Abstract
Introduction
Epidermal growth factor is a single-chain polypeptide consisting of 53 amino acids with potent mitogenic activity that stimulates the proliferation of a range of normal and neoplastic cells through an interaction with its specific receptor (epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR). This interaction plays a key role in tumor progression including the induction of tumor cell proliferation. An increased EGFR copy number have been associated with a favorable response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors therapy. In contrast, K-ras mutations tend to predict a poor response to such therapy. The aim of this study was to determine the correlation between the clinicopathological factors and the upregulation of EGFR expression and K-ras mutations in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Materials and Methods
This study examined the immunohistochemical staining of EGFR, K-ras mutation detection with peptide nucleic acid (PNA)-based real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) clamping in 20 specimens from 20 patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Results
1. In the immunohistochemical study of poorly differentiated and invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma, a high level of EGFR staining was observed. The correlation between immunohistochemical EGFR expression and histological differentiation, as well as the tumor size of the specimens was significant (Pearson correlation analysis, significance [r] >0.5, P<0.05). 2. In PNA-based real-time PCR clamping analysis, a K-ras mutation was not detected in all specimens.
Go to : 
References
1. Kang JH, Kim KW, Lee JH. Study on mRNA expression of p21 and p73 in the cell lines of primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 27:483–490.
2. Cohen S. Isolation of submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962; 237:1544–62.
3. Cohen S, Carpenter G. Human epidermal growth factor: isolation and chemical and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975; 72:1317–21.

4. Ishitoya J, Toriyama M, Oguchi N, Kitamura K, Ohshima M, Asano K, et al. Gene amplification and overexpressi on of EGF receptor in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 1989; 59:559–62.
5. Christensen ME, Therkildsen MH, Hansen BL, Albeck H, Hansen GN, Bretlau P. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression on oral mucosa dysplastic epithelia and squamous cell carcinomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1992; 249:243–7.

6. Sankaranarayanan R, Masuyer E, Swaminathan R, Ferlay J, Whelan S. Head and neck cancer: a global perspective on epidemiology and prognosis. Anticancer Res. 1998; 18:4779–86.
7. Parkin D.M, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000, Int J Cancer. 2001; 94:153–6.
8. Carvalho AL, Ikeda MK, Magrin J, Kowalski LP. Trends of oral and oropharyngeal cancer survival over five decades in 3267 patients treated in a single institution. Oral Oncol. 2004; 40:71–6.

9. Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer. 1999; 83:18–29.

10. Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of 25 major cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer. 1999; 80:827–41.
11. Carvalho AL, Magrin J, Kowalski LP. Sites of recurrence in oral and oropharyngeal cancers according to the treatment approach. Oral Dis. 2003; 9:112–8.

12. Massarelli E, Varella-Garcia M, Tang X, Xavier AC, Ozburn NC, Liu DD, et al. KRAS mutation is an important predictor of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:2890–6.
14. Modjtahedi H, Hickish T, Nicolson M, Moore J, Styles J, Eccles S, et al. Phase I trial and tumor localization of the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody ICR62 in head and neck or lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 1996; 73:228–35.
15. Carpenter G, Zendegui JG. Epidermal growth factor, its receptor, and related proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1986; 164:1–10.

16. Ino M, Ushiro K, Ino C, Yamashita T, Kumazawa T. Kinetics of epidermal growth factor in saliva. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1993; 500:126–30.

17. Gardner DP, Shimizu N. Loss of cytotoxic effect of epidermal growth factor(EGF) on EGF receptor overexpressing cells is associated with attenuation of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase activity. J Cellular Physiol. 1994; 158:245–55.
18. Ozanne B, Richards CS, Hendler F, Burns D, Gusterson B. Overexpression of the EGF receptor is a hallmark of squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1986; 149:9–14.

19. Kunikata M, Yamada K, Yamada T, More M, Tatemoto Y, Osaki T. Epidermal growth factor receptor in squamous cell carcinoma and other epidermal lesions of squamous origin – an immunohistochemical study. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 1992; 25:387–94.
