Abstract
A keratoameloblastoma is a histologically variant of the ameloblastoma group, which varies in size and contains keratin material in the fibrous connective tissue among cystic lesions. A keratoameloblastoma is a rare disease with only 13 cases reported in the literature since Pindborg's first report in 1970. A 41-year-old man visited, complaining of pus discharged from the right maxilla. He had been diagnosed with an odontogenic keratocyst and was treated with cyst enucleation in the past. The clinical and radiology examination found evidence of recurrence and finally diagnosed him with keratoameloblastoma after enucleation and biopsy. This report discusses the clinical, radiological and histological characteristics of keratoameloblastoma and its treatment. In addition, we report another case of keratoameloblastoma that had transformed from an odontogenic keratocyst.
References
1. Whitt JC, Dunlap CL, Sheets JL, Thompson ML. Keratoameloblastoma: a tumor sui generis or a chimera? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 104:368–76.

2. Pindborg JJ. Pathology of the dental hard tissues. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;1970.
3. Altini M, Lurie R, Shear M. A case report of keratoameloblastoma. Int J Oral Surg. 1976; 5:245–9.
4. Norval EJ, Thompson IO, van Wyk CW. An unusual variant of keratoameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 1994; 23:465–7.

5. Altini M, Slabbert HD, Johnston T. Papilliferous keratoamelo-blastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 1991; 20:46–8.

6. Siar CH, Ng KH. 'Combined ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst' or ‘keratinising ameloblastoma'. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 31:183–6.

7. Said-al-Naief NA, Lumerman H, Ramer M, Kopp W, Kringstein GJ, Persenchino F, et al. Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla. A case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997; 84:535–9.
8. Takeda Y, Satoh M, Nakamura S, Ohya T. Keratoameloblastoma with unique histological architecture: an undescribed variation of ameloblastoma. Virchows Arch. 2001; 439:593–6.

9. Collini P, Zucchini N, Vessecchia G, Guzzo M. Papilliferous keratoameloblastoma of mandible: a papillary ameloblastic carcinoma: report of a case with a 6-year follow-up and review of the literature. Int J Surg Pathol. 2002; 10:149–55.
10. Vered M, Buchner A, Dayan D, Shteif M, Laurian A. Solid variant of odontogenic keratocyst. J Oral Pathol Med. 2004; 33:125–8.

11. Ide F, Mishima K, Saito I. Solid-cystic tumor variant of odontogenic keratocyst: an aggressive but benign lesion simulating keratoameloblastoma. Virchows Arch. 2003; 442:501–3.

12. Odell EW, Morgan PR. Biopsy pathology of the oral tissues. London: Chapman & Hall Medical;1998.
13. Partridge M, Towers JF, Towers JF. The primordial cyst (odontogenic keratocyst): its tumour-like characteristics and behaviour. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987; 25:271–9.

14. Shear M. The aggressive nature of the odontogenic keratocyst: is it a benign cystic neoplasm? Part 1. Clinical and early experimental evidence of aggressive behaviour. Oral Oncol. 2002; 38:219–26.

15. Shear M. The aggressive nature of the odontogenic keratocyst: is it a benign cystic neoplasm? Part 2. Proliferation and genetic studies. Oral Oncol. 2002; 38:323–31.
Fig. 1.
