Abstract
There have been reports that hyperammonemia and amino acid disturbance can cause loss of consciousness in patients with multiple myelomas and normal liver function. We experienced a case of a 71-years-old female patient with amyloidosis, who had shown disturbance of consciousness. At that time, the serum ammonia level was elevated; serum amino acids disturbance was also noted. In particular, the decrease in branched-chain amino acids and increase in aromatic amino acids results in a low Fisher ratio. The Fisher ratio, the ratio of branched-chain to aromatic amino acids, has been suggested as an important indicator of consciousness disturbance. We report, for the first time in Korea, a case of amyloidosis, with mental disturbance due to serum amino acid disturbance.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2). Lee JH, Ko YW, Maeng HY, et al. A case of serum amino acid disturbance with hyperammonemia in a patient with multiple myeloma. Korean J Hematol. 2002; 37:84–7.
3). Seo YM, Eom HS, Kim JK, et al. A case of hyperammonemic encephalopathy with serum amino acid alteration in multiple myeloma. Korean J Hematol. 2003; 38:64–7.
4). Matsuzaki H, Hata H, Sonoki T, et al. Serum amino acid disturbance in multiple myeloma with hyperammonemia. Int J Hematol. 2006. 131–7.
5). Matsuzaki H, Uchiba M, Yoshimura K, et al. Hyperammonemia in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol. 1990; 84:130–4.

6). Fujii S, Fukuda S, Sezaki T, Murakami M. Clinicopathological study of multiple myeloma associated with hyperammonemia. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1998; 39:27–33.
7). Watson AJ, Chambers T, Karp JE, Risch VR, Walker WG, Brusilow SW. Transient idiopathic hyperammo-naemia in adults. Lancet. 1985; 2:1271–4.

8). Takimoto Y, Imanaka F, Hayashi Y, Morioka S. A patient with ammonia-producing multiple myeloma showing hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Leukemia. 1996; 10:918–9.
9). Kwan L, Wang C, Levitt L. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1674–5.

10). Holahan JR. Hyperammonemia: elevated ammonia levels in multiple myeloma. Am J Med. 2004; 116:210–1.

11). Weng TI, Shih FF, Chen WJ. Unusual causes of hyperammonemia in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2004; 22:105–7.

12). Tsunoda S, Sasaki R, Miwa A, Sakurabayashi I, Miura Y. Coma, hyperviscosity syndrome, hyperammonemia and myelofibrosis in a patient with IgG, lambda type multiple myeloma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1989; 30:361–5.
Go to : 
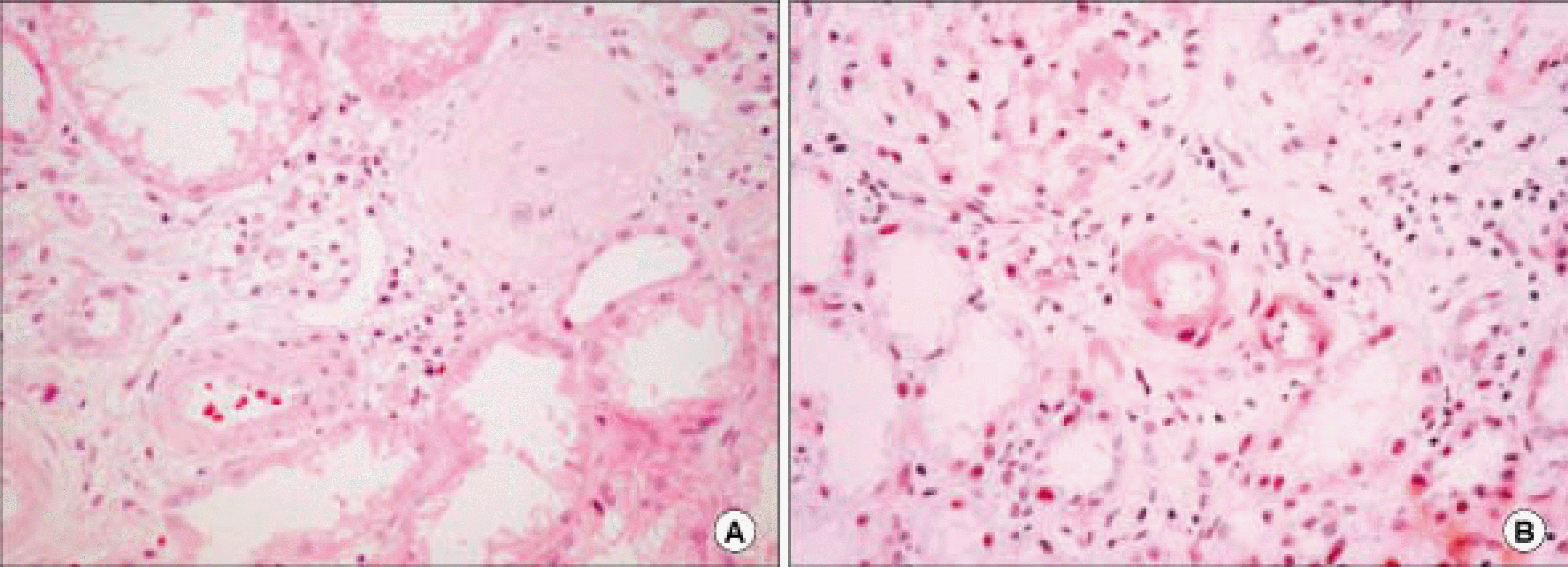 | Fig. 1.Some arteriolar walls are thickened by amorphous material deposits. There are multifocal chronic inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis associated tubular atrophy. The deposits are Congo-red positive (A: H&E ×400, B: Congo-red, ×400). |
Table 1.
Characteristics of serum amino acid disturbance in this case (nmol/mL)
| Compounds | Results | Results | Normal range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital day | D+9 | D+16 | |
| Glycine | 91.2 | 271.1 | 151.0~490.0 |
| Tylosine | 35.9 | 9.8 | 34.0~112.0 |
| Valine | 109.2 | 139.7 | 119.0~336.0 |
| Leucine | 53.5 | 76.4 | 72.0~201.0 |
| Isoleucine | 35.0 | 63.6 | 30.0~108.0 |
| Phenyalanine | 330.1 | 22.3 | 35.0~85.0 |
| Fisher ratio∗ | 0.53 | 8.71 | 2.6~4.3 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download