1. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Development of surveillance system on alcohol consumption and alcohol-related harms based on community health survey. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011.
2. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2013: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-1). Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2014.
3. World Health Organization. Global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol. Geneva: World Health Organization;2010.
4. Foxcroft DR, Lister-Sharp D, Lowe G. Alcohol misuse prevention for young people: a systematic review reveals methodological concerns and lack of reliable evidence of effectiveness. Addiction. 1997; 92:531–537. PMID:
9219376.

5. Chen YC, Peng GS, Wang MF, Tsao TP, Yin SJ. Polymorphism of ethanol-metabolism genes and alcoholism: correlation of allelic variations with the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic consequences. Chem Biol Interact. 2009; 178:2–7. PMID:
19014920.

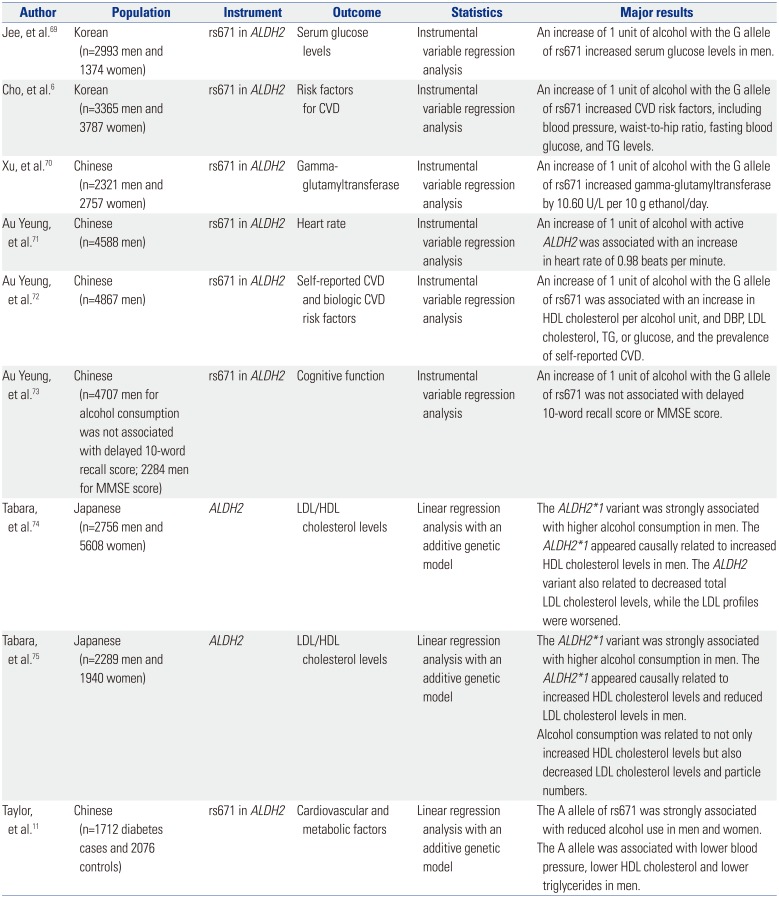
6. Cho Y, Shin SY, Won S, Relton CL, Davey Smith G, Shin MJ. Alcohol intake and cardiovascular risk factors: a Mendelian randomisation study. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:18422. PMID:
26687910.

7. Boccia S, Hashibe M, Gallì P, De Feo E, Asakage T, Hashimoto T, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis implementing a Mendelian randomization approach. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009; 18:248–254. PMID:
19124505.

8. Lewis SJ, Smith GD. Alcohol, ALDH2, and esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis which illustrates the potentials and limitations of a Mendelian randomization approach. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14:1967–1971. PMID:
16103445.

9. Yokoyama A, Omori T, Yokoyama T. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase polymorphisms and a new strategy for prevention and screening for cancer in the upper aerodigestive tract in East Asians. Keio J Med. 2010; 59:115–130. PMID:
21187698.

10. He L, Deng T, Luo H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) polymorphism and the risk of alcoholic liver cirrhosis among East Asians: a meta-analysis. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:879–884. PMID:
27189280.

11. Taylor AE, Lu F, Carslake D, Hu Z, Qian Y, Liu S, et al. Exploring causal associations of alcohol with cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors in a Chinese population using Mendelian randomization analysis. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:14005. PMID:
26364564.

12. Enomoto N, Takase S, Yasuhara M, Takada A. Acetaldehyde metabolism in different aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 genotypes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991; 15:141–144. PMID:
2024727.

13. Matsumoto C, Miedema MD, Ofman P, Gaziano JM, Sesso HD. An expanding knowledge of the mechanisms and effects of alcohol consumption on cardiovascular disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2014; 34:159–171. PMID:
24667667.