The panoramic radiograph showing radiolucent lesion occupying right maxilla. Ji-Hoon Won et al: Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
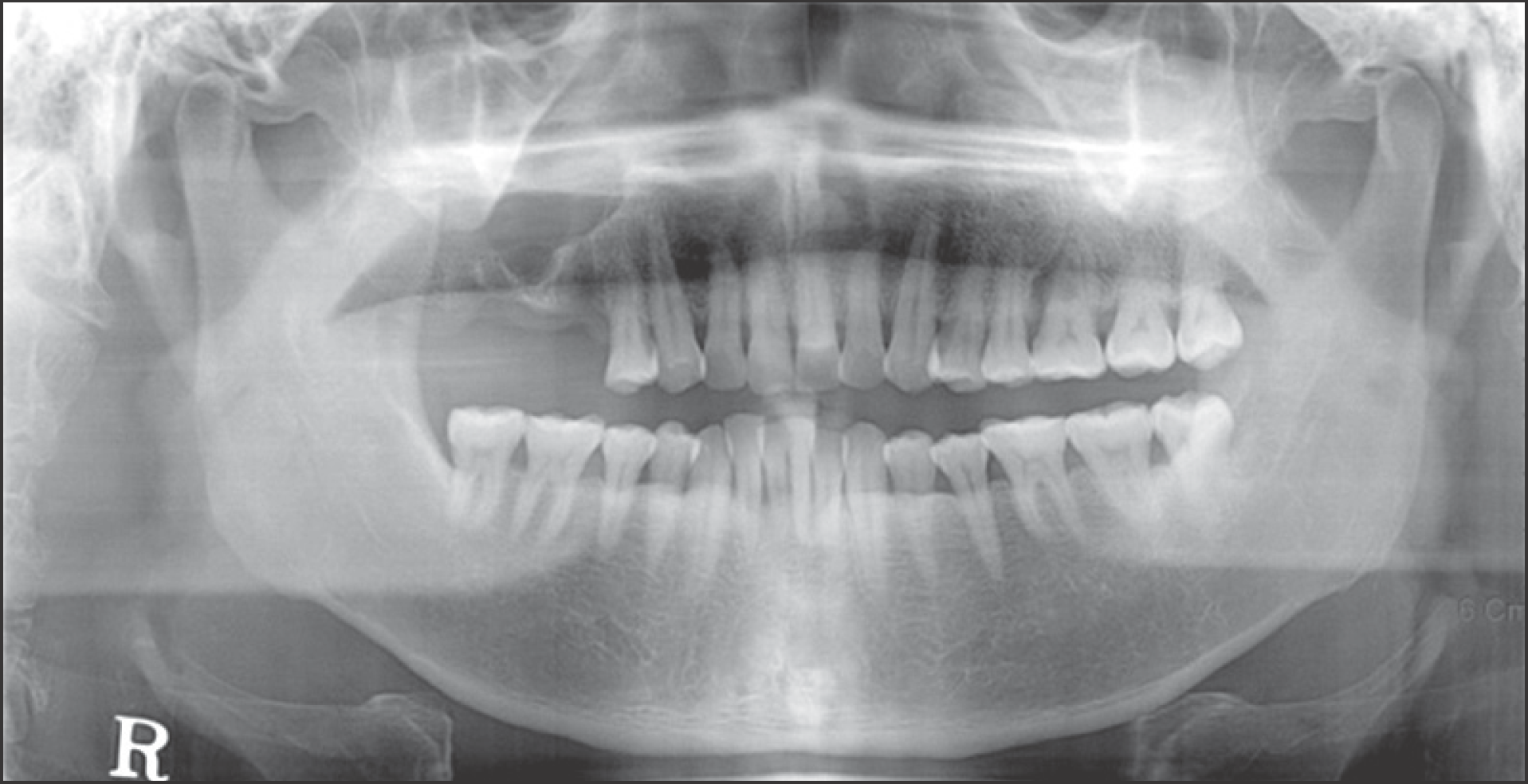
Fig. 2.
