Abstract
We describe here a 64-year-old woman who simultaneously presented with chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) and multiple myeloma (MM). The patient presented with mature neutrophilic leukocytosis, hepatosplenomegaly, the absence of Philadelphia chromosome and the BCR-ABL fusion gene, along with IgG kappa type monoclonal gammopathy in her serum and urine. The bone marrow aspirates showed hypercellularity with marked granulocytic hyperplasia and an increase in immature plasma cells. The neutrophil function tests showed increased phagocytosis, chemotaxis and respiratory burst activity, but there was normal microbial killing activity. The patient was treated with dexamethasone and pamidronate for MM and with hydroxyurea for CNL, and she was discharged from the hospital in an improved condition.
REFERENCES
1). Imbert M., Bain B., Pierre R., Vardiman JW., Brunning RD., Flandrin G. Chronic neutrophilic leukaemia. Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, Vardiman J, editors. World health organization classification of tumour: Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2001. p. 27–8.
2). Campbell DE., Douglas SD. Phagocytic cell functions. I. Oxidation and chemotaxis. Rose NR, de Macario EC, Folds JD, Lane HC, Nakamura RM, editors. Manual of clinical laboratory immunology. 5th ed.Washington, D.C.: ASM Press;1997. p. 320–8.
3). O'Gorman MR. Phagocytic cell functions. Ii. Adhesion and phagocytosis. Rose NR, de Macario EC, Folds JD, Lane HC, Nakamura RM, editors. Manual of clinical laboratory immunology. 5th ed.Washington, D.C.: ASM Press;1997. p. 329–33.
4). Krishnan Y., Sreedharan P., Ramanan S., Sagar T. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2004. 25:46–8.
5). Ohtsuki T., Katsura Y., Mizukami H, et al. Elevated neutrophil function in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 1992. 41:50–6.

6). Mehrotra PK., Winfield DA., Fergusson LH. Cellular abnormalities and reduced colony-forming cells in chronic neutrophilic leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 1985. 73:47–50.

7). Dotten DA., Pruzanski W., Wong D. Functional characterization of the cells in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 1982. 12:157–65.

8). Oogushi K., Shimamoto Y., Hamasaki Y, et al. The discrepancy between chemotaxis and leukotriene B4 production in a patient with chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Jpn J Med. 1989. 28:717–21.

9). Kim KH., Kim OY., Jo CH, et al. A case of chronic neutrophilic leukemia with multiple myeloma. Korean J Hematol. 1998. 33:454–9.
10). You ST., Lee TH., Shun DJ., Lee KS., Cho HC. A case of multipe myeloma detected from long term follow up of chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Korean J Hematol. 1990. 25:597–603.
11). Ito T., Kojima H., Otani K, et al. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Acta Haematol. 1996. 95:140–3.

12). Dinçol G., Nalçaci M., Doğan O, et al. Coexistence of chronic neutrophilic leukemia with multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. 43:649–51.
13). Böhm J., Kock S., Schaefer HE., Fisch P. Evidence of clonality in chronic neutrophilic leukaemia. J Clin Pathol. 2003. 56:292–5.
14). Standen GR., Jasani B., Wagstaff M., Wardrop CA. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia and multiple myeloma. An association with lambda light chain expression. Cancer. 1990. 66:162–6.
15). Kohmura K., Miyakawa Y., Kameyama K., Kizaki M., Ikeda Y. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing multiple myeloma associated with neutrophilia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. 45:1475–9.

