Abstract
Myxofibrosarcoma, also known as a myxoid variant of a malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH), is one of the most common sarcomas in the extremities of elderly people. The lesion is characterized by a high frequency of local recurrence but is uncommon in the head and neck regions.
Low-grade myxofibrosarcoma, which is commonly misinterpreted as being benign, has a tendency for histological and biological progression in local recurrences, highlighting the importance of an accurate diagnosis and wide surgical excision of the primary lesion.
We report a rare case of low-grade myxofibrosarcoma of the mandible located in the left mandibular body and angle area. The tumor was first diagnosed as a myxofibroma and was resected initially. After the final biopsy the patient underwent combined chemoradiotherapy. The progress of the patent was uneventful until the one year follow up.
References
1. Gugatschka M, Beham A, Stammberger H, Schmid C, Friedrich G. First case of a myxofibrosarcoma of the vocal folds: case report and review of the literature. J Voice. 2010; 24:374–6.

2. Nishimura G, Sano D, Hanashi M, Yamanaka S, Tanigaki Y, Taguchi T, et al. Myxofibrosarcoma of the hypopharynx. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2006; 33:93–6.

3. Wada T, Hasegawa T, Nagoya S, Kawaguchi S, Kaya M, Ishii S. Myxofibrosarcoma with an infiltrative growth pattern: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2000; 30:458–62.

4. Huang HY, Lal P, Qin J, Brennan MF, Antonescu CR. Low-grade myxofibrosarcoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of 49 cases treated at a single institution with simultaneous assessment of the efficacy of 3-tier and 4-tier grading systems. Hum Pathol. 2004; 35:612–21.

5. Angervall L, Kindblom LG, Merck C. Myxofibrosarcoma. A study of 30 cases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977; 85A:127–40.
6. Mentzel T, Calonje E, Wadden C, Camplejohn RS, Beham A, Smith MA, et al. Myxofibrosarcoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 75 cases with emphasis on the low-grade variant. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996; 20:391–405.
8. Nascimento AF, Bertoni F, Fletcher CD. Epithelioid variant of myxofibrosarcoma: expanding the clinicomorphologic spectrum of myxofibrosarcoma in a series of 17 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:99–105.

9. Kummoona R. Central myxofibrosarcoma of the mandible treated by radical resection. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1975; 39:713–7.

10. Lam PK, Trendell-Smith N, Li JH, Fan YW, Yuen AP. Myxofibrosarcoma of the sphenoid sinus. J Laryngol Otol. 2002; 116:464–6.

11. Pomerantz JM, Sanfacon DG, Dougherty TP, Hanson S. Myxofibrosarcoma of the maxillary sinus. Del Med J. 1982; 54:147–52.
12. Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Cancer. 1977; 39:1672–85.

13. Soper CP, Andrews PA, Bending MR, Singh L, Fisher C. Cervical myxofibrosarcoma in a renal allograft recipient treated with murine anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998; 13:1902–3.