14. Knott C, Bell S, Britton A. Alcohol consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response metaanalysis of more than 1.9 million individuals from 38 observational studies. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1804–1812. PMID:
26294775.

15. Corrao G, Rubbiati L, Bagnardi V, Zambon A, Poikolainen K. Alcohol and coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis. Addiction. 2000; 95:1505–1523. PMID:
11070527.

16. Freiberg MS, Samet JH. Alcohol and coronary heart disease: the answer awaits a randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2005; 112:1379–1381. PMID:
16145011.
17. Ng Fat L, Cable N, Marmot MG, Shelton N. Persistent long-standing illness and non-drinking over time, implications for the use of lifetime abstainers as a control group. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2014; 68:71–77. PMID:
24166583.

18. Ronksley PE, Brien SE, Turner BJ, Mukamal KJ, Ghali WA. Association of alcohol consumption with selected cardiovascular disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2011; 342:d671. PMID:
21343207.

19. Park JE, Choi TY, Ryu Y, Cho SI. The relationship between mild alcohol consumption and mortality in Koreans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2015; 15:918. PMID:
26385795.

20. Holmes MV, Dale CE, Zuccolo L, Silverwood RJ, Guo Y, Ye Z, et al. Association between alcohol and cardiovascular disease: Mendelian randomisation analysis based on individual participant data. BMJ. 2014; 349:g4164. PMID:
25011450.
22. Scoccianti C, Cecchini M, Anderson AS, Berrino F, Boutron-Ruault MC, Espina C, et al. European code against cancer 4th edition: alcohol drinking and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015; 39(Suppl 1):S67–S74. PMID:
26115567.

23. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Cancer Center. Guideline for prevension of cancer (Korean). Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2016.
24. Buscemi L, Turchi C. An overview of the genetic susceptibility to alcoholism. Med Sci Law. 2011; 51(Suppl 1):S2–S6. PMID:
22021628.

25. Dragan WŁ, Oniszczenko W, Czerski PM, Dmitrzak-Weglarz M. [Family-based association study of dopaminergic genes polymorphisms and EAS temperamental traits]. Psychiatr Pol. 2013; 47:185–195. PMID:
23888754.
26. Heath AC, Bucholz KK, Madden PA, Dinwiddie SH, Slutske WS, Bierut LJ, et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol dependence risk in a national twin sample: consistency of findings in women and men. Psychol Med. 1997; 27:1381–1396. PMID:
9403910.

27. Bujarski S, Lau AS, Lee SS, Ray LA. Genetic and environmental predictors of alcohol use in Asian American young adults. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2015; 76:690–699. PMID:
26402349.

28. Wall TL, Luczak SE, Hiller-Sturmhöfel S. Biology, genetics, and environment: underlying factors influencing alcohol metabolism. Alcohol Res. 2016; 38:59–68. PMID:
27163368.
29. Eng MY, Luczak SE, Wall TL. ALDH2, ADH1B, and ADH1C genotypes in Asians: a literature review. Alcohol Res Health. 2007; 30:22–27. PMID:
17718397.
30. Luczak SE, Pandika D, Shea SH, Eng MY, Liang T, Wall TL. ALDH2 and ADH1B interactions in retrospective reports of low-dose reactions and initial sensitivity to alcohol in Asian American college students. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011; 35:1238–1245. PMID:
21355870.

31. Wall TL. Genetic associations of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase with alcohol dependence and their mechanisms of action. Ther Drug Monit. 2005; 27:700–703. PMID:
16404797.

32. Baik I, Cho NH, Kim SH, Han BG, Shin C. Genome-wide association studies identify genetic loci related to alcohol consumption in Korean men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011; 93:809–816. PMID:
21270382.

33. Dickson PA, James MR, Heath AC, Montgomery GW, Martin NG, Whitfield JB, et al. Effects of variation at the ALDH2 locus on alcohol metabolism, sensitivity, consumption, and dependence in Europeans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006; 30:1093–1100. PMID:
16792555.

34. Kim DJ, Choi IG, Park BL, Lee BC, Ham BJ, Yoon S, et al. Major genetic components underlying alcoholism in Korean population. Hum Mol Genet. 2008; 17:854–858. PMID:
18056758.

35. Hendershot CS, Neighbors C, George WH, McCarthy DM, Wall TL, Liang T, et al. ALDH2, ADH1B and alcohol expectancies: integrating genetic and learning perspectives. Psychol Addict Behav. 2009; 23:452–463. PMID:
19769429.

36. Duranceaux NC, Schuckit MA, Luczak SE, Eng MY, Carr LG, Wall TL. Ethnic differences in level of response to alcohol between Chinese Americans and Korean Americans. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2008; 69:227–234. PMID:
18299763.