20. Pusztai L, Lewis CE, Lorenzen J, Mcgee JO. Growth factors: regulation of normal and neoplastic growth. J Pathol. 1993; 169:191–201.

21. Kim KW, Kim MJ. Expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and cell cycle analysis in the head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 26:154–163.
22. Shirasuna K, Hayashido Y, Sugiyama M, Yoshioka H, Matsuya T. Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF receptor in human oral mucosa and its malignancy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1991; 418:349–53.

23. Kranenburg O. The KRAS oncogene: past, present, and future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005; 1756:81–2.
Go to : 
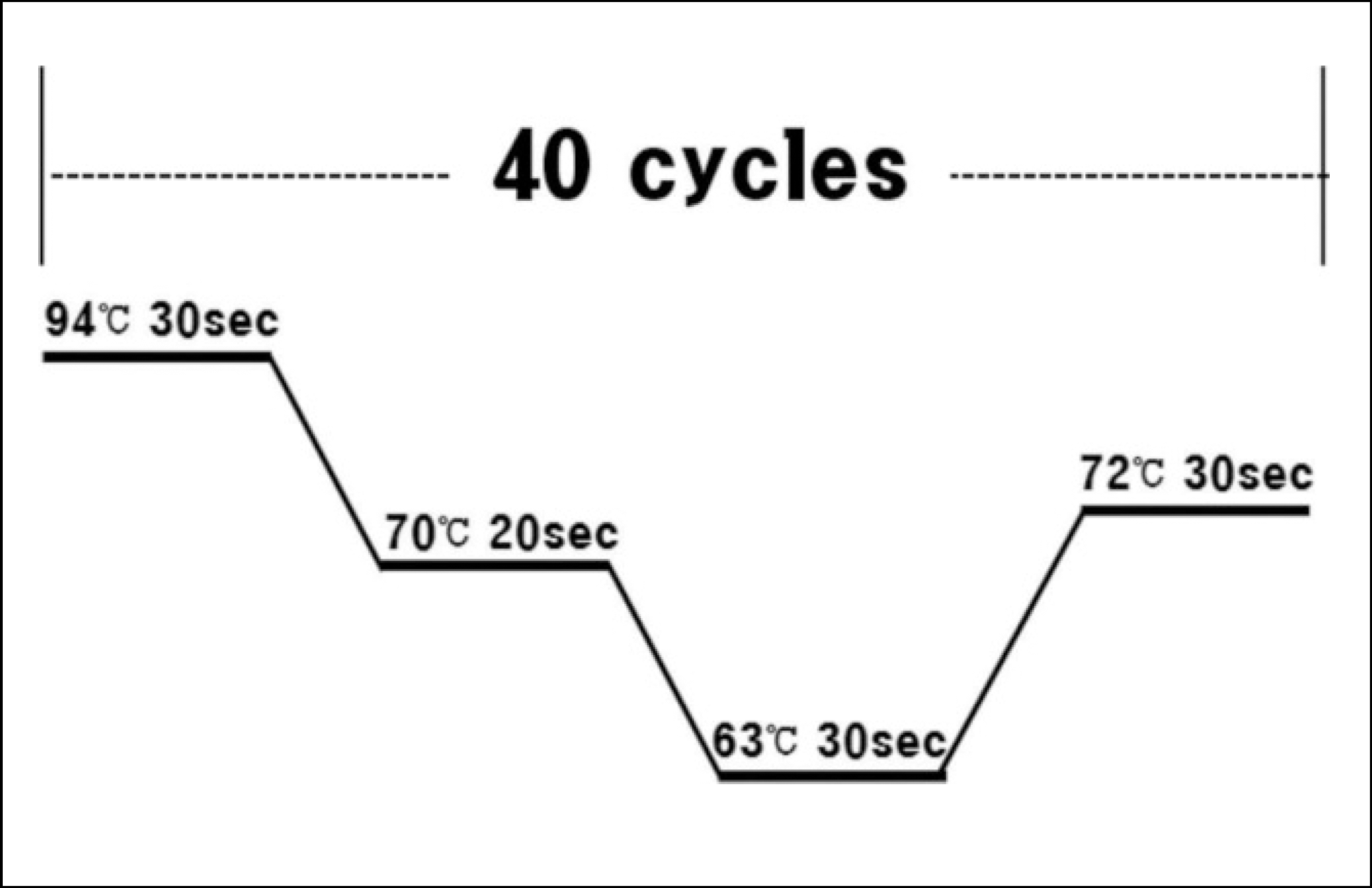 | Fig. 1.Real-time PCR cyclining condition. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