14. Merck C, Angervall L, Kindblom LG, Ode′n A. Myxofibrosarcoma. A malignant soft tissue tumor of fibroblastic-histiocytic origin. A clinicopathologic and prognostic study of 110 cases using multivariate analysis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1983; 282:1–40.
15. Kearney MM, Soule EH, Ivins JC. Malifnant fibrous histiocytoma: a retrospective study of 167 cases. Cancer. 1980; 45:167–78.
Fig. 1.
A. Extraoral photograph. Left facial swelling. B. Intraoral photograph. A well-circumscribed bony and gingival swelling of the left mandible, which measured 4 cm at its greatest diameter, suggesting benign tumor.
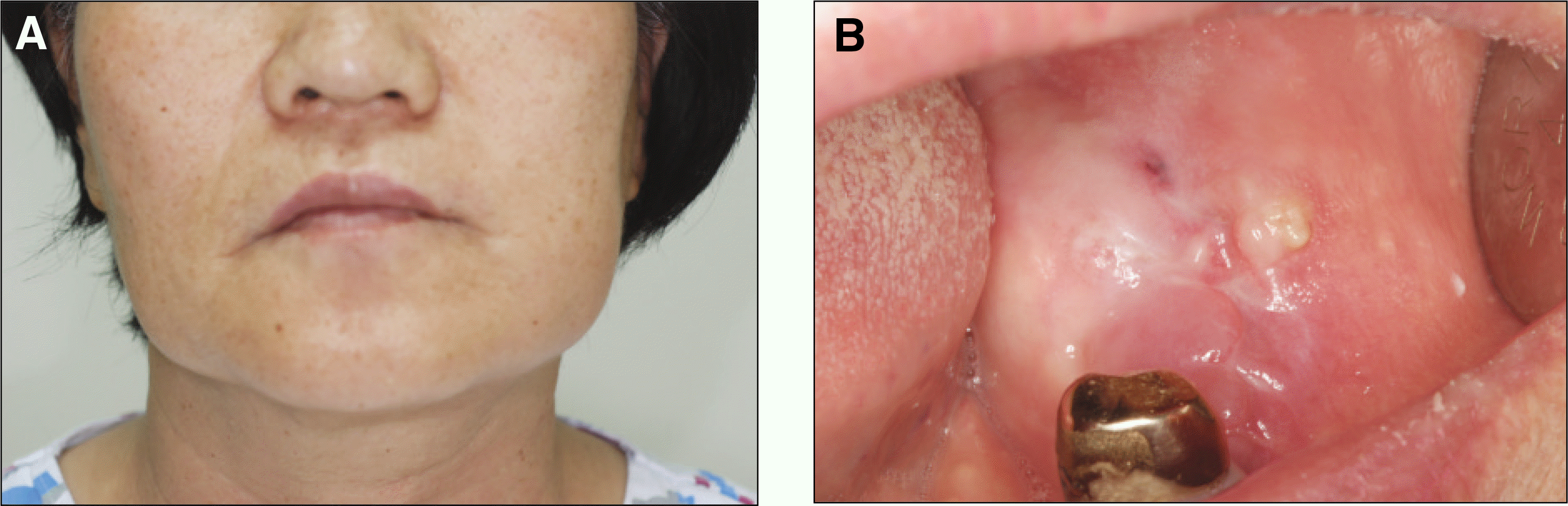
Fig. 2.
A. Preoperative Panorama. A destructive process with osteolytic changes near the angle, effacement of adjacent cortical outline on these lesion. B. Preoperative