Abstract
Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fractures are frequently associated with high energy concomitant craniofacial trauma. When a displacement of the orbital roof and supraorbital rim occurs, exploration, stabilization and reconstruction are warranted to limit the ocular complications. The management of fractures involving the frontal sinus must consider the possible need for obliteration or cranialization of the sinus. Many incisions have been described and used to approach these fractures, such as a coronal incision, eyebrow incision, and an incision through the laceration. We report 3 cases of orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture patients with a review of the relevant literature.
References
1. Penfold CN, Lang D, Evans BT. The management of orbital roof fractures. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992; 30:97–103.

2. McLachlan DL, Flanagan JC, Shannon GM. Complications of orbital roof fractures. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:1274–8.

4. Piotrowski WP, Beck-Mannagetta J. Surgical techniques in orbital roof fractures: early treatment and results. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1995; 23:6–11.

5. Haug RH. Management of the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle in the repair of orbital roof trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 58:602–6.

6. Flanagan JC, McLachlan DL, Shannon GM. Orbital roof fractures: neurologic and neurosurgical considerations. Ophthalmology. 1980; 87:325–9.
7. Holck DE, Ng JD. Evaluation and treatment of orbital fractures: a multidisciplinary approach. 1st ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2006.
8. Raflo GT. Blow-in and blowout fracture of the orbit: clinical correlation and proposed mechanisms. Ophthalmic Surg. 1984; 15:114–9.
9. Haug RH, Likavec M. Frontal sinus reconstruction. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 1994; 2:65–83.

10. Anderson RL, Panje WL, Gross CE. Optic nerve blindness following blunt forehead trauma. Opthalmology. 1982; 89:445–55.

11. Haug RH, van Sickels JE, Jenkins WS. Demographics and treatment options for orbital roof fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 93:238–46.

12. Conforti PJ, Haug RH, Likavec M. Management of closed head injury in the patient with maxillofacial trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 51:298–303.

13. Alpert B, Seligson D. Removal of asymptomatic bone plates used for orthognathic surgery and facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:618–21.

14. Suuronen R. Biodegradable fracture-fixation devices in maxillofacial surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 22:50–7.

15. Shetty V, Caputo AA, Kelso I. Torsion-axial force characteristics of SR-PLLA screws. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1997; 25:19–23.

16. Ilankovan V, Jackson IT. Experience in the use of calvarial bone grafts in orbital reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992; 30:92–6.

17. Kosaka M, Matsuzawa Y, Mori H, Matsunaga K, Kamishii H. Orbital wall reconstruction with bone grafts from the outer cortex of the mandible. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004; 32:374–80.

18. Metzer MC, Schön R, Schmelzeisen R. Preformed titanium meshes: a new standard? Skull Base. 2007; 17:269–72.

19. Kokiewicz M, Elgalal M, Lopa P, Komuński P, Arkuszewski P, Broniarczyk-Loba A, et al. Clinical application of 3D pre-bent titanium implants for orital floor fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009; 37:229–34.
20. Gear AJ, Lokeh A, Aldridge JH, Migliori MR, Benjamin CI, Schubert W. Safety of titanium mesh for orbital reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2002; 48:1–7.

