Abstract
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
References
 | Fig. 1.Gentle-Pulse Pulp Vitality Tester D624MS (Parkell Inc., Edgewood, NY, USA). Myong-Suk Ku et al. Evaluation of the change of lower lip sensation after inferior alveolar nerve block by using the electric pulp tester. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
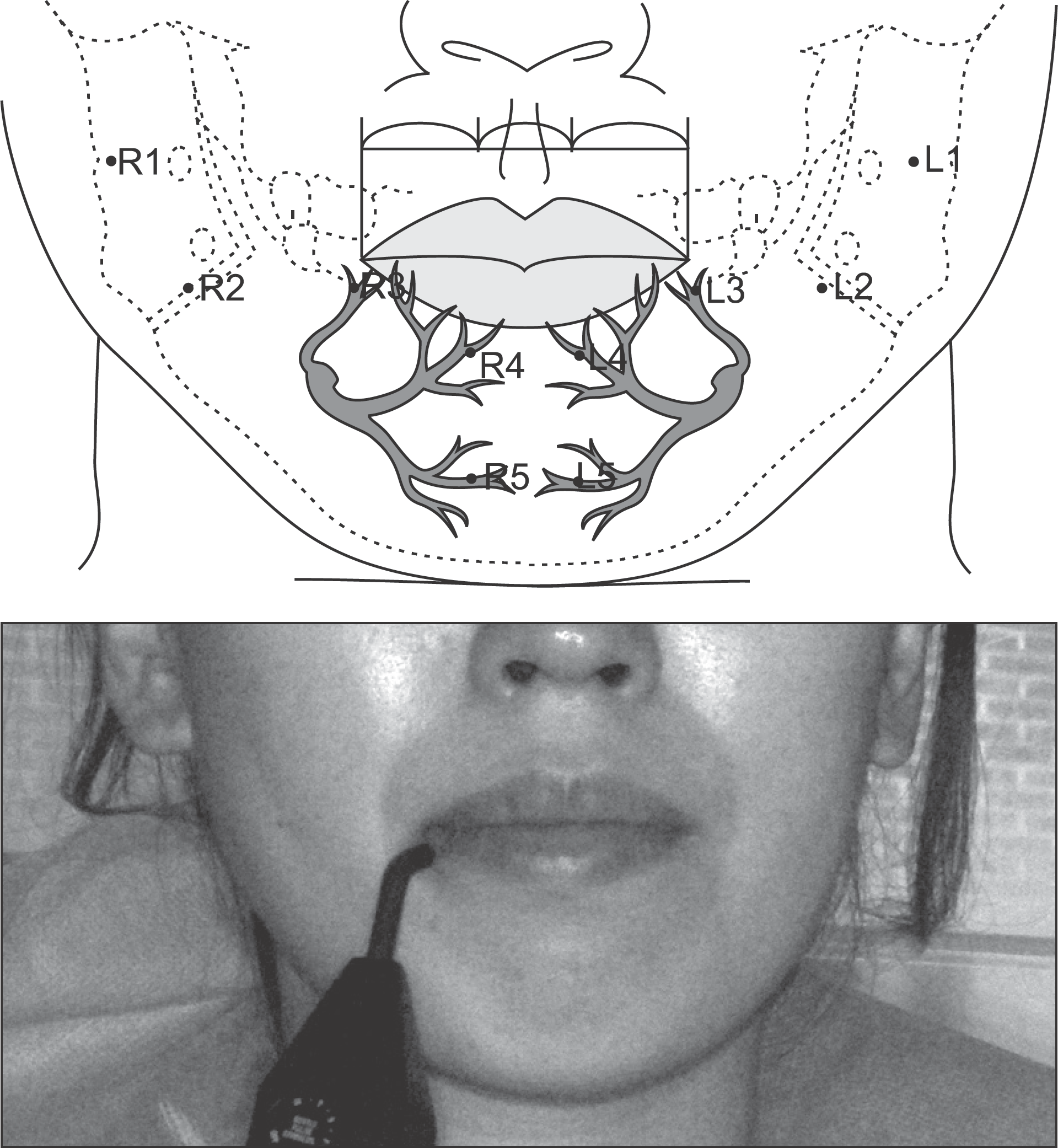 | Fig. 2.Schematic diagram of the evaluation landmarks for electric pulp tester included inferior alveolar nerves and photo of measuring patient. ① R1: a center of right mandible posterior 1/3, ② R2: a center of right mandible middle 1/3, ③ R3: the point 5 mm beneath right commissure of the lip (angular branch), ④ R4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: right (inferior labial branch), ⑤ R5: a center of perpendicular line from R4 to chin (mental branch), ⑥ L5: a center of perpendicular line from L4 to chin (mental branch), ⑦ L4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: left (inferior labial branch), ⑧ L3: the point 5 mm beneath left commissure of the lip (angular branch), ⑨ L2: a center of left mandible middle 1/3, ⑩ L1: a center of left mandible posterior 1/3. Myong-Suk Ku et al. Evaluation of the change of lower lip sensation after inferior alveolar nerve block by using the electric pulp tester. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
Table 1.
(EPT: electric pulp tester, R1: a center of right mandible posterior 1/3, R2: a center of right mandible middle 1/3, R3: the point 5 mm beneath right commissure of the lip (angular branch), R4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: right (inferior labial branch), R5: a center of perpendicular line from R4 to chin (mental branch), L1: a center of left mandible posterior 1/3, L2: a center of left mandible middle 1/3, L3: the point 5 mm beneath left commissure of the lip (angular branch), L4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: left (inferior labial branch), L5: a center of perpendicular line from L4 to chin (mental branch)) Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. Statistical significance tested by paired t-test. Myong-Suk Ku et al. Evaluation of the change of lower lip sensation after inferior alveolar nerve block by using the electric pulp tester. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
Table 2.
(EPT: electric pulp tester, R1: a center of right mandible posterior 1/3, R2: a center of right mandible middle 1/3, R3: the point 5 mm beneath right commissure of the lip (angular branch), R4: one third of lower ip vermilion border: right (inferior labial branch), R5: a center of perpendicular line from R4 to chin (mental branch), L1: a center of left mandible posterior 1/3, L2: a center of left mandible middle 1/3, L3: he point 5 mm beneath left commissure of the lip (angular branch), L4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: left (inferior labial branch), L5: a center of perpendicular line from L4 to chin (mental branch)) Statistical significance tested by ANOVA and Post-hoc analysis with Tukey test. Myong-Suk Ku et al. Evaluation of the change of lower lip sensation after inferior alveolar nerve block by using the electric pulp tester. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
Table 3.
(EPT: electric pulp tester, R1: a center of right mandible posterior 1/3, R2: a center of right mandible middle 1/3, R3: the point 5 mm beneath right commissure of the lip (angular branch), R4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: right (inferior labial branch), R5: a center of perpendicular line from R4 to chin (mental branch), L1: a center of left mandible posterior 1/3, L2: a center of left mandible middle 1/3, L3: the point 5 mm beneath left commissure of the lip (angular branch), L4: one third of lower lip vermilion border: left (inferior labial branch), L5: a center of perpendicular line from L4 to chin (mental branch)) Myong-Suk Ku et al. Evaluation of the change of lower lip sensation after inferior alveolar nerve block by using the electric pulp tester. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download