Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
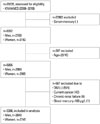 | Fig. 1Flow chart of study subjects. KNHANES, Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; DM, type 2 diabetes; YO, years old. |
Table 1
Clinical Characteristics of the 5388 Study Subjects
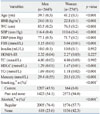
BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBS, fasting blood sugar; TC, total cholesterol; HDLC, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; Mercury, blood Mercury; HOMA-IR, Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance.
Data represent mean (standard error) after weighting in complex sample analysis. p values were from a general linear model without adjustment.
*Missing data were not included.
†Percentage of total study subjects.
‡p value from the χ2 test.
Table 2
Correlation of Log (Hg) with Metabolic Parameters
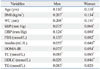
Log (Hg), log transformed blood mercury for normal distribution; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBS, fasting blood sugar; TC, total cholesterol; HDLC, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HOMA-IR, Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance.
Data represent Pearson correlation coefficient.
*p<0.05.
†p<0.001.
Table 3
Comparison of Clinical Characteristics of Study Subjects According to Quartiles of Blood Mercury

BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBS, fasting blood sugar; HOMA-IR, Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance; TC, total cholesterol; HDLC, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; Mercury, blood Mercury; SE, standard error.
Data represent mean (SE). Each Q represents quartiles of blood mercury concentrations. p values are p for trend from a general linear model after data weighting in complex sample analysis without adjustment.
*Represent p<0.05 by ANCOA test after adjustments with job, education, smoking, alcohol intake, and moderate physical activity and history of hypertension.
Table 4
Linear Regression Analysis of the Relationship between HOMA-IR and Clinical Parameters
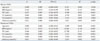
Table 5
Logistic Regression Analysis of Having the Highest Quartile of HOMA-IR According to Blood Mercury Quartile
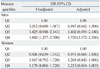
HOMA-IR, Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance.
Data represent odds ratio (OR) of being in the highest quartile of HOMA-IR with 95% confidence interval (CI) by logistic regression analysis before (unadjusted) and after adjustments for age, total cholesterol, and triglyceride, job, education, smoking, alcohol intake, and moderate physical activity.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download