21. Yimaz M, Vayvada H, Aydin E, Mederes A, Atabey A. Repair of fractures of the orbital floor with porous polyethylene implants. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 45:640–4.
Fig. 1.
A. Exposure to the supraorbital rim fracture was afforded through the laceration without the need for additional incisions. B. Preoperative computed tomography in Case 1. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
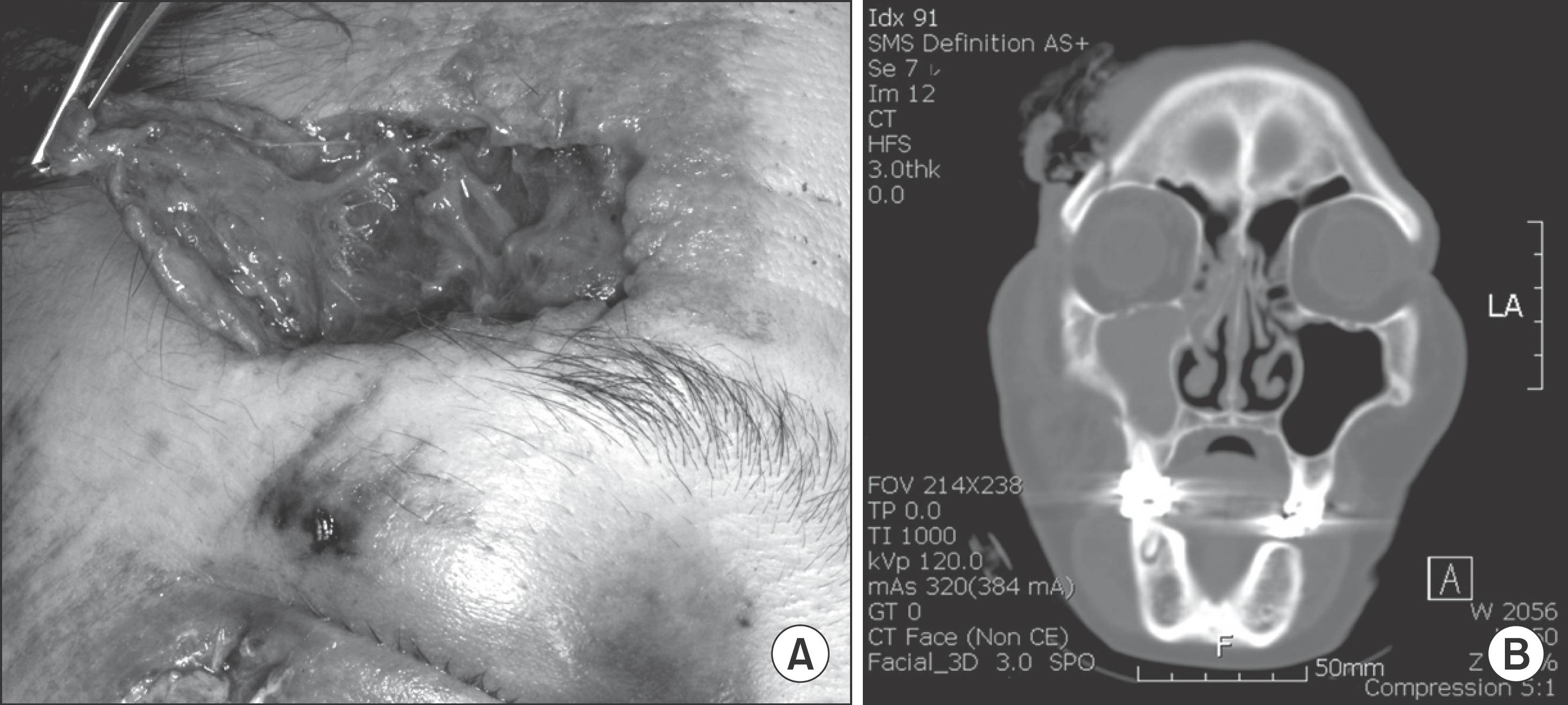
Fig. 2.
