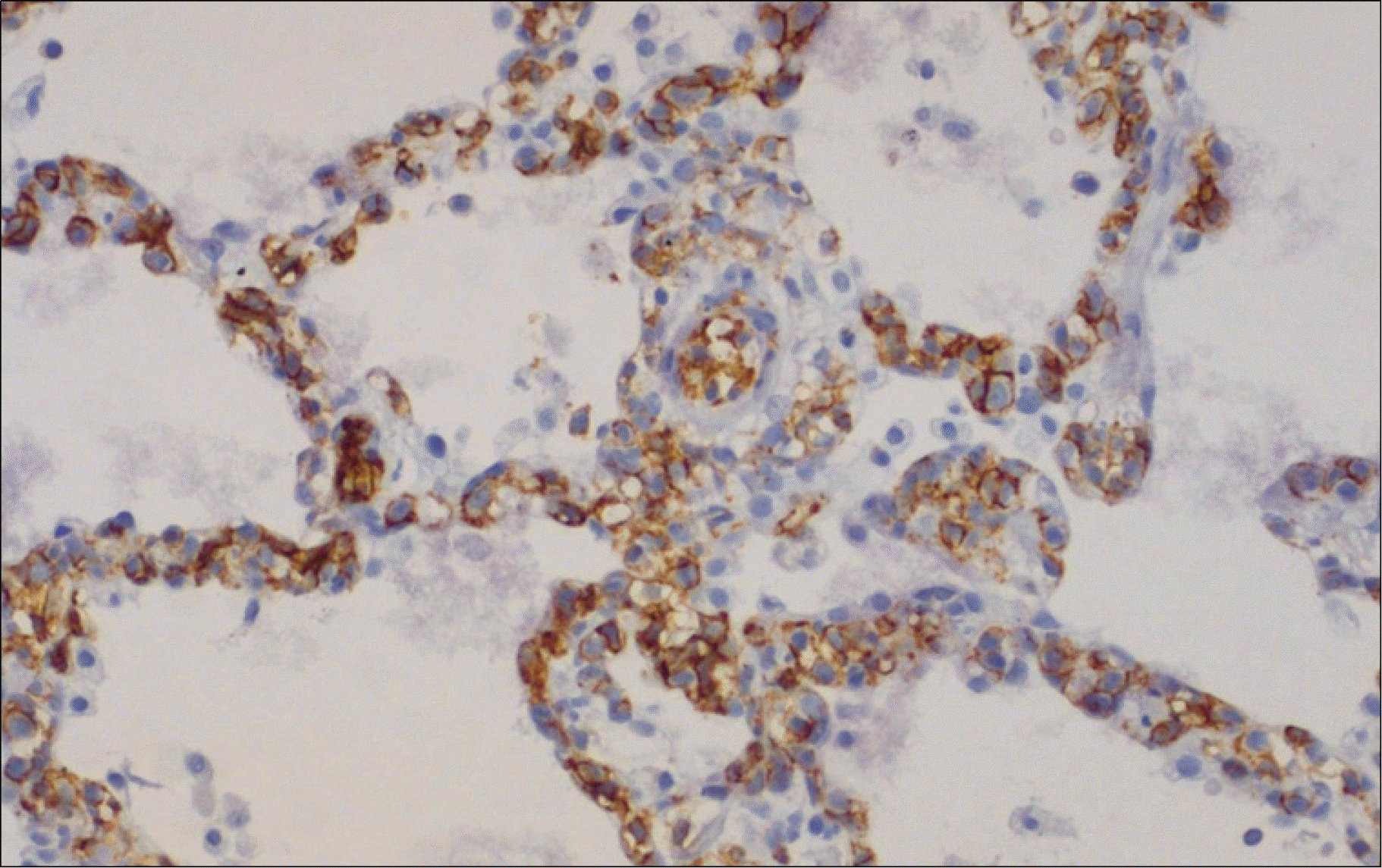
Fig. 2
Lung window of a coronal reformatted CT scan shows extensive ground-glass opacity in both lungs except for some areas (arrows). Ground-glass opacity lesions suggest the presence of interstitial disease process.