16). Kusaba N., Yoshida H., Ohkubo F, et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor-producing myeloma with clinical manifestations mimicking chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2004. 45:228–32.
Fig. 1
Peripheral blood and bone marrow findings in the patient showing coexistence of chronic neutrophilic leukemia and multiple myeloma. (A) Neutrophilia, toxic changes of neutrophils and rouleaux formation of red cells in peripheral blood (Wright stain, ×400). (B) Markedly increased granulocytic series and frequent plasmablasts and plasma cells in bone marrow aspirate (Wright stain, ×400). (C) Hypercellular marrow with granulocytic hyperplasia and increased plasmablasts and plasma cells (H&E stain, ×400).
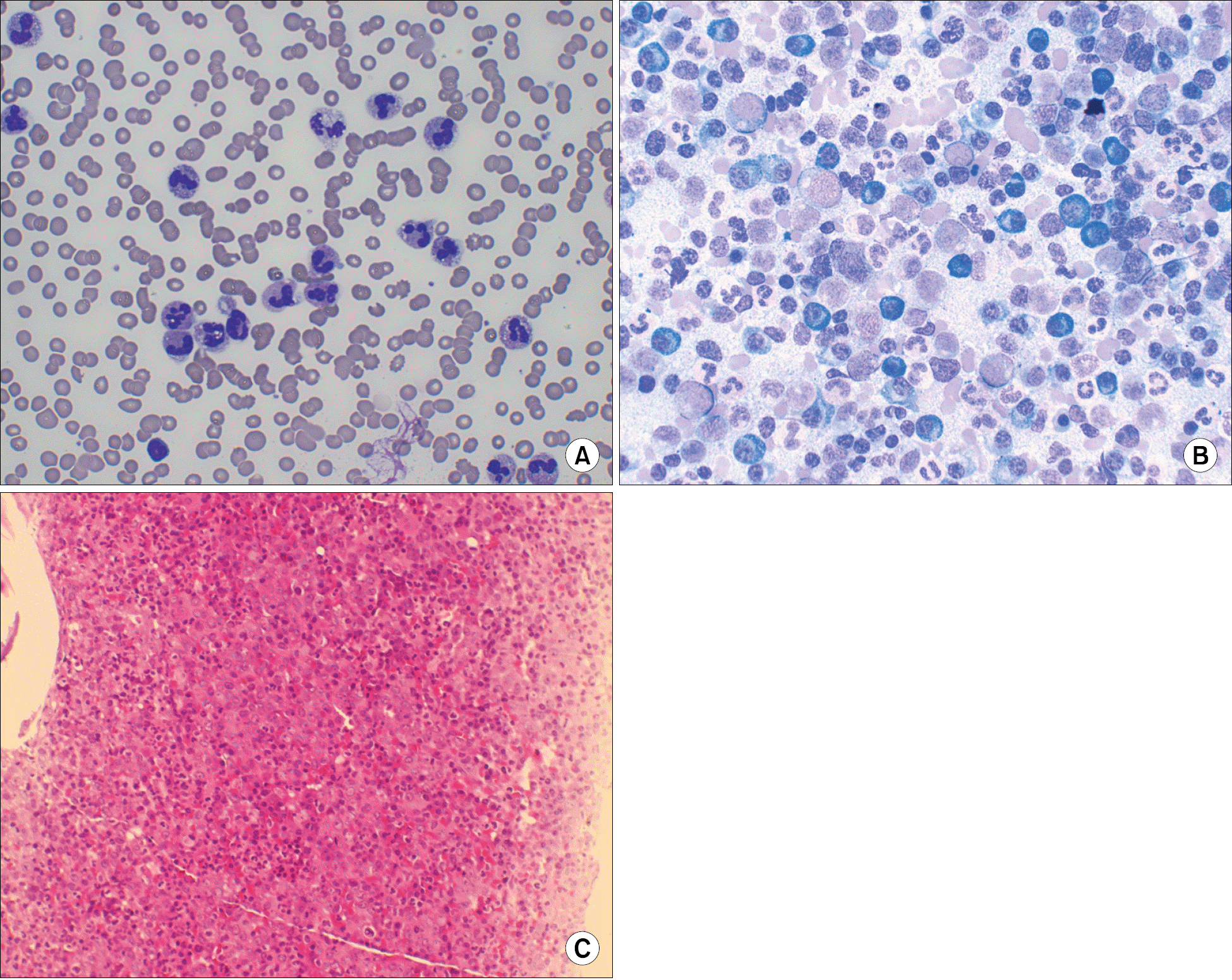
Fig. 2
Immunofixation electrophoresis shows IgG kappa type monoclonal gammopathy in serum (A) and IgG kappa and free kappa type Bence-Jones proteinuria in urine (B). SPE, serum protein electrophoresis; UPE, concentrated urine electrophoresis.
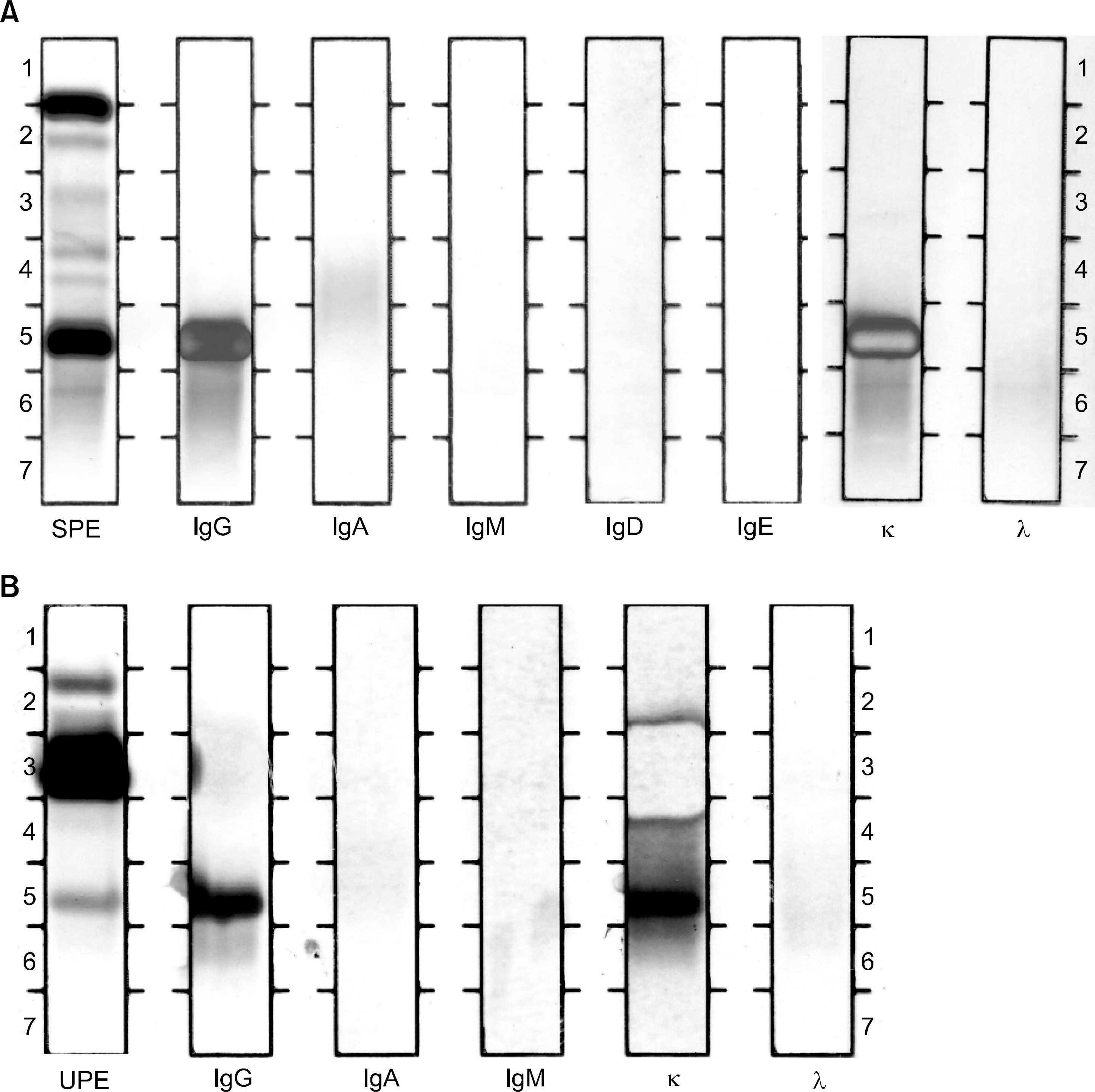
Table 1.
Neutrophil function in the patient with coexisting chronic neutrophilic leukemia and multiple myeloma
| Chemotaxis | Neutrophil No./Boyden chamber well (8mm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulants | Patient | Normal control | Ratio (Patient/Normal control) | |
| Phosphate buffered saline (random motility) | 46,080 | 16,896 | 2.73 | |
| FMLP∗ 10?8 M/L | 83,968 | 52,224 | 1.61 | |
| Heat-inactivated normal plasma | 73,728 | 35,840 | 2.06 | |
| Zymosan activated normal plasma | 100,352 | 72,704 | 1.38 | |
| Phagocytosis | Candida albicans | Patient | Normal control | Ratio (Patient/Normal control) |
| Median channel of fluorescence | 178 | 1,863 | 440 | 4.23 |
| Respiratory burst activity | Mean channel of fluorescence (H2O2 production) | |||
| Stimulants | Patient | Normal control | Ratio (Patient/Normal control) | |
| Rest (no stimulant) | 1,106 | 166 | 6.66 | |
| PMA† 200ng/mL | 7,032 | 3,020 | 2.33 | |
| Microbial killing | Patient | Normal control | ||
| % of C. albicans killing by neutrophils | 40.8% | 43.1% | ||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download