Preoperative radiological finding in Case 2. A. 3-dimensional computed tomography. B. Water's view. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
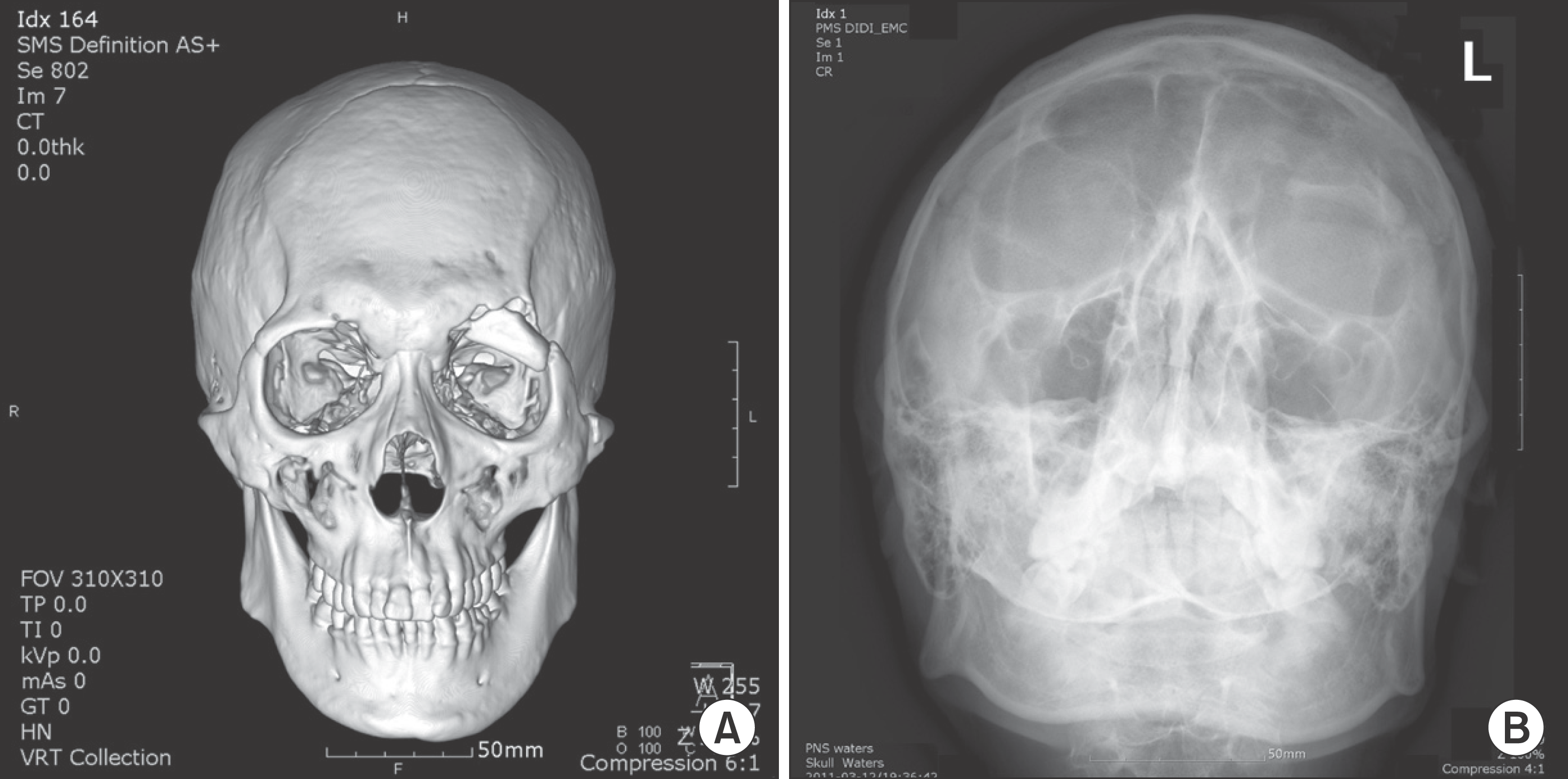
Fig. 3.
A. Preoperative photograph in Case 2. B. Postoperative photograph. Note the proper position of the globe subsequent to reduction. C. Postoperative Water's view. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
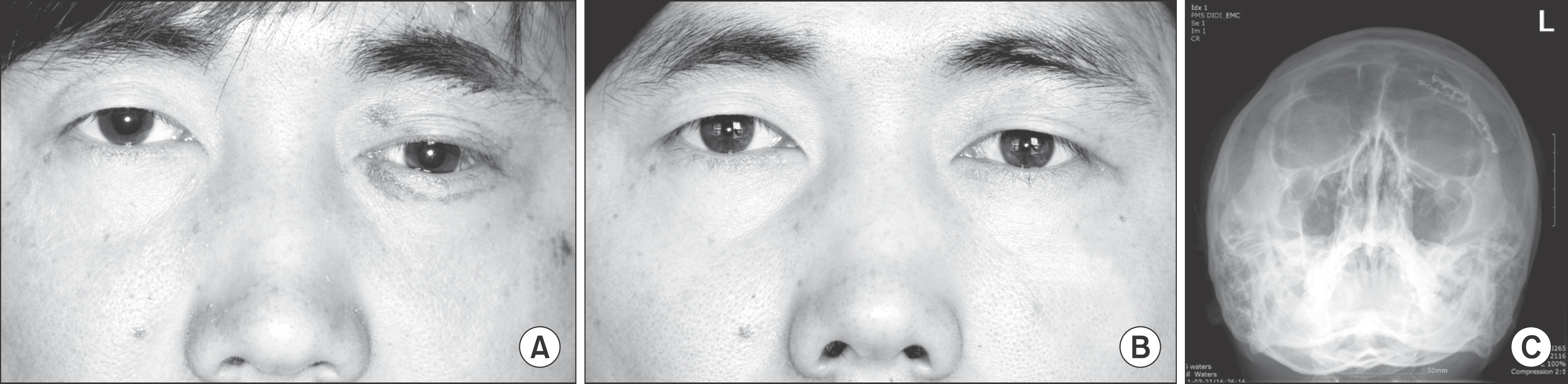
Fig. 4.