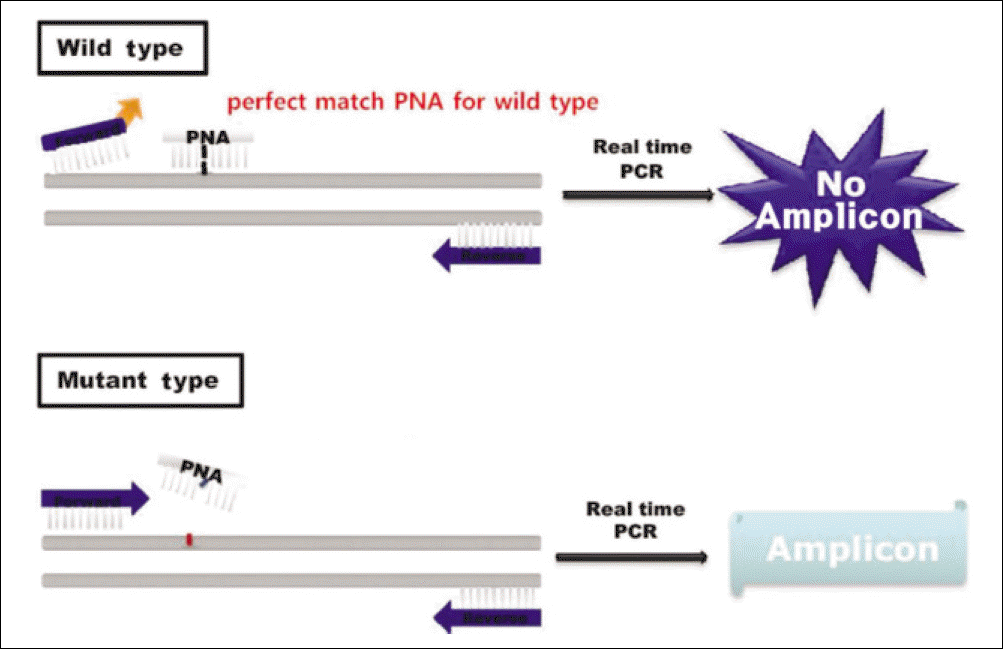 | Fig. 2.The PNA probe which is complementary to the wild type K-ras binds to the K-ras gene completely and the PCR is inhibited, while on mutant K-ras gene, the PNA probe binds to the mutan K-ras gene imcompletely and PCR is not inhibited resulting in amplicon. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
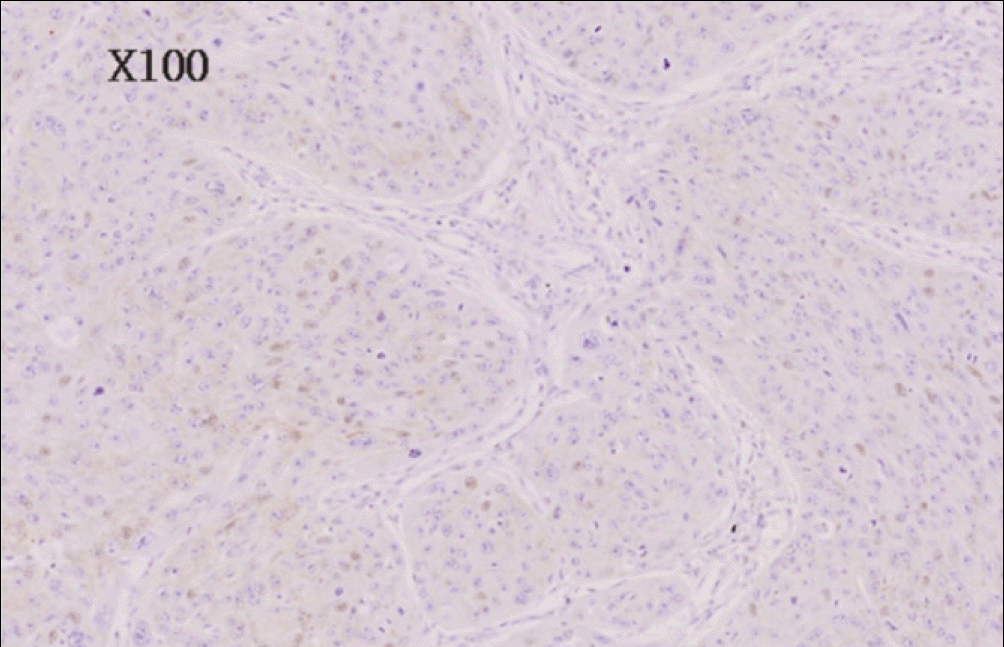 | Fig. 3.Negative immunohistochemical staining for EGFR of well differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma (anti-EGFR Immunoperoxidase, ×100). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
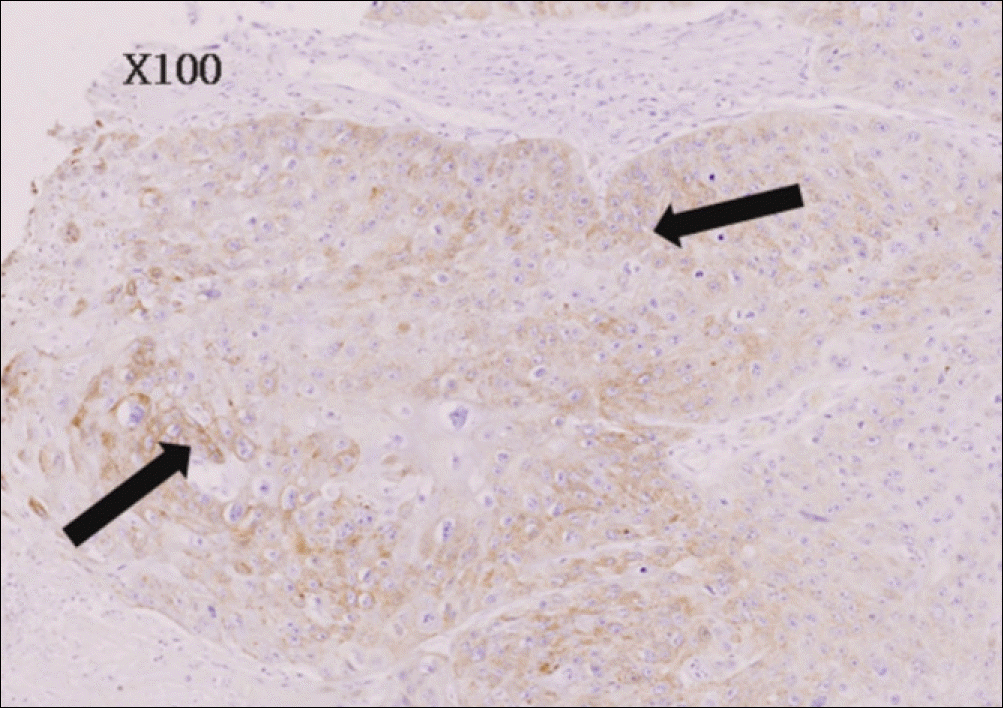 | Fig. 4.Mild immunohistochemical staining for EGFR of moderate differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma (anti-EGFR Immunoperoxidase. ×100). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
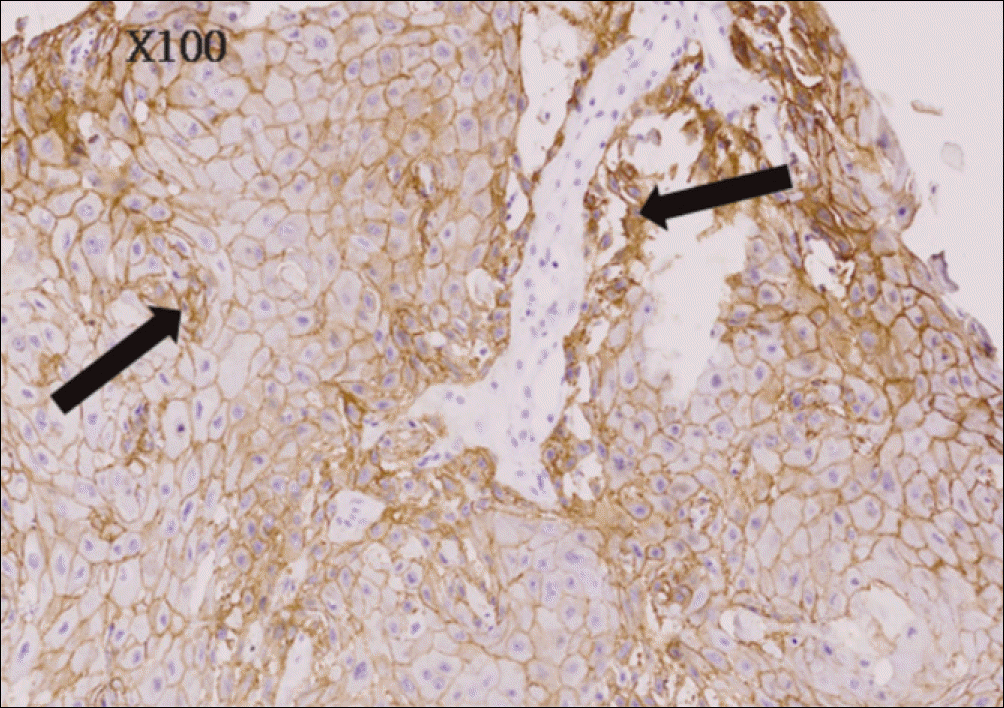 | Fig. 5.Moderate immunohistochemical staining for EGFR of poor differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma (anti-EGFR Immunoperoxidase, ×100). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
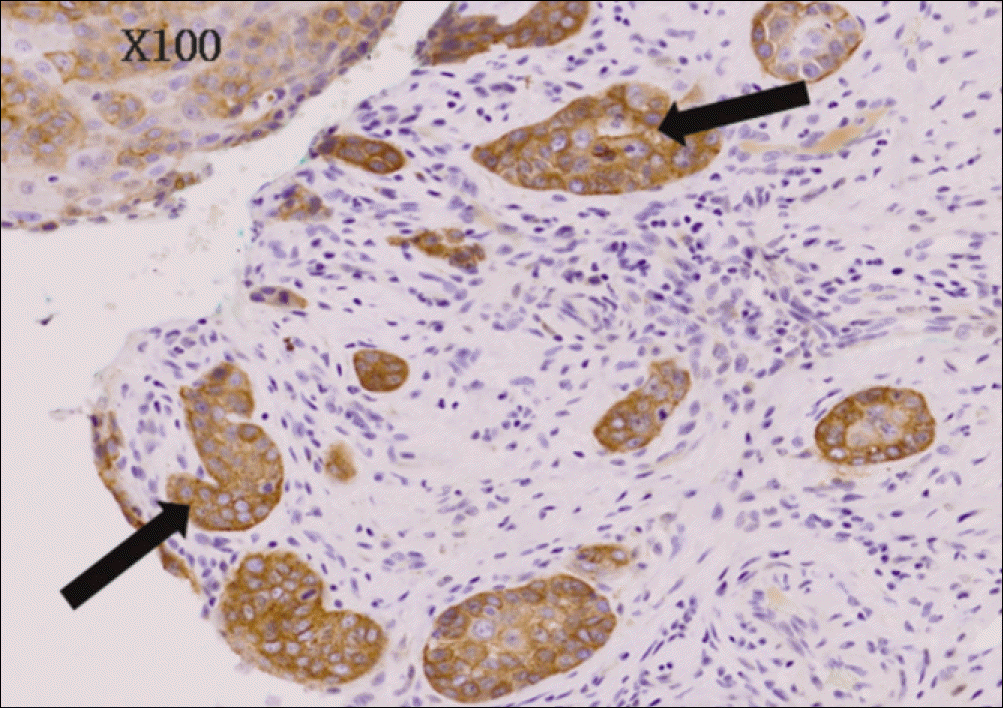 | Fig. 6.Severe immunohistochemical staining for EGFR of poor differentiated and invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma (anti-EGFR Immunoperoxidase, ×100). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
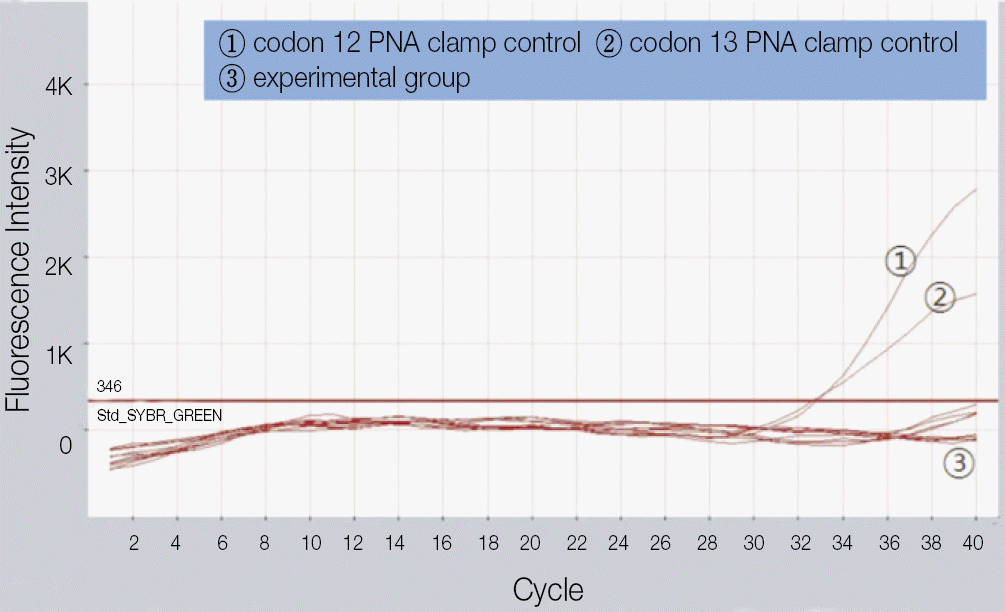 | Fig. 7.K-ras mutation detection with PNA-based real-time PCR clamping. Byeong-Chool Moon et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and K-ras mutation detection in the oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011
|
Table 1.
The correlation between immunohistochemical EGFR expression and clinical and pathological factors
| Variable | Case (n) | EGFR staining pattern | r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-staining (n=) | High-staining (n=) | P | |||
| Sex | Male | 11 | 8 | 3 | −0.071 |
| Female | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0.396 | |
| Age | 60≤ | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0.188 |
| 60> | 15 | 11 | 4 | 0.351 | |
| Histological differentiation | Well | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0.697* |
| Moderate | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.021* | |
| Poor | 4 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Tumor size | T1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| T2 | 11 | 10 | 1 | 0.599* | |
| T3 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0.032* | |
| T4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Nodal status | N(−) | 11 | 8 | 3 | 0.441 |
| N(+) | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0.335 | |
| Metastasis | M(−) | 17 | 13 | 4 | 0.394 |
| M(+) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.239 | |
| TNM stage | I | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| II | 8 | 6 | 2 | 0.419 | |
| III | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0.072 | |
| IV | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download