Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
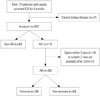 | Fig. 1Flow chart of inclusion and exclusion process for enrollment of patients in the study. A total of 179 patients were enrolled, and 162 patients were included in the analysis. AKI, acute kidney injury; ICU, intensive care unit. |
 | Fig. 2Time course of kidney markers in the AKI and non-AKI groups (n=162). Data for creatinine (A), eGFR (B), and cystatin C (C) are shown. Data were collected on day of admission, as well as on days 1, 3, and 7. Circle and square represent the mean value, and bar represents standard deviation of the mean. *Significant differences between two groups. AKI, acute kidney injury; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. |
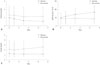 | Fig. 3Time course of kidney markers in the recovery and non-recovery groups (n = 83). Data for creatinine (A), eGFR (B), and cystatin C (C) are shown. Data were collected on day of admission, as well as on days 1, 3, and 7. Circle and square represent the mean value, and bar represents standard deviation of the mean. *Significant differences between two groups. eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. |
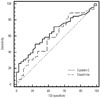 | Fig. 4Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves of creatinine and cystatin C levels on day 0 to predict renal function recovery. ROC curve using cystatin C showed a higher area under the curve (AUC) value than that using creatinine; however, the difference between cystatin C and creatinine AUC values was not statistically significant. |
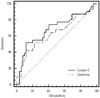 | Fig. 5Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves of creatinine and cystatin C levels on day 0 to predict renal replacement therapy. ROC curve using cystatin C showed a higher area under the curve value than the one using creatinine; however, the difference was not statistical significant. |
Table 1
Baseline Characteristics of AKI and Non-AKI Patients at Day 0 of ICU Admission (n=162)

AKI, acute kidney injury; BMI, body mass index; ICU, intensive care unit; APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; IGF-1, insulin-like glomerular factor-1; CRP, C-reactive protein.
*Chronic lung disease includes asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and structural lung diseases, such as bronchiectasis and interstitial lung disease.
Table 2
Multivariate Analysis of Cystatin C for AKI Development in ICU Sepsis Patients (n=155, at Day 0 of ICU Admission)

AKI, acute kidney injury; ICU, intensive care unit; OR, odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
*Chronic lung disease includes asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and structural lung diseases, such as bronchiectasis and interstitial lung disease.
Table 3
Clinical Characteristics of Recovery and Non-Recovery of AKI Patients at Day 0 of ICU Admission (n=83)
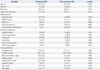
AKI, acute kidney injury; BMI, body mass index; ICU, intensive care unit; APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; IGF-1, insulin-like glomerular factor-1; CRP, C-reactive protein.
*Chronic lung disease includes asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and structural lung diseases, such as bronchiectasis and interstitial lung disease.
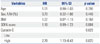
Table 4
Multivariate Analysis of Cystatin C for Non-Recovery of AKI in Sepsis-Induced AKI Patients (n=83, at Admission, Day 0)

| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.99 | 0.96–1.02 | 0.537 |
| Sex, F/M (%) | 0.69 | 0.25–1.93 | 0.479 |
| BMI | 0.99 | 0.87–1.12 | 0.819 |
| APACHE II score | 1.10 | 0.99–1.22 | 0.064 |
| Cystatin C | 1.64 | 1.00–2.68 | 0.048 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download