Preoperative radiological finding in Case 3. A. Coronal view of computed tomography (CT). B. Reformatted sagittal view of CT. C. 3-dimensional CT. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
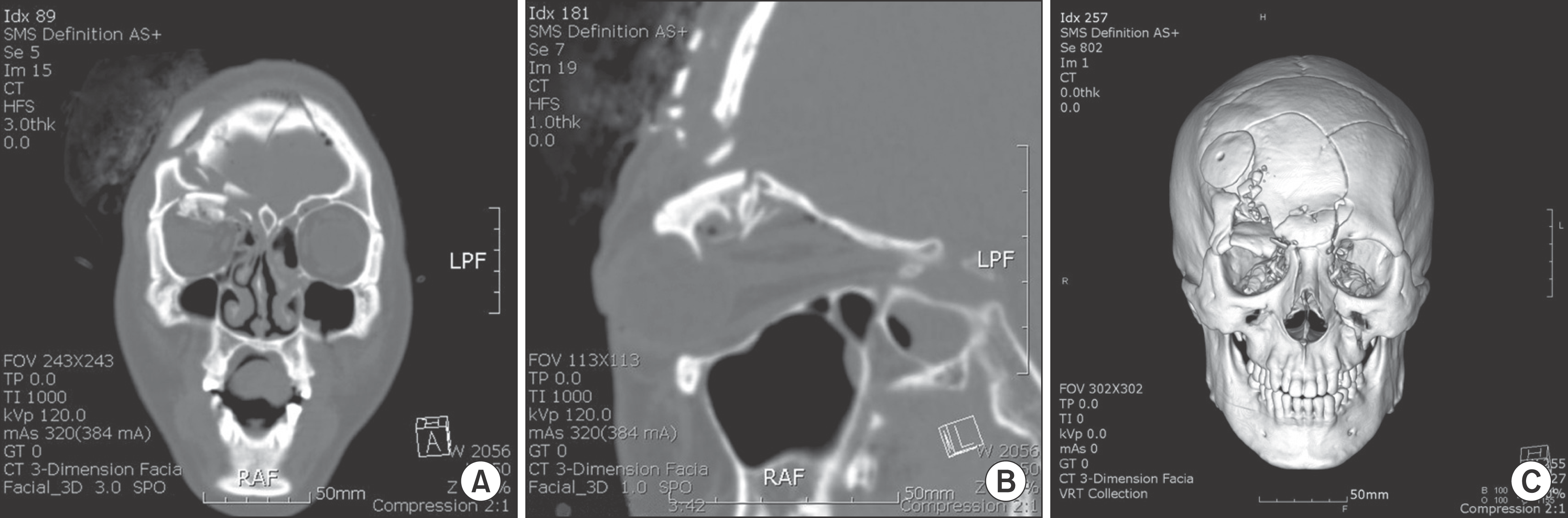
Fig. 5.
Intraoperative photograph of the reconstructed right orbital roof in Case 3. The Medpor (arrow) sheet has been fashioned into shape which reconstitutes the natural curve of orbital roof. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011

