Abstract
We report the unusual case of an APL patient with a familial t(9;15)(q34;q22) and acquired t(15;17) (q22;q21). This is unique in that the patient had a constitutional abnormality with the same breakpoints as those observed in the tumor clone from the APL. It is unclear if the breakpoint, 15q22, in the constitutional aberration influenced the induction of the PML/RARA translocation in the APL. If a specific translocation in a patient with leukemia does not go away with clinical improvement, a congenital or familial chromosomal abnormality should be considered. Additional patients with similar findings are needed to understand the pathogenesis of these events.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Garcia-Casado Z., Cervera J., Valencia A, et al. A t(17;20)(q21;q12) masking a variant t(15;17)(q22;q21) in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006. 168:73–6.
2). Yamamoto K., Hamaguchi H., Nagata K., Kobayashi M., Takashima T., Taniwaki M. A new complex translocation (15;20;17)(q22;p13;q21) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1998. 101:89–94.

3). Eclache V., Viguie F., Frocrain C, et al. A new variant t(6;15;17)(q25;q22;q21) in acute promyelocytic leukemia: fluorescence in situ hybridization confirmation. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005. 159:69–73.

4). Fujishima M., Takahashi N., Miura I, et al. A PML/RARA chimeric gene on chromosome 2 in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3) associated with a new variant translocation: t(2;15;17)(q21;q22; q21). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2000. 120:80–2.
5). Osella P., Wyandt H., Vosburgh E., Milunsky A. Report of a variant t(1;15;17)(p36;q22;q21.1) in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991. 57:201–7.

6). Macedo Silva ML., Land M., Heller A, et al. New rearrangement t(3;17)(q26.3;q12) in an AML patient with a poor outcome. Oncol Rep. 2005. 14:663–6.

7). Nicci C., Ottaviani E., Luatti S, et al. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a new case of t(5;17) (q35;q21) variant acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2005. 19:470–2.
9). Hecht F. Risks of hematologic malignancy with constitutional chromosome abnormalities. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987. 24:375–7.

10). Maserati E., Aprili F., Vinante F, et al. Trisomy 8 in myelodysplasia and acute leukemia is constitutional in 15∼20% of cases. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002. 33:93–7.

11). Weinstein HJ. Congenital leukaemia and the neonatal myeloproliferative disorders associated with Down's syndrome. Clin Hematol. 1978. 7:147–54.

12). Kurkjian C., Patel S., Kamble R., Dunn ST., Kern W., Kharfan-Dabaja MA. Acute promyelocytic leukemia and constitutional trisomy 21. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006. 165:176–9.

13). Panani AD., Pappa V., Raptis SA. Novel constitutional translocations t(3;5)(p25;q22) and t(1;14)(p31;q21) in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2004. 83:156–9.

14). Ledbetter DH., Rich DC., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Carey JC. Precise localization of NF1 to 17q11.2 by balanced translocation. Am J Hum Genet. 1989. 44:20–4.
15). Turleau C., de Grouchy J., Chavin-Colin F, et al. Cytogenetic forms of retinoblastoma: their incidence in a survey of 66 patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1985. 16:321–34.

16). Riccardi VM., Sujansky E., Smith AC., Francke U. Chromosomal imbalance in the Aniridia-Wilms' tumor association: 11p interstitial deletion. Pediatrics. 1978. 61:604–10.

17). Yunis JJ., Ramsay N. Retinoblastoma and subband deletion of chromosome 13. Am J Dis Child. 1978. 132:161–3.

18). Sreekantaiah C., Han T., Baer MR., Sandberg AA. Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia in a patient with a constitutional inv(4). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989. 39:119–23.

