Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
References
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Supplementary Table 1
In Vitro Characteristics of Selected Chemicals with Docking Score Order 1-50
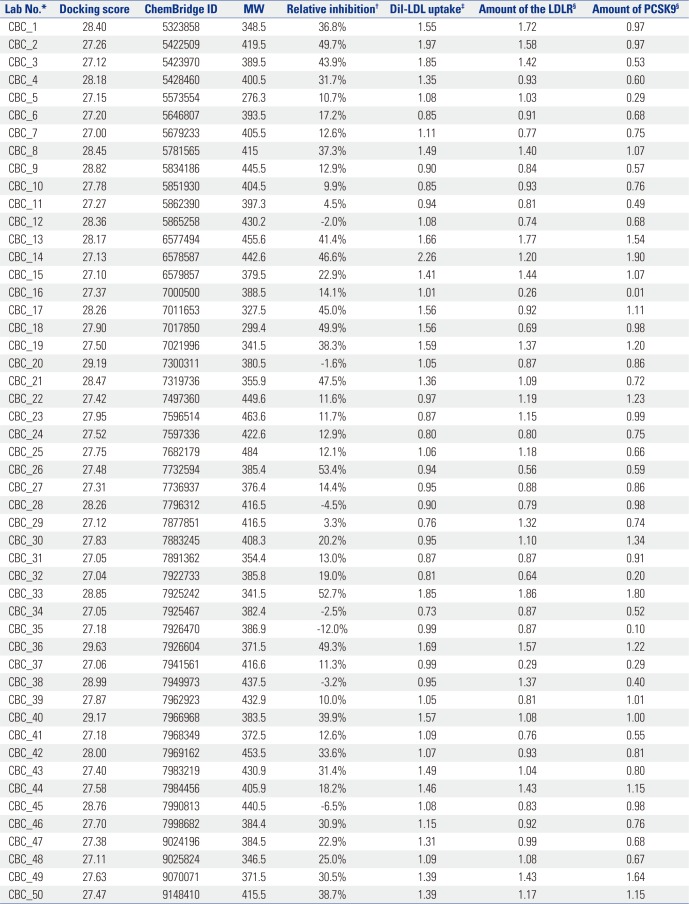
MW, molecular weight; LDL, low density lipoprotein; LDLR, LDL receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
*Lab No. is arbitrarily denoted according to the order of the ChemBridge ID number, †Relative inhibition represents the difference in percentile between the intensity of PCSK9-LDLR in the presence of the chemical and that in the presence of the vehicle (DMSO), which was set as 100%, ‡Dil-LDL uptake denotes the factor of the mean fluorescence intensity in HepG2 cells treated with each chemical compared to that in cells treated with the vehicle, §The amount of LDLR or PCSK9 denotes the factor of the signal for LDLR or PCSK9, respectively, from immunoblot data analyzed by ImageJ.
Supplementary Table 2
In Vitro Characteristics of Selected Chemicals with Docking Score Order 51-100
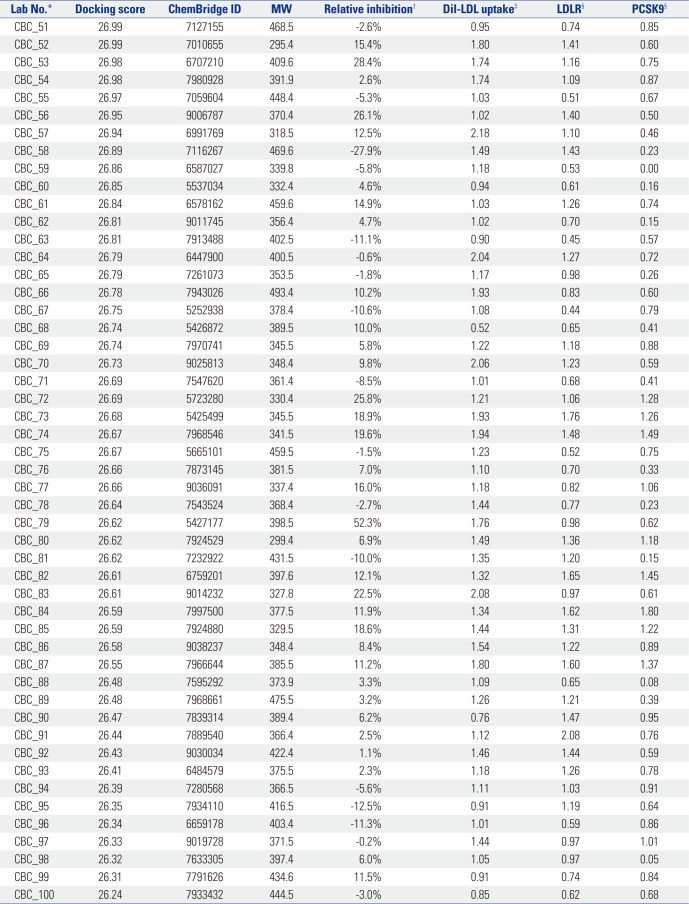
MW, molecular weight; LDL, low density lipoprotein; LDLR, LDL receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
*Lab No. is arbitrarily denoted according to the order of the ChemBridge ID number, †Relative inhibition represents the difference in percentile between the intensity of PCSK9-LDLR in the presence of the chemical and that in the presence of the vehicle (DMSO), which was set as 100%, ‡Dil-LDL uptake denotes the factor of the mean fluorescence intensity in HepG2 cells treated with each chemical compared to that in cells treated with the vehicle, §The amount of LDLR or PCSK9 denotes the factor of the signal for LDLR or PCSK9, respectively, from immunoblot data analyzed by ImageJ.
Fig. 2
