Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
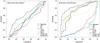 | Fig. 1Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves. Sensitivity represents the true-positive results and 1-specificity, the false-positive results. The best markers have ROC curves that are shifted to the left with areas under the curve near unity. Non-diagnostic markers are represented by diagnosis with areas under the ROC curves close to 0.5. AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; hs-CRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. |
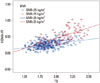 | Fig. 2Correlation between TG and HOMA-IR categorized by BMI. Data for HOMA-IR and TG were skewed and log-transformed for analysis. The lines of best fit (BMI<25.0 kg/m2: r2=0.095, p<0.001; BMI≥25.0 kg/m2: r2=0.336, p<0.001) are indicated. BMI, body mass index; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; TG, triglyceride. |
Table 1
Characteristics of Subjects Categorized by Body Mass Index in PCOS Patients
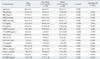
BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; TT, total testosterone; FT, free testosterone; SHBG, sex hormone-binding globulin; OHP, hydroxyprogesterone; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; γ-GT, gamma-glutamyltransferase; hs-CRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome.
Data presented are mean±standard deviation. Data for TT, SHBG, 17α-OHP, ALT, AST, ALT/AST ratio, TC, TG, LDL-C, and γ-GT were skewed, and are presented as median (interquartile range), and were log-transformed for analysis.
*Unadjusted p-value by Student's t-test or χ2 test.
†Age adjusted p-value by analysis of covariance.
Table 2
Insulin Resistance of Subjects Categorized by Body Mass Index

FPG, fasting plasma glucose; PPG, post-load 2-hr plasma glucose; FPI, fasting plasma insulin; PPI, post-load 2-hr plasma insulin; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
Data for FPG, PPG, FPI, PPI, and HOMA-IR were skewed, and are presented as median (interquartile range). HOMA-IR was calculated using the following formula; [FPG (mg/dL)×FPI (uIU/mL)]/405. Data for FPG, FPI, PPI, and HOMA-IR were log-transformed for analysis.
*Unadjusted p-value by Student's t-test or χ2 test.
†Age adjusted p-value by analysis of covariance.
Table 3
Comparison of Areas Under the ROC Curves (95% CI) for Potential Markers of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR≥2.5) of Subjects Categorized by Body Mass Index

ROC, receiver operating characteristics; CI, confidence interval; AUC, area under ROC curve; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; hs-CRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
Data for ALT, AST, ALT/AST ratio, LDL-C, TG were skewed and log-transformed for analysis.
Table 4
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis of the Correlation between Various Confounding Factors and HOMA-IR of Subjects Categorized by Body Mass Index

BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; hs-CRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
Data for ALT/AST ratio, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-C were skewed and log-transformed for analysis.
*p value<0.05.
Table 5
Comparison of Triglycerides for Predicting of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR≥2.5) of Subjects Categorized by Body Mass Index




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download