37. Li H, Borinskaya S, Yoshimura K, Kal'ina N, Marusin A, Stepanov VA, et al. Refined geographic distribution of the oriental ALDH2*504Lys (nee 487Lys) variant. Ann Hum Genet. 2009; 73(Pt 3):335–345. PMID:
19456322.
38. Yukawa Y, Muto M, Hori K, Nagayoshi H, Yokoyama A, Chiba T, et al. Combination of ADH1B*2/ALDH2*2 polymorphisms alters acetaldehyde-derived DNA damage in the blood of Japanese alcoholics. Cancer Sci. 2012; 103:1651–1655. PMID:
22703580.

39. Paik IH, Lee C, Lee SJ, Lee CU, Kim JJ, Jun TY, et al. Genetic frequencies of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in Korea patients with alcohol dependence. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1998; 37:149–158.
40. Paik K. The studies on the differences in personality trait by aldehyde dehydrogenase-I genotype variances in Korean male alcoholics. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1995; 34:15–26.
41. Hashimoto M, Watanabe M, Uematsu Y, Hattori S, Miyai N, Utsumi M, et al. Relationships of alcohol dehydrogenase 1B (ADH1B) and aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) genotypes with alcohol sensitivity, drinking behavior and problem drinking in Japanese older men. Environ Health Prev Med. 2016; 21:138–148. PMID:
26825972.

42. Mulligan MK, Ponomarev I, Hitzemann RJ, Belknap JK, Tabakoff B, Harris RA, et al. Toward understanding the genetics of alcohol drinking through transcriptome meta-analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:6368–6373. PMID:
16618939.

43. Kim SW, Bae KY, Shin HY, Kim JM, Shin IS, Youn T, et al. The role of acetaldehyde in human psychomotor function: a double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Biol Psychiatry. 2010; 67:840–845. PMID:
19914598.

44. Lee B, Nam B, Seo JS, Jang S, Lee S, Yi SH. Elimination rate and pharmacokinetics of alcohol in Korean healthy male adults. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2015; 54:427–434.

45. Kawano Y. Physio-pathological effects of alcohol on the cardiovascular system: its role in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Hypertens Res. 2010; 33:181–191. PMID:
20075936.

46. Brooks PJ, Enoch MA, Goldman D, Li TK, Yokoyama A. The alcohol flushing response: an unrecognized risk factor for esophageal cancer from alcohol consumption. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e50. PMID:
19320537.

47. Assanangkornchai S, Noi-pha K, Saunders JB, Ratanachaiyavong S. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genotypes, alcohol flushing symptoms and drinking patterns in Thai men. Psychiatry Res. 2003; 118:9–17. PMID:
12759156.

48. Crabb DW, Edenberg HJ, Bosron WF, Li TK. Genotypes for aldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and alcohol sensitivity. The inactive ALDH2(2) allele is dominant. J Clin Invest. 1989; 83:314–316. PMID:
2562960.

49. Kim JM, Shin IS, Kim SW, Lee H, Yoon BH, Yoon JS. Relationships between Lifetime alcohol consumption and cognitive function in an elderly population: effect modification by level of education. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2003; 14:239–243.
50. Sin IS, Yoon JS, Kim H, Lee HY, Yoon BH, Lee H, et al. Effects of alcohol on neurocognitive function, psychomotor performance and subjective response in Koreans with different ALDH2 genotypes. J Korean Soc Biol Psychiatry. 1999; 6:176–188.
51. Zhao Y, Wang C. Glu504Lys single nucleotide polymorphism of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene and the risk of human diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:174050. PMID:
26491656.

52. Gu JY, Li LW. ALDH2 Glu504Lys polymorphism and susceptibility to coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction in East Asians: a meta-analysis. Arch Med Res. 2014; 45:76–83. PMID:
24333098.

53. Wang Q, Zhou S, Wang L, Lei M, Wang Y, Miao C, et al. ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism and coronary heart disease risk among Asian populations: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. DNA Cell Biol. 2013; 32:393–399. PMID:
23697560.
54. Jia K, Wang H, Dong P. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) Glu-504Lys polymorphism is associated with hypertension risk in Asians: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8:10767–10772. PMID:
26379870.
55. Rehm J, Shield KD, Roerecke M, Gmel G. Modelling the impact of alcohol consumption on cardiovascular disease mortality for comparative risk assessments: an overview. BMC Public Health. 2016; 16:363. PMID:
27121289.

56. Chen L, Smith GD, Harbord RM, Lewis SJ. Alcohol intake and blood pressure: a systematic review implementing a Mendelian randomization approach. PLoS Med. 2008; 5:e52. PMID:
18318597.