19). Mozziconacci MJ., Sobol H., Philip N, et al. Constitutional balanced pericentric inversions of chromosome X, 2, and 5 in myeloid malignancies. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1998. 107:28–31.
20). Ganly P., McDonald M., Spearing R., Morris CM. Constitutional t(5;7)(q11;p15) rearranged to acquire monosomy 7q and trisomy 1q in a patient with mye-lodysplastic syndrome transforming to acute myelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004. 149:125–30.
21). Becher R., Mahmoud HK., Schaefer UW., Schmidt CG. Ph-positive CML in a family with a constitutional Robertsonian translocation 14;15. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1985. 18:229–34.

22). Qian J., Xue Y., Sun J, et al. Constitutional Robertsonian translocations in (9;22)-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002. 132:79–80.

23). Swan J., Lee CL., Yhap M. Constitutional t(5;11) (p15.3;q23) in an adolescent male with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2001. 128:178–80.
24). Fraccaro M., Zuffardi O., Buhler E, et al. Deficiency, transposition, and duplication of one 15q region may be alternatively associated with Prader-Willi (or a similar) syndrome. Analysis of seven cases after varying ascertainment. Hum Genet. 1983. 64:388–94.

25). Sandig KR., Mucke J., Veit H. Trisomy 9p resulting from de novo 9/15 translocation and a 9p isochromosome. Hum Genet. 1979. 52:175–8.
Go to : 
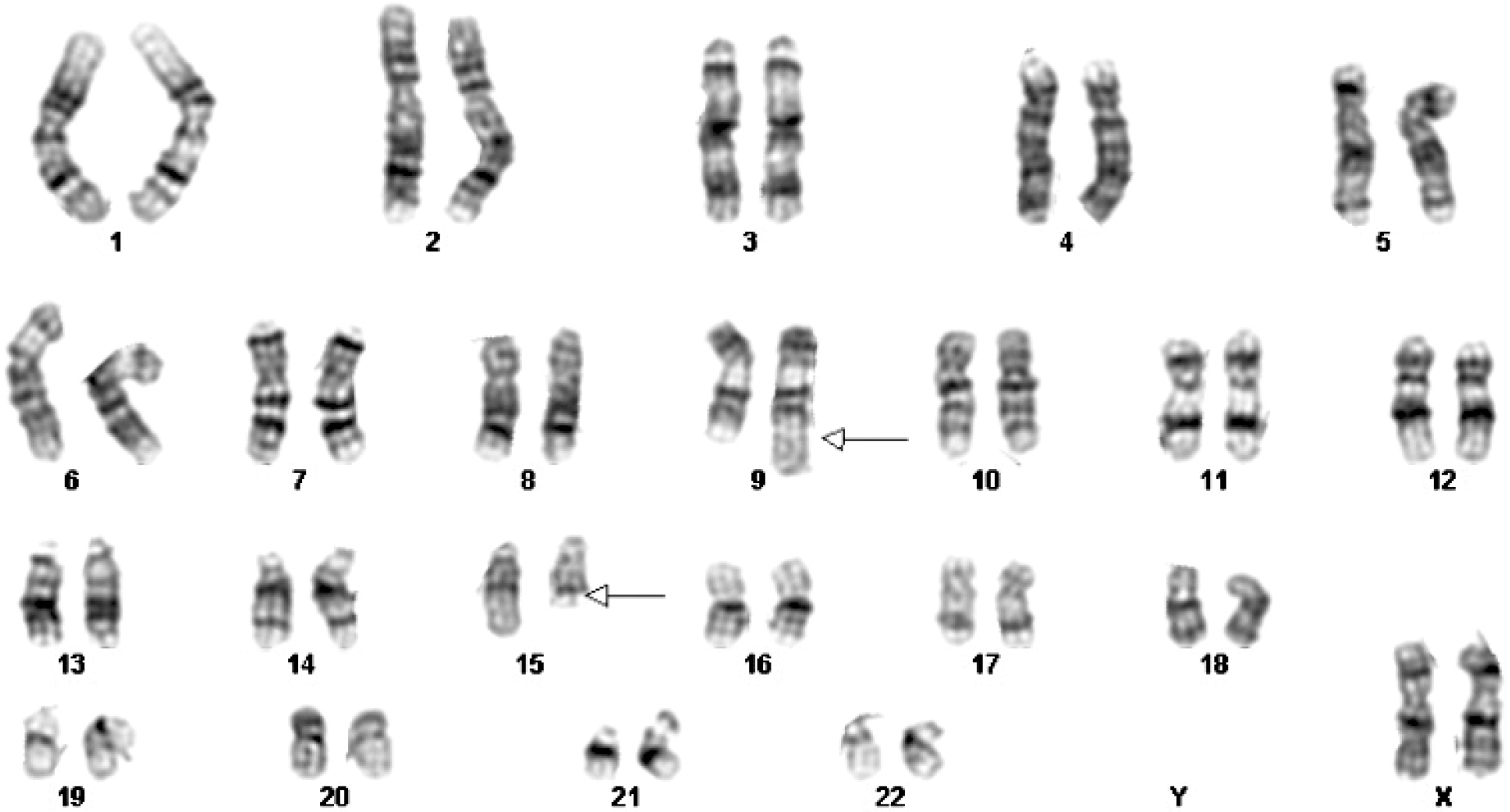
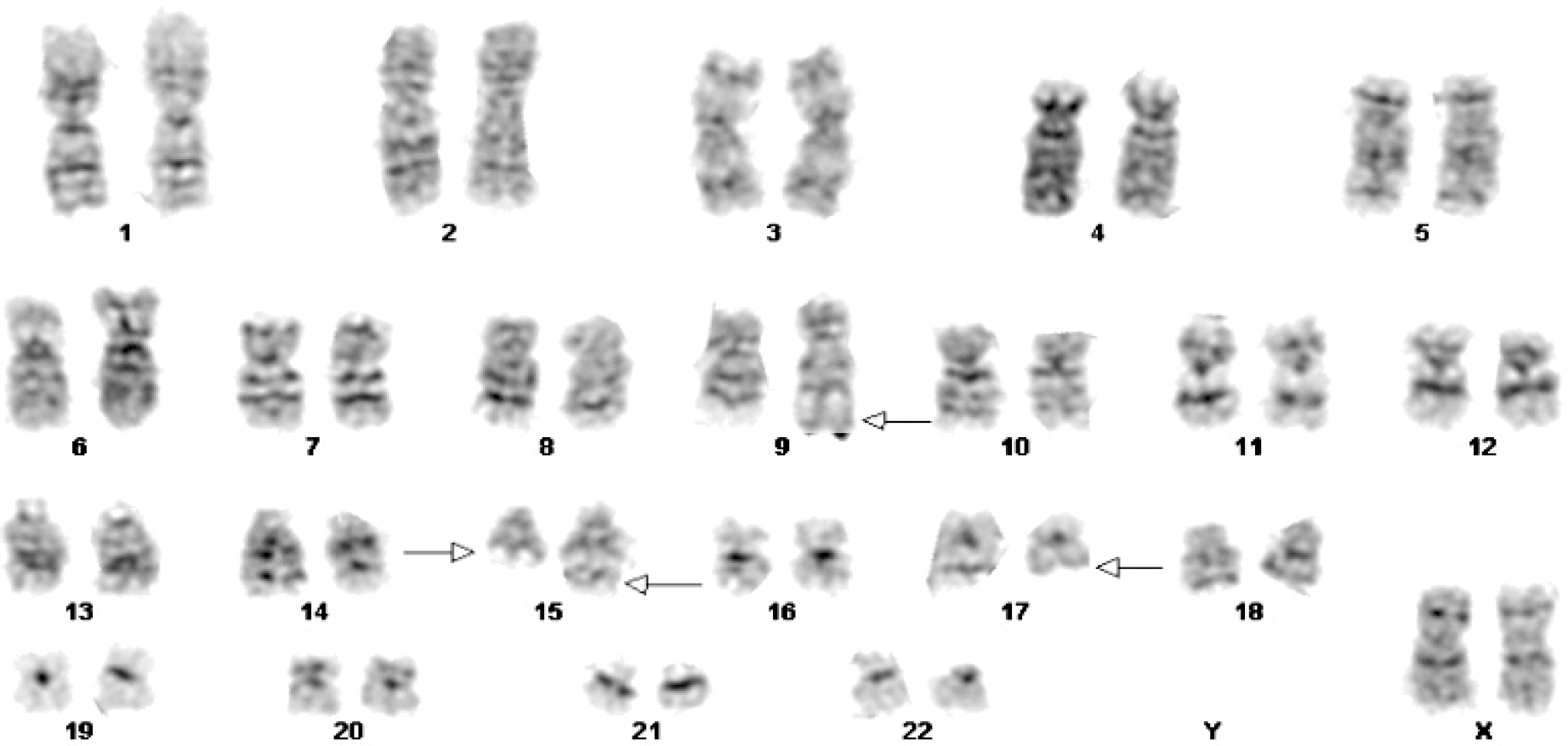 | Fig. 2G-banded karyotype of bone marrow cells showing 46,XX,t(9;15)(q34;q22),t(15;17)(q22;q21). |
