Abstract
Various treatment methods for huge cystic lesion of the jaw exist, such as, resection of the involved bone, enucleation and decompression. Among these methods, enucleation after decompression is a conservative technique that decreases the size of the cystic cavity and reduces the risk of intra-bony defects, which could be induced by primary enucleation. In addition, it can save the adjacent anatomic structures. In these cases, the decompression combined with partial enucleation, which was performed before complete cyst enucleation was performed on huge cystic lesions of the mandible. During the process, a decrease in the size of the lesion and the growth of normal oral tissues was observed. The size of the lesion decreased until the time of complete enucleation, and surgery could be performed under local anesthesia. No damage to inferior alveolar nerve was observed. We report these cases with a review of the relevant literature.
Go to : 
References
1. Wiliams TP, Connor FA Jr. Surgical management of the odontogenic keratocyst: aggressive approach. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994; 52:964–6.
2. Bramley P. The odontogenic keratocyst-an approach to treatment. Int J Oral Surg. 1974; 3:337–41.
3. Jung YS, Lee SH, Park HS. Decompression of large odontogenic keratocysts of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:267–71.

4. Marker P, Br � ndum N, Clausen PP, Bastian HL. Treatment of large odontogenic keratocysts by decompression and later cystectomy: a longterm follow-up and a histologic study of 23 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996; 82:122–31.
