Abstract
Introduction
The placement of a single miniplate is not sufficient to achieve rigid fixation in mandibular angle fractures. It often causes difficulties in reducing the intermaxillary fixation (IMF) period. Consequently, the placement of 2 miniplates is preferable. The intraoral approach in an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of a mandibular angle fracture with 2 miniplates is often challenging. Accordingly, an alternative of transbuccal approach is performed. However, this method leaves a scar on the face and can result in facial nerve injury. This clinical study suggests a protocol that can maintain rigid fixation without a transbuccal approach in mandibular angle fractures.
Materials and Methods
The subjects were 7 patients who sustained fractures of the mandibular angle and treated at Department of Oral and maxillofacial surgery, Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University. ORIF under general anesthesia was done using the intraoral approach. One miniplate was inserted on external oblique ridge of the mandible, and the other was placed on lateral surface of the mandibular body with contra-angle drill and driver. A radiographic assessment and occlusal contact point examination was carried out before surgery, and 2, 4 and 6 weeks after surgery.
Go to : 
References
1. Kreutziger KL, Kreutziger KL. Comprehensive surgical management of mandibular fractures. South Med J. 1992; 85:506–18.

2. Stacey DH, Doyle JF, Mount DL, Snyder MC, Gutowski KA. Management of mandible fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 117:48e–60e.

3. Murr AH. Mandibular angle fractures and noncompression plating techniques. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005; 131:166–8.

4. Ellis E 3rd. Treatment methods for fractures of the mandibular angle. Int J Oral Maxillfac Surg. 1999; 28:243–52.

5. Lazow SK, Tarlo I. Mandible fracture: transoral 2.0-mm locking miniplate plus 1 week maxillomandibular fixation. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009; 17:27–34.

6. Fox AJ, Kellman RM. Mandibular angle fractures: two-miniplate fixation and complications. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2003; 5:464–9.
7. Sugar AW, Gibbons AJ, Patton DW, Silvester KC, Hodder SC, Gray M, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing fixation of mandibular angle fractures with a single miniplate placed either transbuccally and intraorally, or intraorally alone. Int J Oral Maxillfac Surg. 2009; 38:241–5.

8. Michelet FX, Deymes J, Dessus B. Osteosynthesis with miniaturized screwed plates in maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg. 1973; 1:79–84.

9. Champy M, Lodde JP, Schmitt R, Jaeger JH, Muster D. Mandibular osteosynthesis by miniature screwed plates via a buccal approach. J Maxillofac Surg. 1978; 6:14–21.

10. Mehra P, Murad H. Internal fixation of mandibular angle fractures: a comparison of 2 techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:2254–60.

11. Barry CP, Kearns GJ. Superior border plating technique in the management of isolated mandibular angle fractures: a retrospective study of 50 consecutive patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:1544–9.

12. Schierle HP, Schmelzeisen R, Rahn B, Pytlik C. One- or two-plate fixation of mandibular angle fractures? J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1997; 25:162–8.

13. Seeman R, Schicho K, Wutzl A, Koinig G, Poeschl WP, Krennmair G, et al. Complication rates in the operative treatment of mandibular angle fractures: a 10-year retrospective. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:647–50.
Go to : 
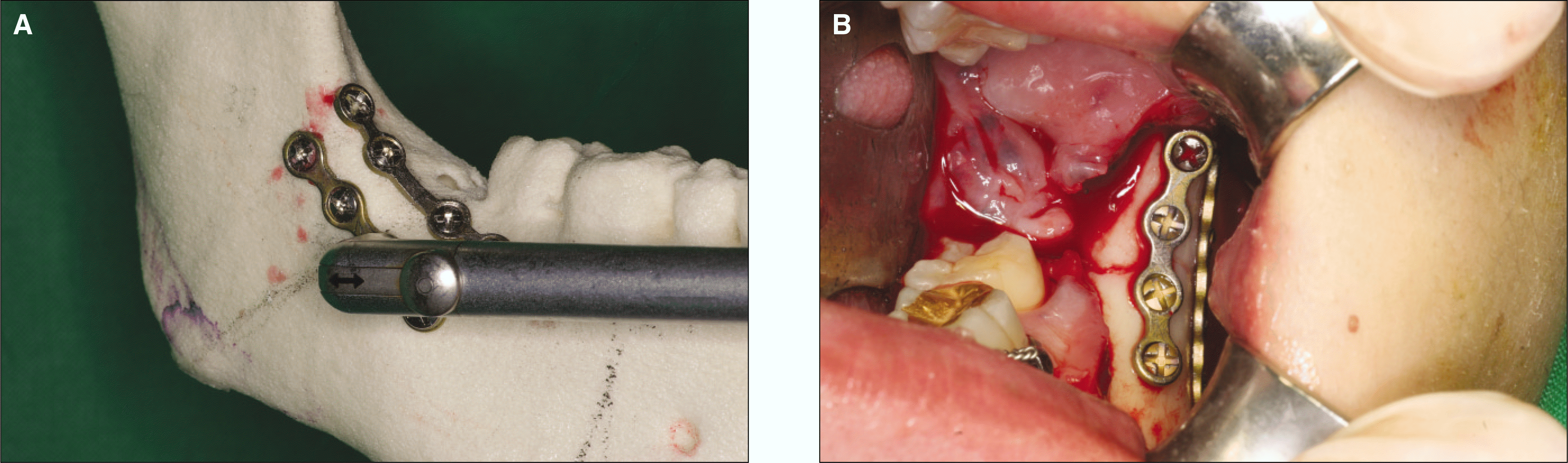 | Fig. 1.Internal fixation on mandibular angle was performed using contra-angle drill laterally. A. Approach of contra-angle drill, B. Clinical view after internal fixation in case 6. |
 | Fig. 2.Radiograph of case 3. A. Preoperative panoramic view, B. Postoperative panoramic view after 6 weeks, C. Preoperative computed tomography (CT) view, D. Postoperative CT view. |
STable 1.
Summary of patient received ORIF by this protocol
Table 2.
Treatment results of patient received ORIF by this protocol
| Time of operation1 | IMF period2 | NCP-pre-op. | NCP-post-op.3 | NCP-6 weeks | Pre-op. complication | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 60 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Paresthesia |
| Case 2 | 90 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 7 | − |
| Case 3 | 60 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Paresthesia |
| Case 4 | 110 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 4 | Paresthesia |
| Case 5 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | − |
| Case 6 | 80 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 10 | − |
| Case 7 | 80 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 8 | Infection |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download