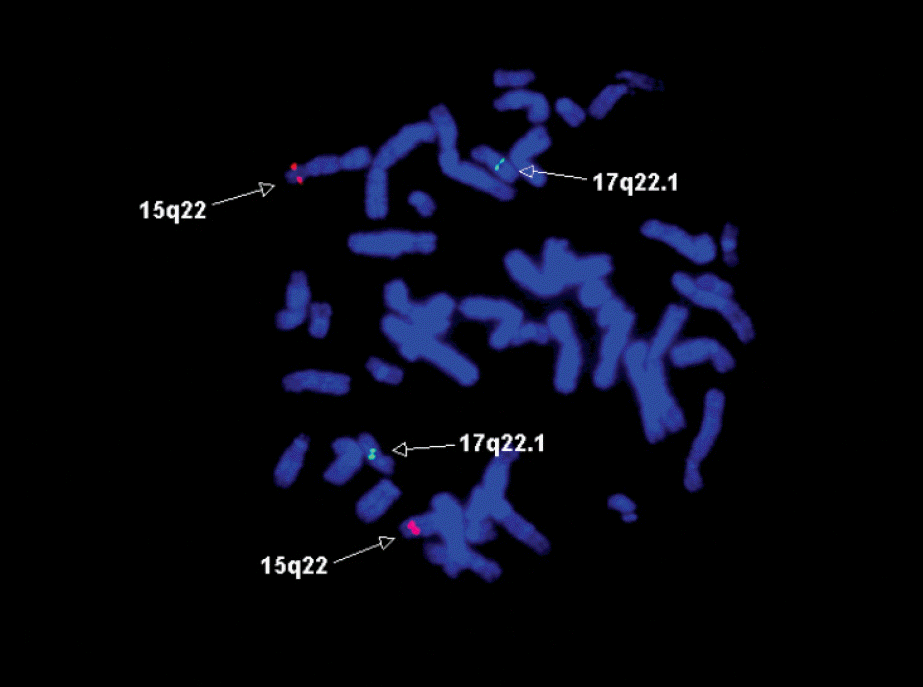
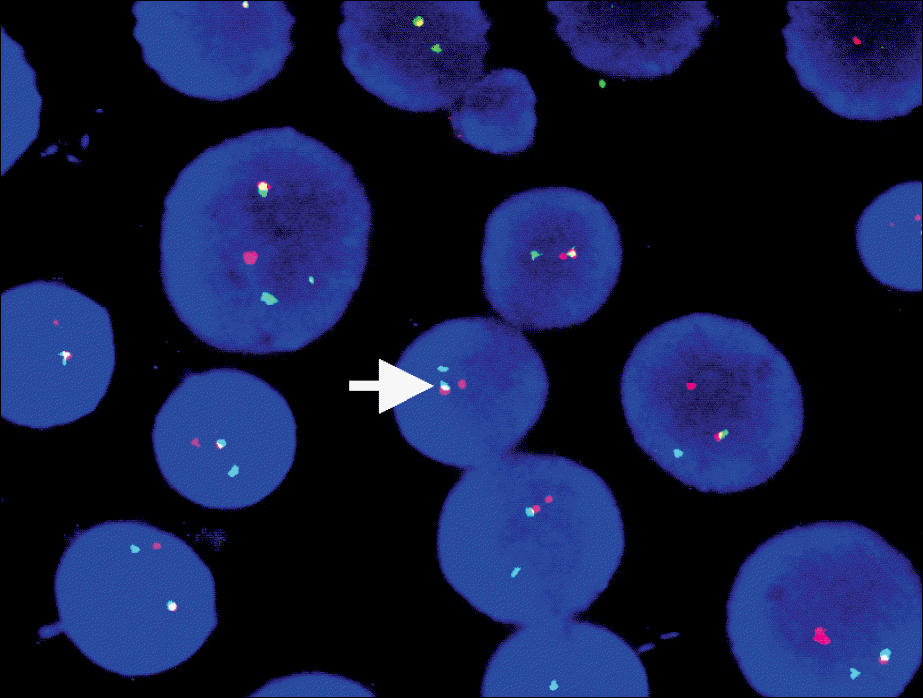 | Fig. 3In FISH study, 99% cells show fusion signals (white arrow) of PML/RARA (LIS PML/RARA dual color translocation probe;15q22 LSI PML spectrumOrange/17q21.1 LSI RARA spectrumGreen). |
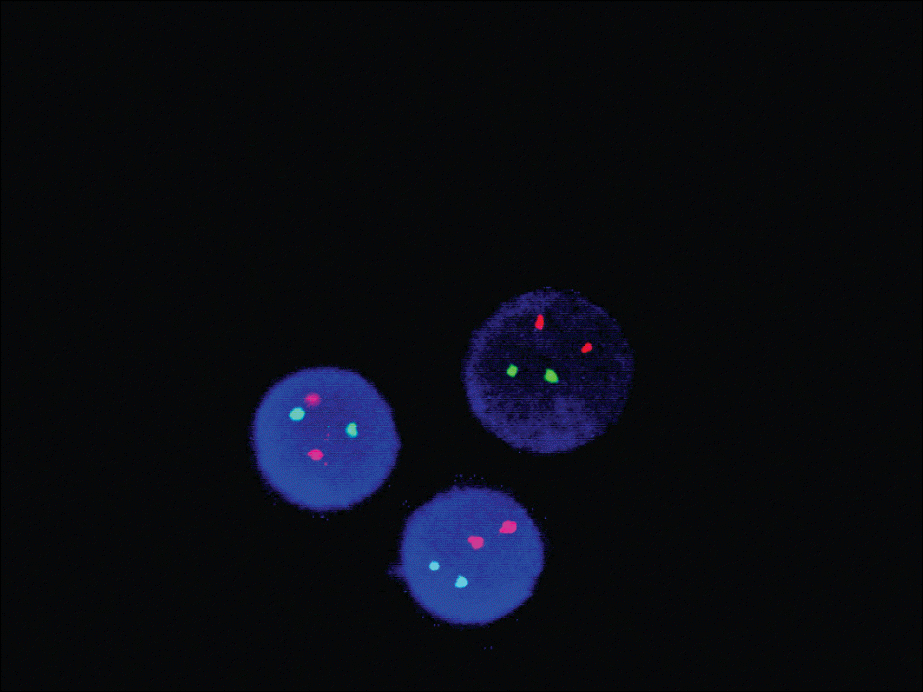 | Fig. 4After treatment, follow up FISH studies show no fusion signal of PML/RARA (LIS PML/RARA dual color translocation probe;15q22 LSI PML spectrumOrange/17q21.1 LSI RARA spectrumGreen). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download