Axial and coronal computed tomography (CT) view. A. The axial CT scan shows well-defined and low attenuated cystic lesion about 3.5 cm sized in the right maxilla posterior region. Also, we can find marked expansion of the maxilla with perforation of cortical plates. B. The coronal scan shows elevation and thickening of right sinus mucosa of floor. The lesion is involved with nasal cavity. Ji-Hoon Won et al: Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
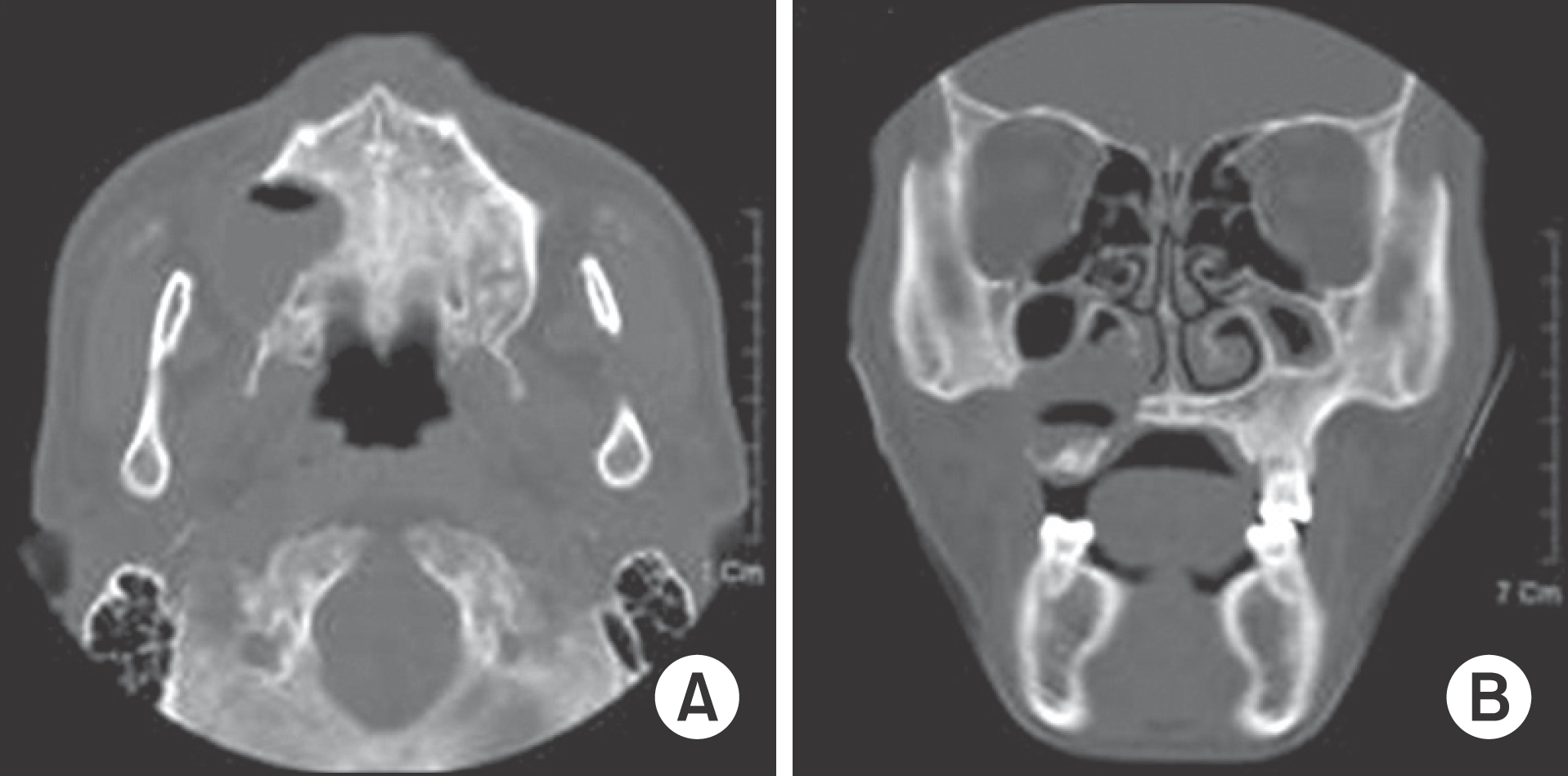
Fig. 3.