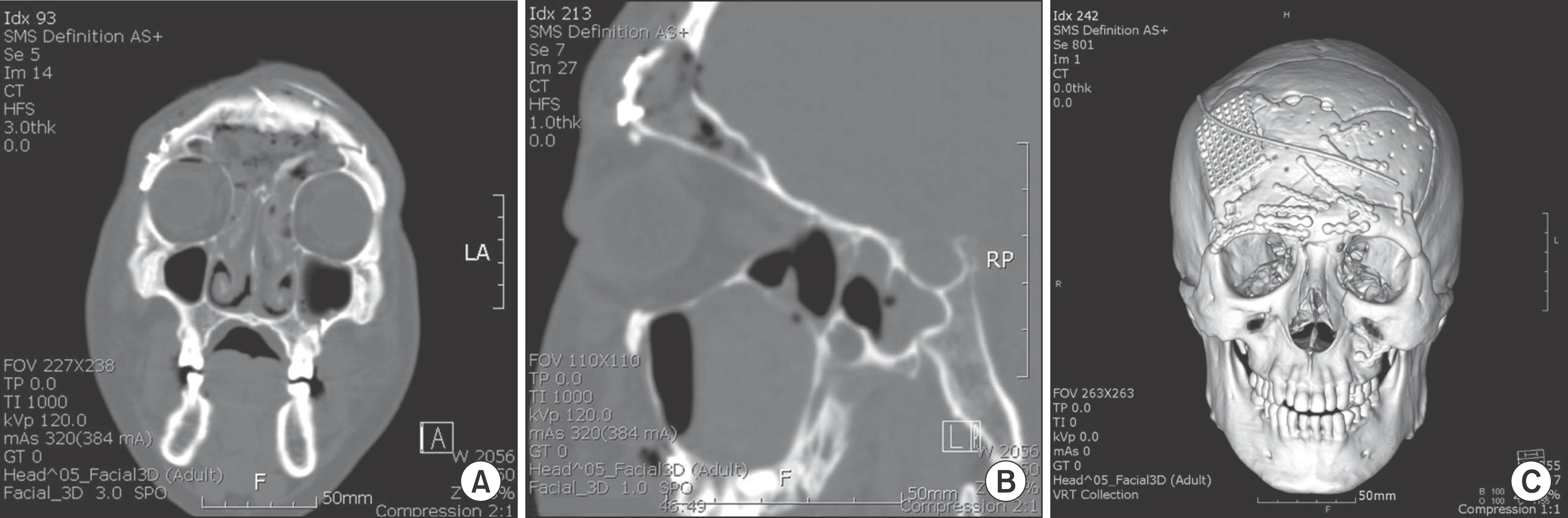
Fig. 6.
Postoperative radiological finding in Case 3. A. Coronal view of computed tomography (CT). B. Reformatted sagittal view of CT. C. 3-dimensional CT. Jae-Yeol Lee et al: Orbital roof and supraorbital ridge fracture: a report of three cases. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download