57. Ota M, Hisada A, Lu X, Nakashita C, Masuda S, Katoh T. Associations between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) genetic polymorphisms, drinking status, and hypertension risk in Japanese adult male workers: a case-control study. Environ Health Prev Med. 2016; 21:1–8. PMID:
26318866.

58. Yin G, Naito M, Wakai K, Morita E, Kawai S, Hamajima N, et al. ALDH2 polymorphism is associated with fasting blood glucose through alcohol consumption in Japanese men. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2016; 78:183–193. PMID:
27303105.
59. Jo SA, Kim EK, Park MH, Han C, Park HY, Jang Y, et al. A Glu487Lys polymorphism in the gene for mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 is associated with myocardial infarction in elderly Korean men. Clin Chim Acta. 2007; 382:43–47. PMID:
17459359.

60. Eom SY, Zhang YW, Kim SH, Choe KH, Lee KY, Park JD, et al. Influence of NQO1, ALDH2, and CYP2E1 genetic polymorphisms, smoking, and alcohol drinking on the risk of lung cancer in Koreans. Cancer Causes Control. 2009; 20:137–145. PMID:
18798003.

61. Smith GD, Ebrahim S. ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol. 2003; 32:1–22. PMID:
12689998.
62. Shin C, Kwack K, Cho NH, Kim SH, Baik I. Sex-specific differences in the association of a common aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene polymorphism and alcohol consumption with stroke risk in a Korean population: a prospective cohort study. Nutr Res Pract. 2015; 9:79–86. PMID:
25671072.

63. Yun KE, Chang Y, Yun SC, Davey Smith G, Ryu S, Cho SI, et al. Alcohol and coronary artery calcification: an investigation using alcohol flushing as an instrumental variable. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 1. 10. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI:
10.1093/ije/dyw237.

64. Zuccolo L, Holmes MV. Commentary: Mendelian randomization-inspired causal inference in the absence of genetic data. Int J Epidemiol. 2016; 12. 26. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI:
10.1093/ije/dyw327.

65. Alcohol Project Supporting Committee. Alcohol statistics white paper. Goyang: Alcohol Project Supporting Committee;2010.
66. Oberbeck N, Langevin F, King G, de Wind N, Crossan GP, Patel KJ. Maternal aldehyde elimination during pregnancy preserves the fetal genome. Mol Cell. 2014; 55:807–817. PMID:
25155611.

67. Yokoyama A, Kumagai Y, Yokoyama T, Omori T, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. Health risk appraisal models for mass screening for esophageal and pharyngeal cancer: an endoscopic follow-up study of cancer-free Japanese men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009; 18:651–655. PMID:
19190142.

68. Shin HY, Shin IS, Yoon JS. ALDH2 genotype-associated differences in the acute effects of alcohol on P300, psychomotor performance, and subjective response in healthy young Korean men: a double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2006; 21:159–166. PMID:
16565959.

69. Jee YH, Lee SJ, Jung KJ, Jee SH. Alcohol intake and serum glucose levels from the perspective of a mendelian randomization design: the KCPS-II biobank. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0162930. PMID:
27632197.

70. Xu L, Jiang CQ, Cheng KK, Au Yeung SL, Zhang WS, Lam TH, et al. Alcohol use and gamma-glutamyltransferase using a Mendelian randomization design in the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0137790. PMID:
26356841.

71. Au Yeung SL, Jiang C, Long M, Cheng KK, Liu B, Zhang W, et al. Evaluation of moderate alcohol use with QT Interval and heart rate using Mendelian randomization analysis among older Southern Chinese men in the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2015; 182:320–327. PMID:
26153479.

72. Au Yeung SL, Jiang C, Cheng KK, Cowling BJ, Liu B, Zhang W, et al. Moderate alcohol use and cardiovascular disease from Mendelian randomization. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68054. PMID:
23874492.

73. Au Yeung SL, Jiang CQ, Cheng KK, Liu B, Zhang WS, Lam TH, et al. Evaluation of moderate alcohol use and cognitive function among men using a Mendelian randomization design in the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2012; 175:1021–1028. PMID:
22302076.

74. Tabara Y, Arai H, Hirao Y, Takahashi Y, Setoh K, Kawaguchi T, et al. The causal effects of alcohol on lipoprotein subfraction and triglyceride levels using a Mendelian randomization analysis: The Nagahama Study. Atherosclerosis. 2017; 257:22–28. PMID:
28038378.

75. Tabara Y, Ueshima H, Takashima N, Hisamatsu T, Fujiyoshi A, Zaid M, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis in three Japanese populations supports a causal role of alcohol consumption in lowering low-density lipid cholesterol levels and particle numbers. Atherosclerosis. 2016; 254:242–248. PMID:
27575649.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download