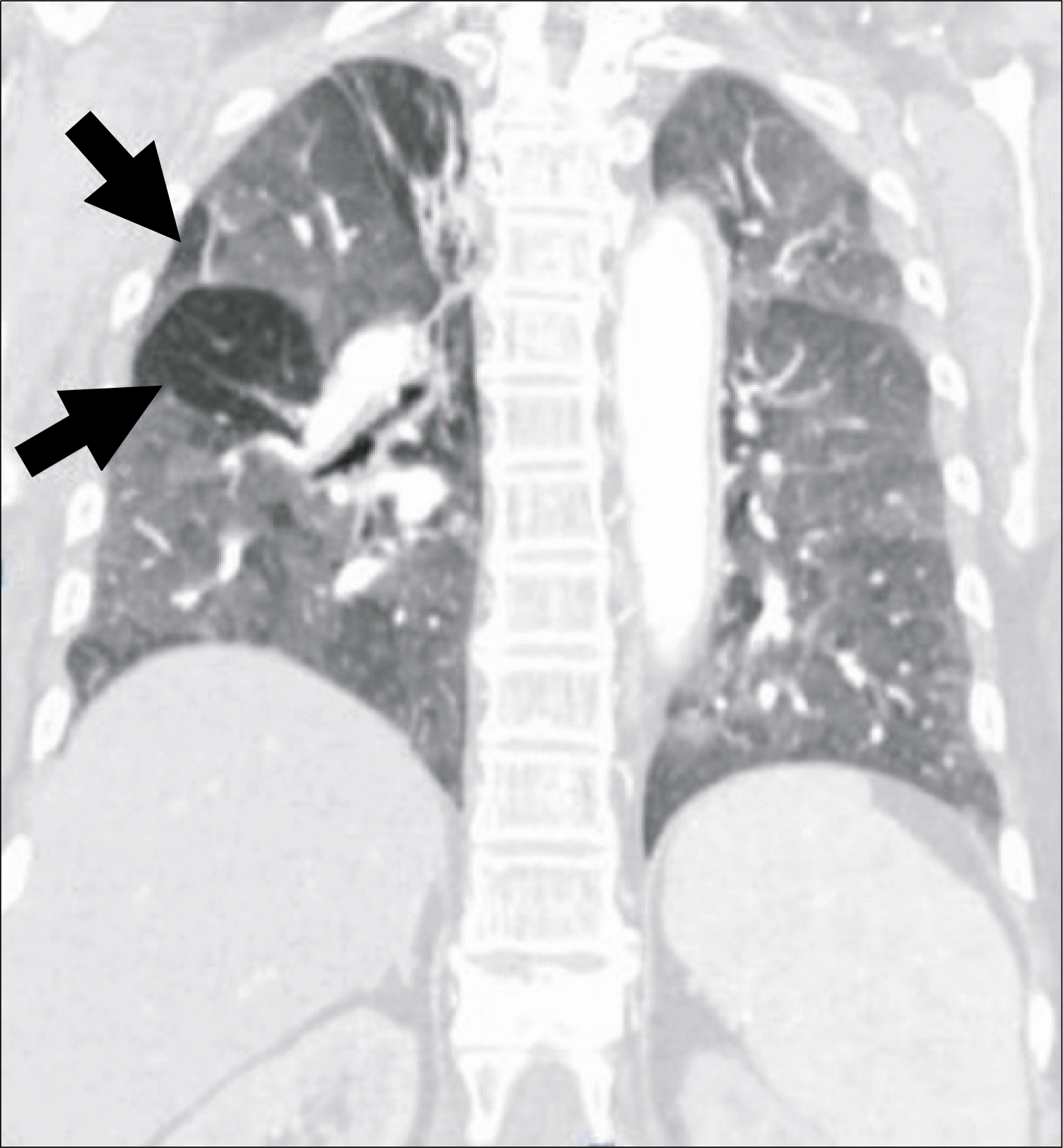
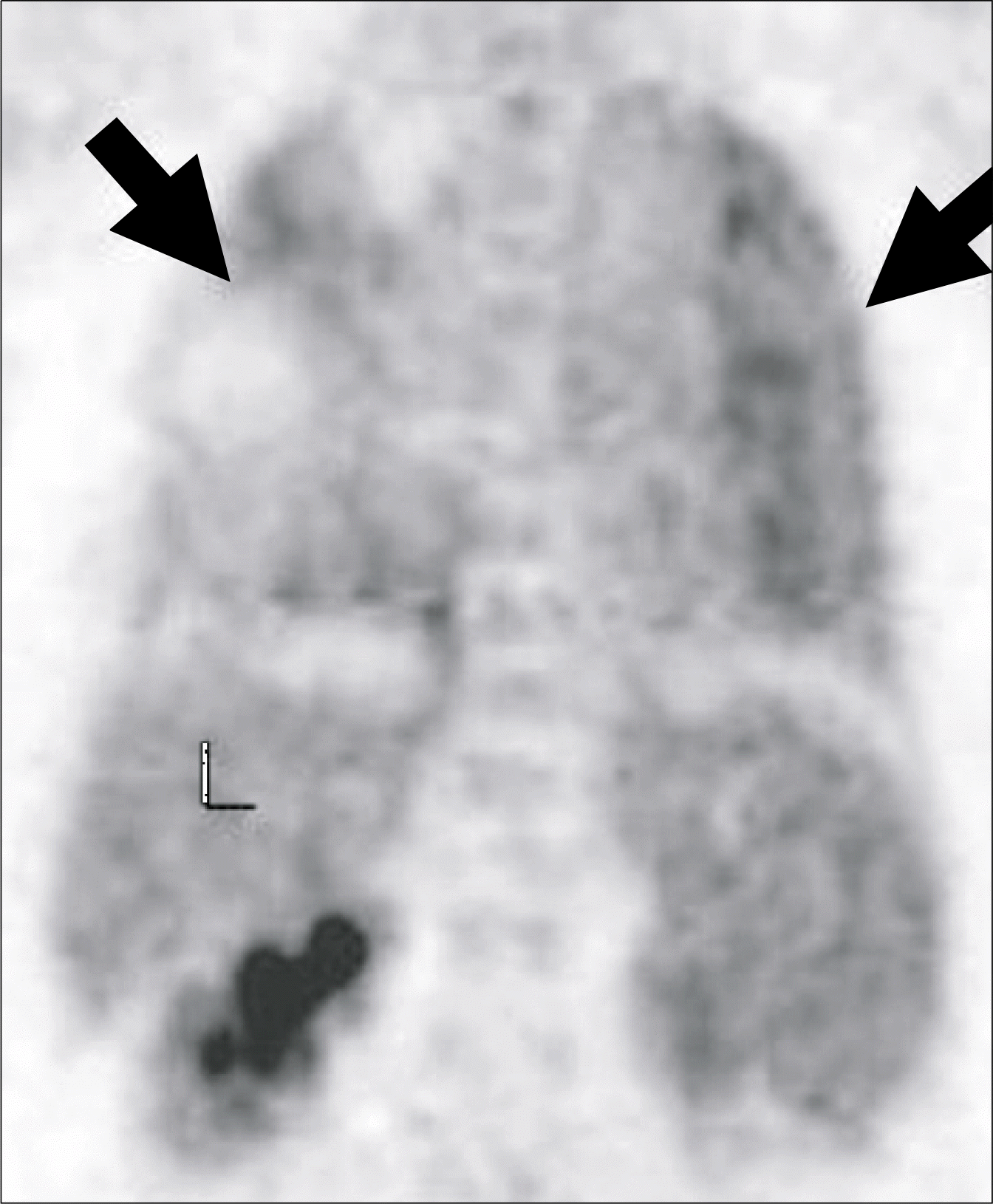
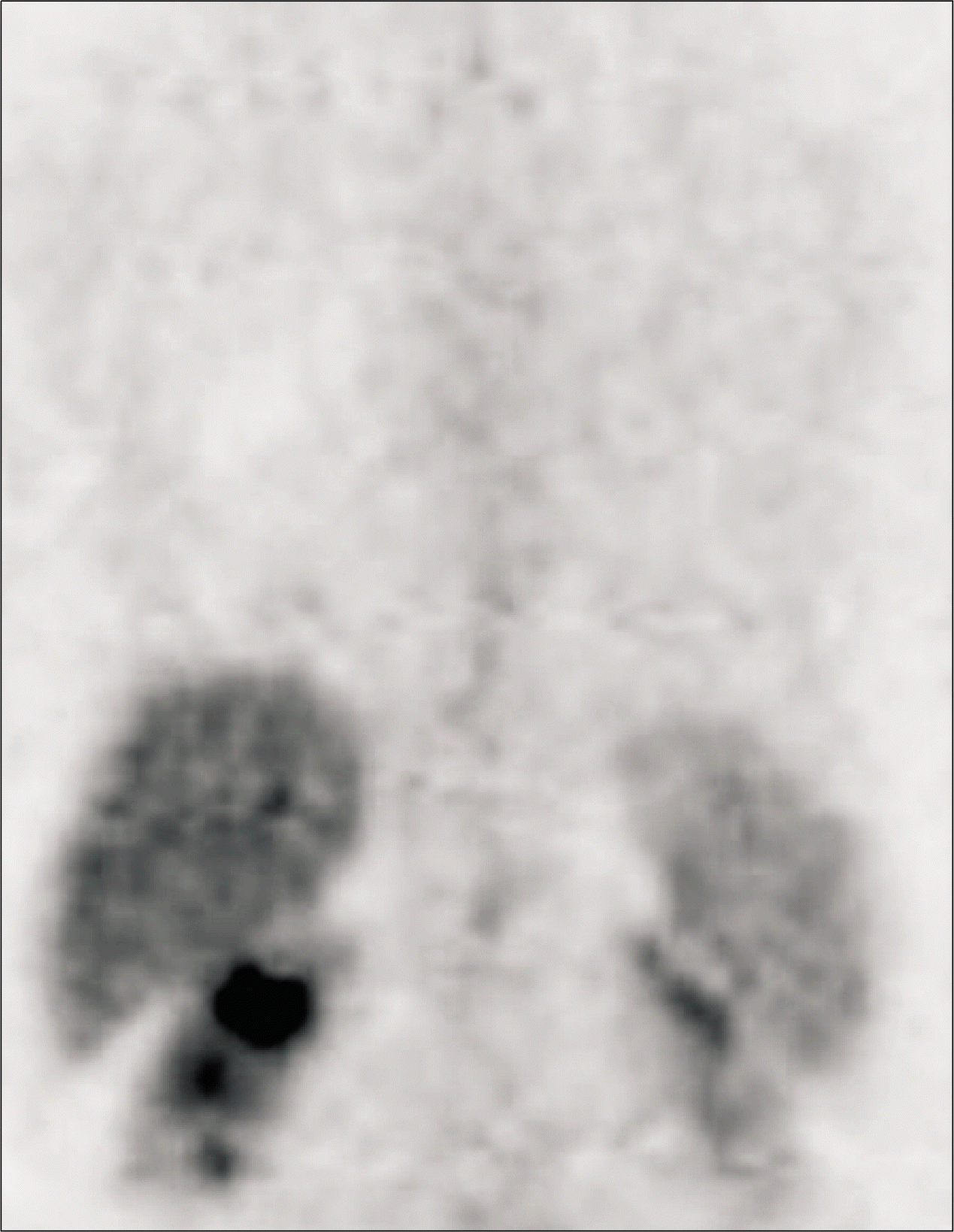
Fig. 3
Maximum intensity projection image of PET demonstrates diffuse FDG uptake in both lungs (arrows). Abbreviation: L, liver.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download