Postoperative panoramic radiograph taken 2 months after decompression of cystic lesion. The lesion become smaller than preoperative panoramic radiograph. Ji-Hoon Won et al: Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
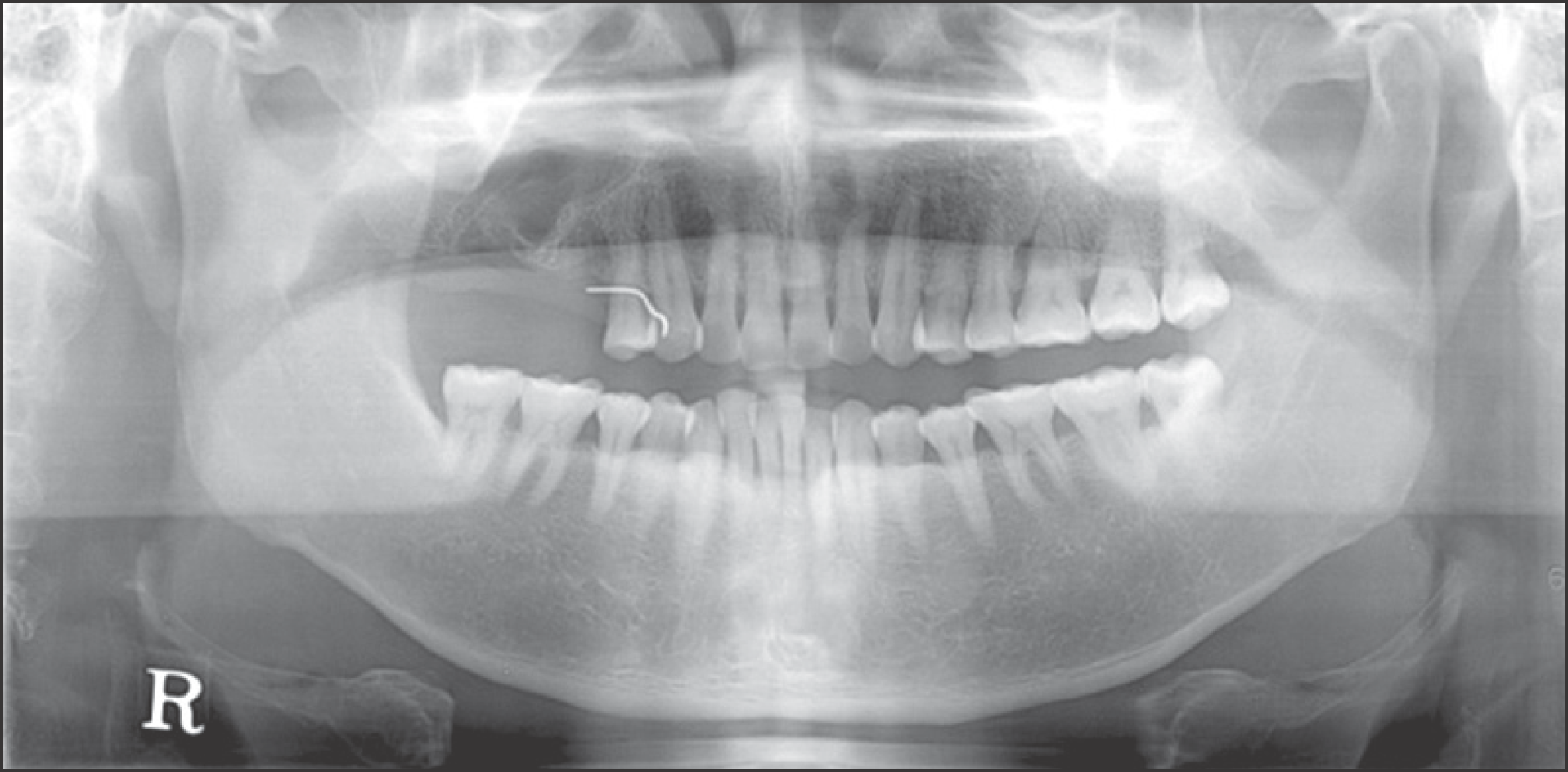
Fig. 4.