CT view. Ill-defined multilocular radiolucent lesion with buccolingual, inferior cortical thinning and buccolingual cortical disruption.(CT: computed tomography)
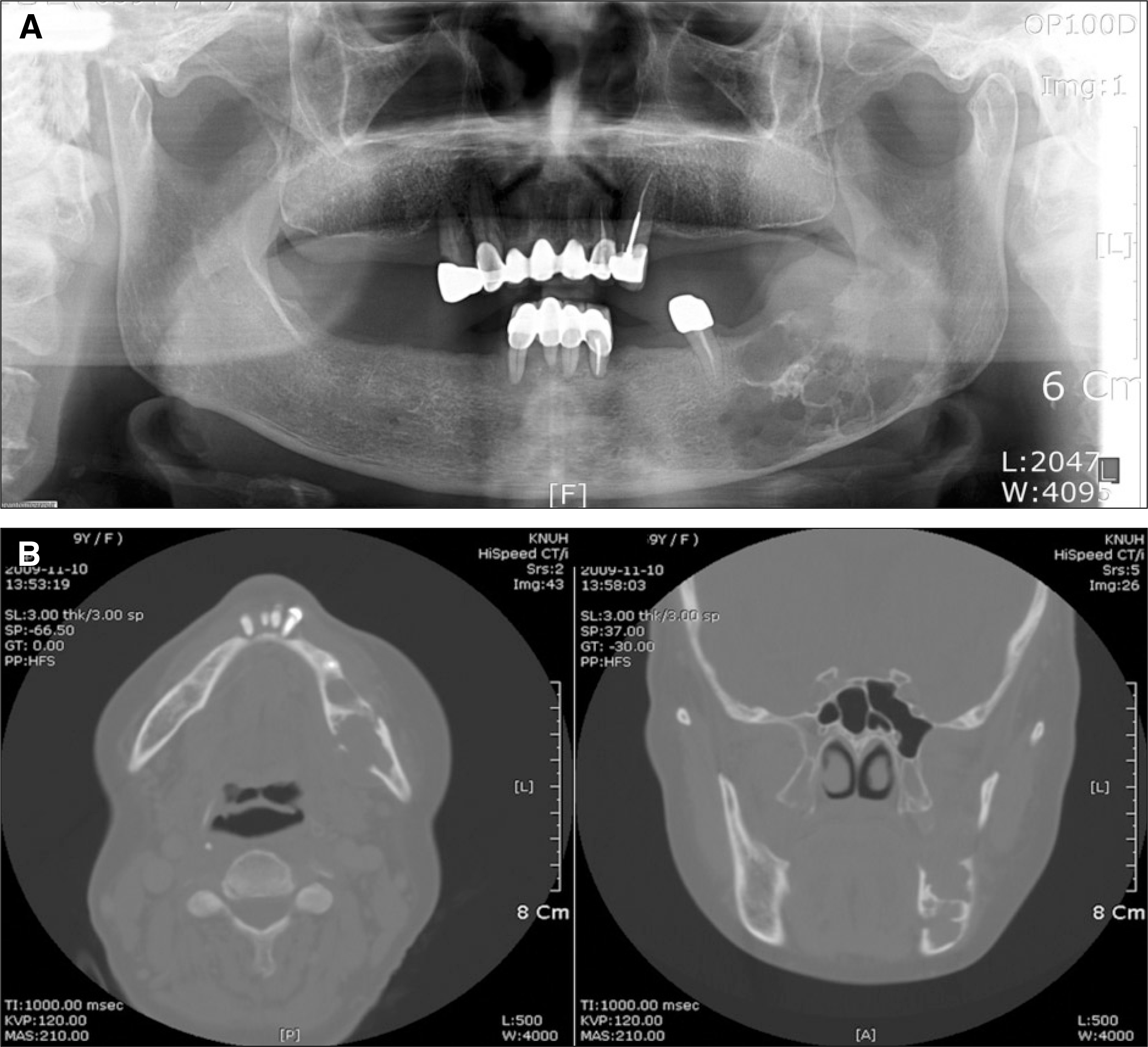
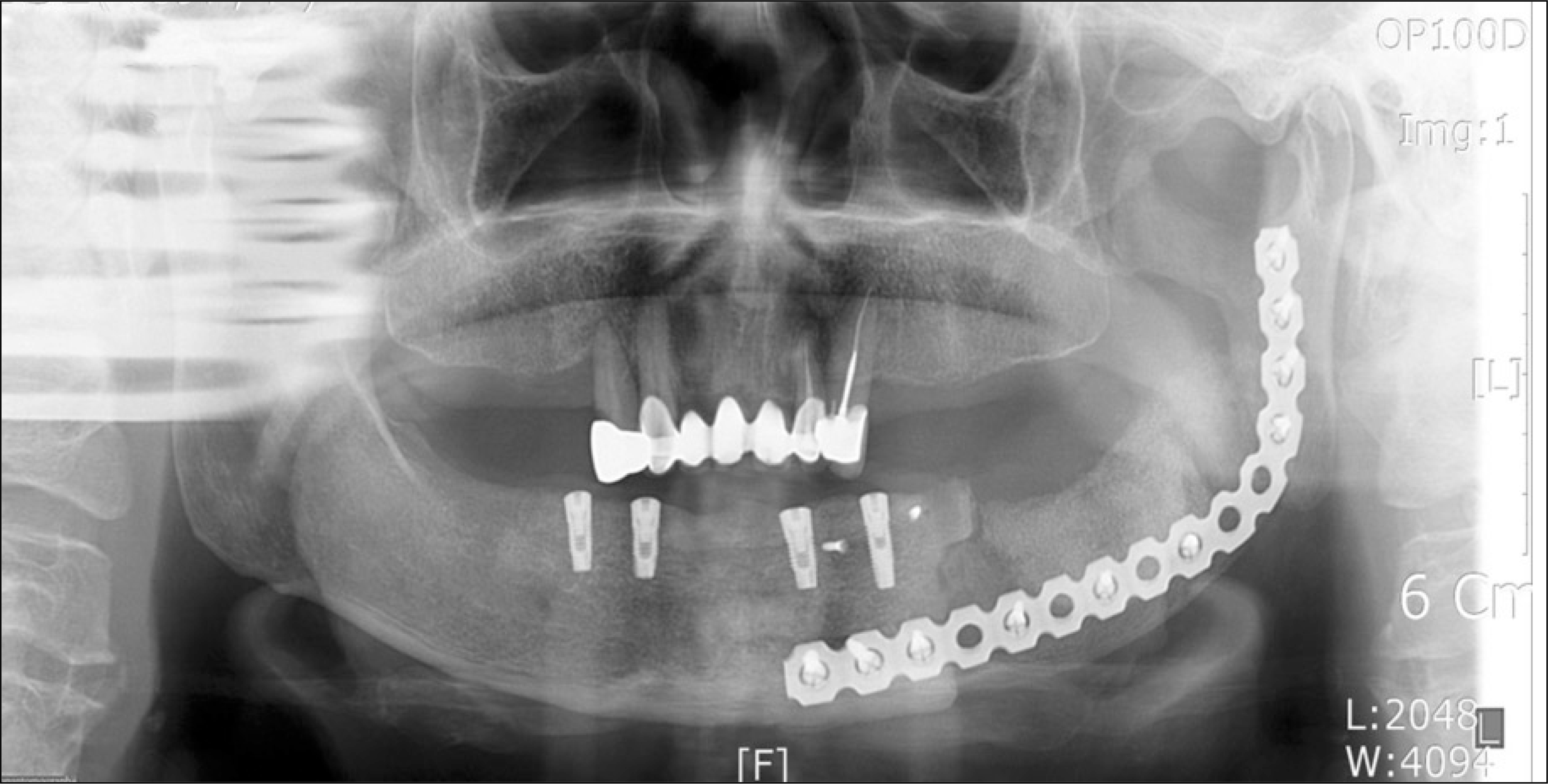
Fig. 3.
A. An intra/extraoral resection of the left mandible from the premolar to the angle was carried out. B. The specimen consisted of a smooth, lobulated mass, the edge of which was well defined and covered with periosteum, there was no evidence of a capsule. C. After the patient underwent extirpation of the lesion, the defect area was reconstructed by iliac bone and reconstruction plate.
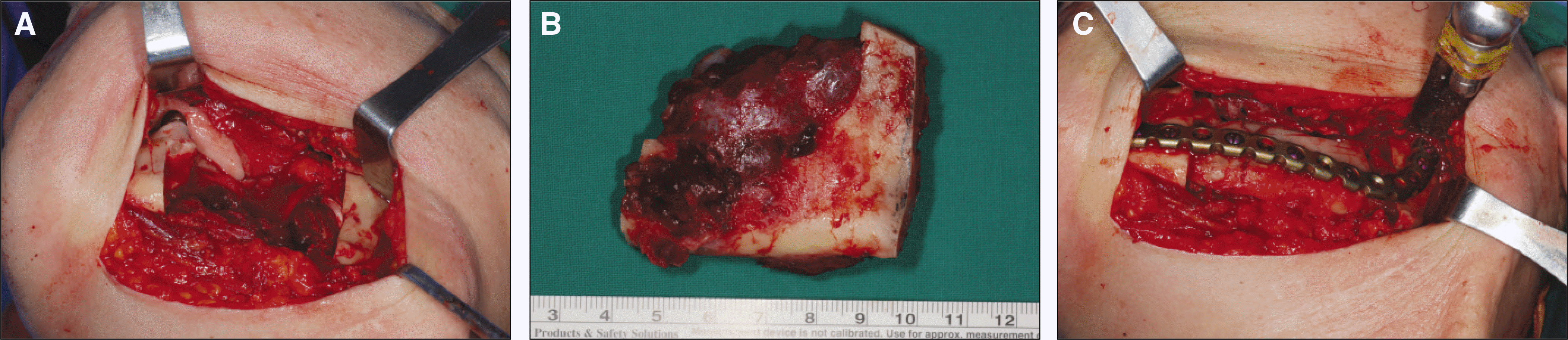
Fig. 4.
A. The tumor is composed of spindle or stellate cells lying in an abundant amorphous myxoid stroma that also contains isolate coarse and fine collagen fiber bundles.(H&E staining, original magnification ×10) B. The tissue is not very vascular, and many of the small vessels are surrounded by a zone of hyalinization.(arrows, H&E staining, original magnification ×40) C. The tumor is composed of elongated and angular cells lying in an abundant amorphous stroma that also contains isolate coarse and fine collagen fiber bundles.(H&E staining, original magnification ×40) D. In sone parts, there is little pleomorphism or hyperchromatism. Mitotic figures are very infrequent, and the appearances are like those of a myxofibroma. In other parts, however, there is greater variation in the cells, mitotic figures are frequent, and these include occasional abnormal forms.(arrows, H&E staining, original magnification ×40)





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download