5. Pogrel MA. Treatment of Keratocysts: the case for decompression and marsupialization. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:1667–73.

6. Webb DJ, Brockbank J. Treatment of the odontogenic keratocysts by combined enucleation and cryosurgery. Int J Oral Surg. 1984; 13:506–10.
7. Jensen J, Sindet-Pedersen S, Simonsen EK. A comparative study of treatment of keratocysts by enucleation or enucleation combined with cryotherapy. A preliminary report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1988; 16:362–5.
8. Meiselman F. Surgical management of the odontogenic keratocyst: conservative approach. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994; 52:960–3.

9. Forssell K, Sainio P. Clinicopathological study of keratinized cysts of the jaws. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1979; 75:36–45.
10. Bramley P. The odontogenic keratocyst-an approach to treatment. Int J Oral Surg. 1974; 3:337–41.
11. Thomas M, Tackett JC, Desai P. The incredible odontogenic keratocyst. N Y State Dent J. 1992. 31–3.
13. Rodu B, Tate AL, Martinez MG Jr. The implication of inflammation in odontogenic keratocysts. J Oral Pathol. 1987; 16:518–21.
14. Jackson RF, Kramer HS, Hyde GM, Eisenberg E, Topazian RG. Clinicopathologic conferences. Case 45, Part II: Dentigerous cyst of the mandible with ameloblastomatous changes. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1983; 41:407–8.
Go to : 