Postoperative computed tomography taken 3 months after decompression of cystic lesion. The surgical site exhibits bone formation without evidence of disease. Also, the lesion is separated from nasal cavity and mucosa. Ji-Hoon Won et al: Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
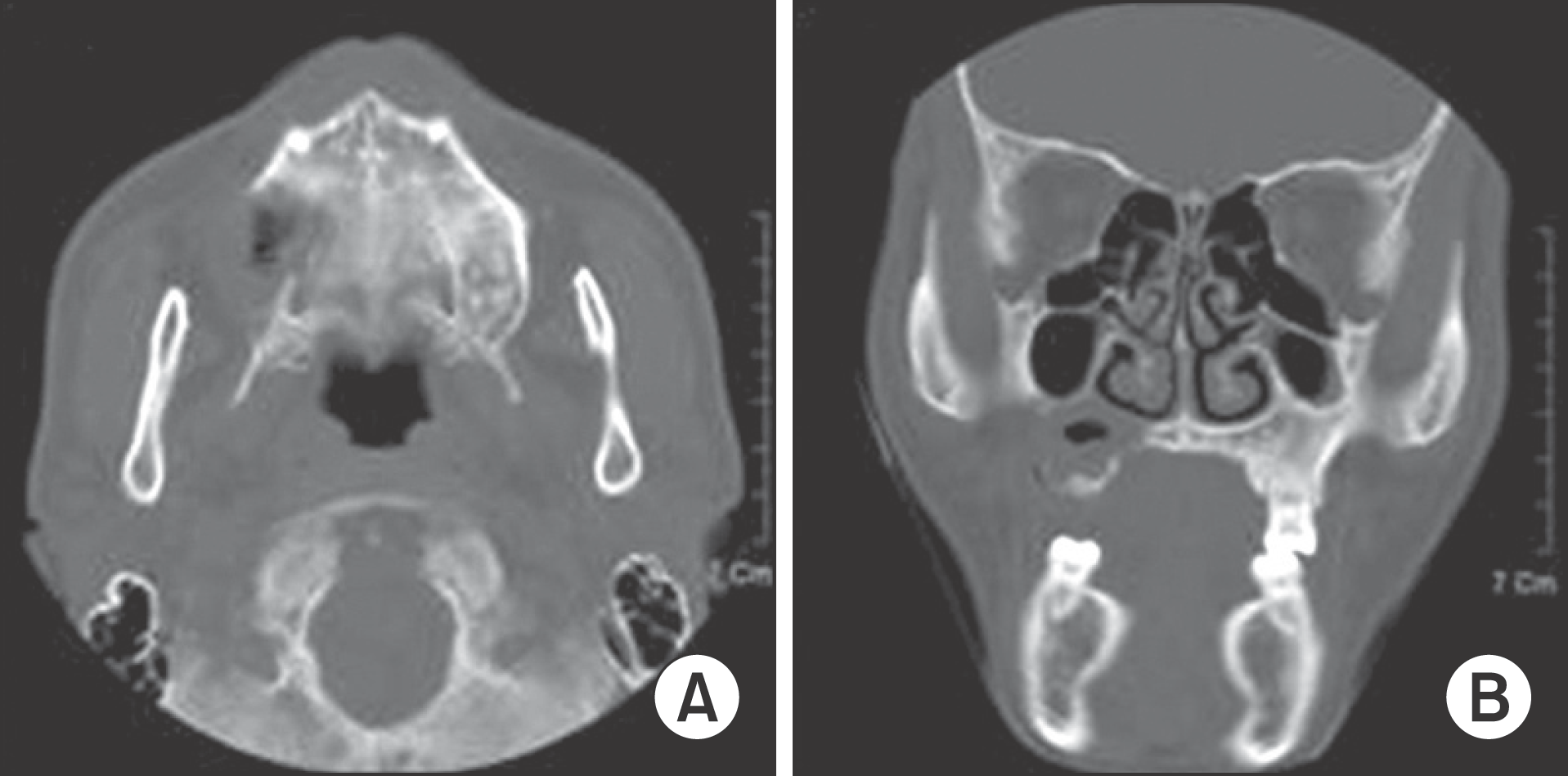
Fig. 5.
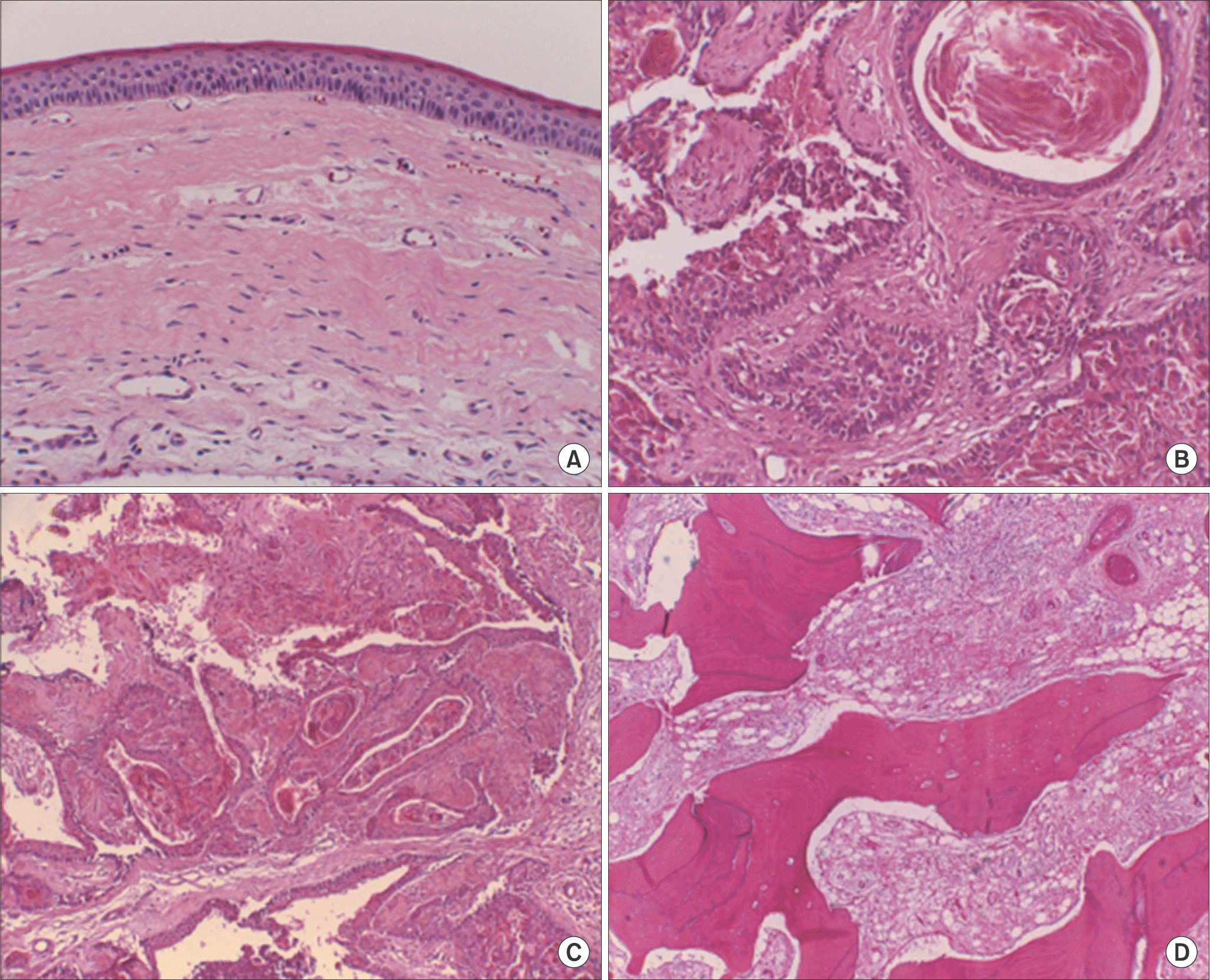
A. Typical epithelial lining of an odontogenic keratocyst (1996. 3.). B, C, D. Follicular epithelial structure containing layers of parakeratin. The follicle is lined by ameloblast-like colummar cells exhibiting hyperchromatism, palisading, reversed polarity. Several solid keratinized epithelial follicles present in stroma (2009. 6) (H&E staining, A: ×40, B, C, D: ×200). Ji-Hoon Won et al: Keratoameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download