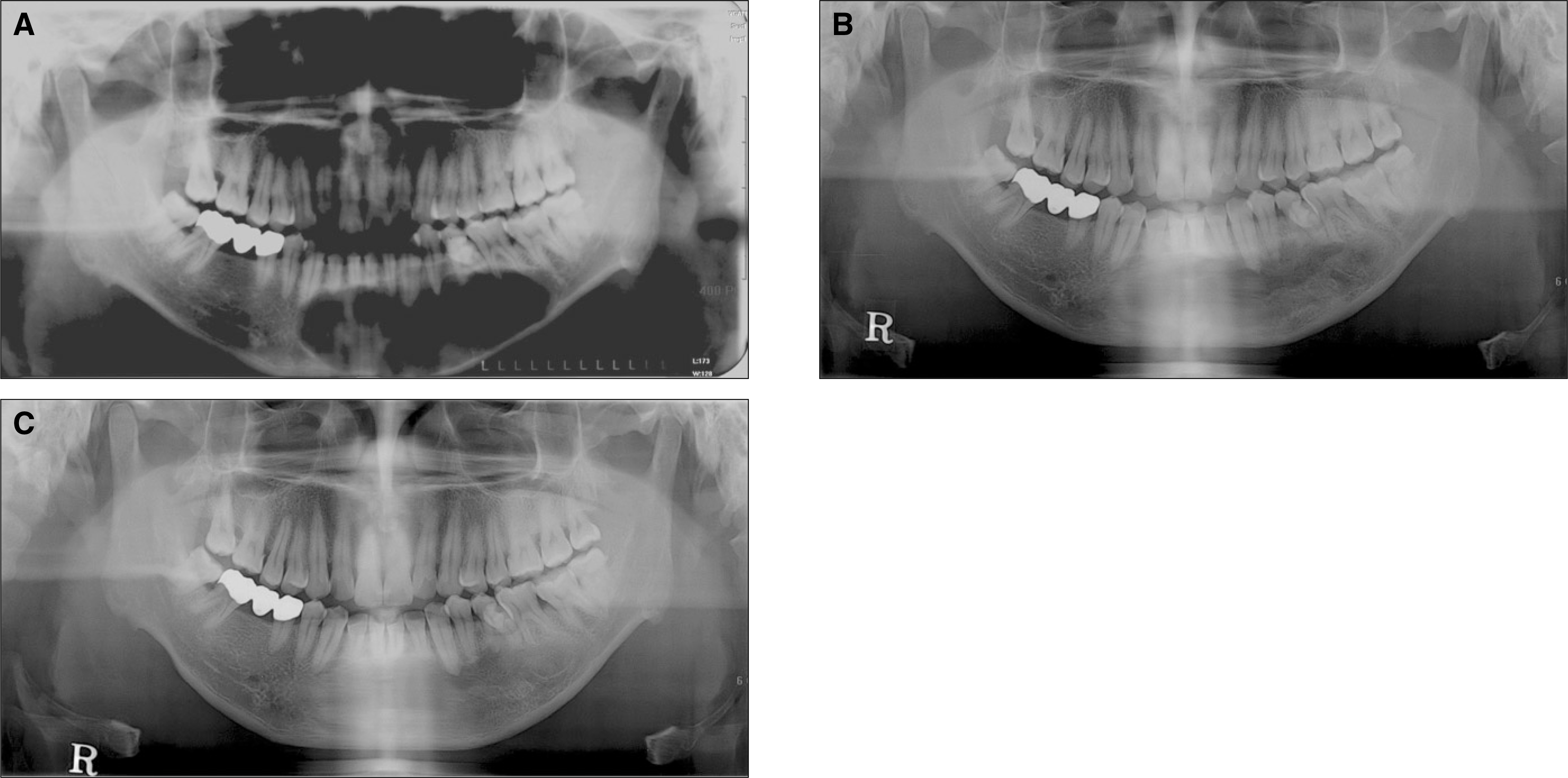 | Fig. 1.Panoramic X-rays of case 1. A. Preoperative panoramic X-ray. Huge cystic lesion is observed on the symphysis and left body of mandible. B. Post operative panoramic X-ray. After the decompression and subsequent enucleation, the cavity size of the lesion is decreased. C. Nine months follow up panoramic X-ray. Almost ossification is observed. |
 | Fig. 2.Panoramic X-rays of case 2. A. Preoperative panoramic X-ray. Scalloped huge cystic lesion is observed on the symphysis and right body of mandible. B. Post operative panoramic X-ray. After the decompression and subsequent enucleation, the cavity size of the lesion is decreased. C. Recurred odontogenic keratocyst is observed on the apex of right canine of mandible. D. One year follow up panoramic X-ray. Almost ossification is observed. |
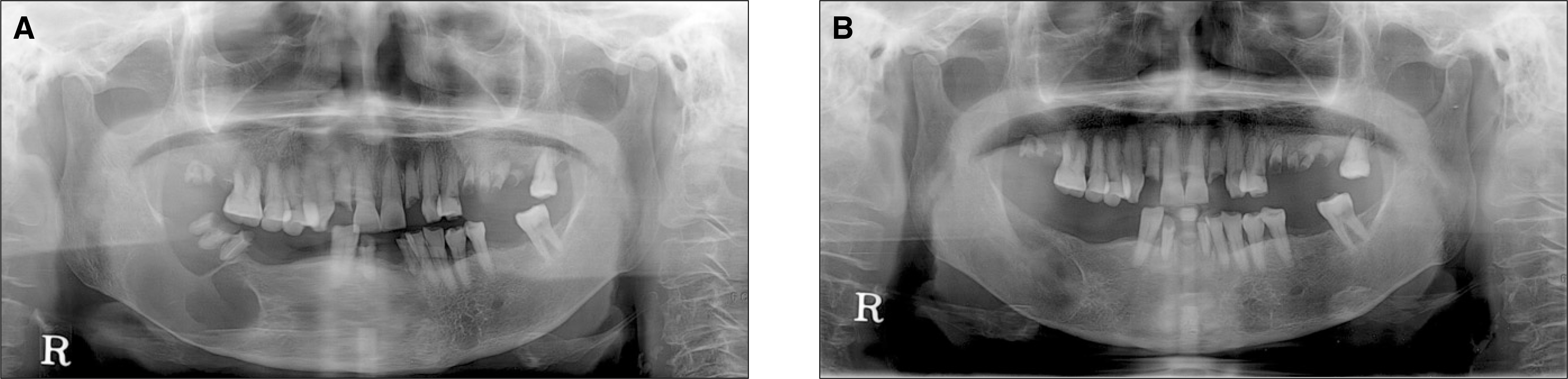 | Fig. 3.Panoramic X-rays of case 3. A. Preoperative panoramic X-ray. Huge radioluscent lesion is observed on the right body and angle of mandible. B. Post operative panoramic X-ray. After the decompression and subsequent enucleation with extraction of root rests, the lesion is almost healed. |
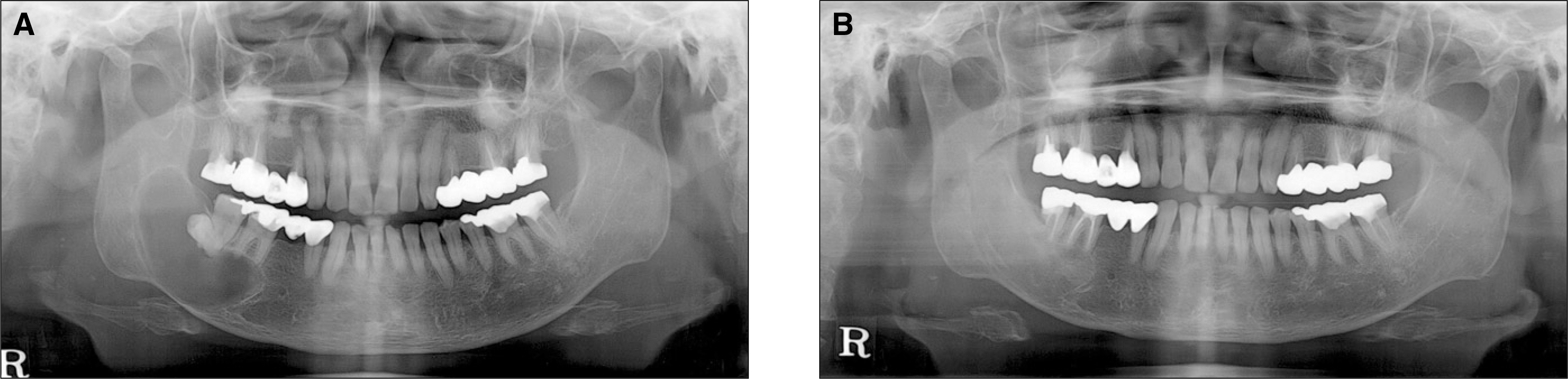 | Fig. 4.Panoramic X-rays of case 4. A. Preoperative panoramic X-ray. Huge radioluscent lesion is observed on the right body and angle of mandible. B. Post operative panoramic X-ray. After the decompression and subsequent enucleation with extraction of #48 and endodontic treatment on #46, 47, the lesion is almost healed with proper ossification. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download