Effects of CB_36 and its analogs in HepG2 cells. (A) At 18 h after treatment of CB_36, amounts of LDLR and PCSK9 were determined by immunoblot analysis. (B) Fluorescence-labeled Dil-LDL was incubated for an additional 2 h, and the uptake of Dil-LDL was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. (C) The intensity of fluorescence was quantitated by flow cytometry analysis. Each value represents the ratio of the mean fluorescence intensity relative to that in vehicle-treated cells (DM). Error bars represent the SD of triplicate reactions. Similar results were obtained from at least three independent experiments. *p<0.05, †p<0.01 Student's t-test when compared with values in DMSO-treated cells. PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; LDL, low density lipoprotein; LDLR, LDL receptor; GAPDH, glyceraledhyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.

Fig. 3
In vivo effects of CB_36 in wild-type and Pcsk9 knockout mice. (A) FPLC profiles of plasma cholesterol from wild-type (WT) and Pcsk9-/- mice after injection with CB_36. The pooled plasma from mice described in Table 2 was fractionated by FPLC, and the concentration of cholesterol in each fraction was measured as described under "Materials and Methods." (B) Aliquots of liver lysates were subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (livers from two mice were pooled for lanes 1-6 in WT and for lanes 7, 8, 10, and 11 in Pcsk9-/-), and amounts of Ldlr and Pcsk9 were determined by immunoblot analysis. Gapdh was used as an invariant control. FPLC, fast performance liquid chromatography.
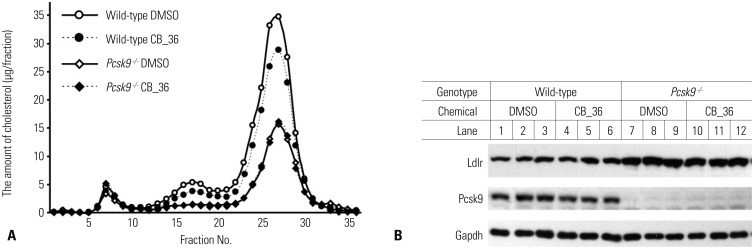
Table 1
Spearman's Rank-Order Correlation Analysis of Docking Scores and Effects of Chemicals
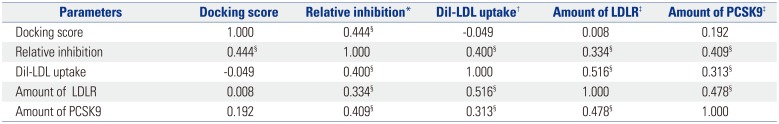
LDL, low density lipoprotein; LDLR, LDL receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
*Relative inhibition represents the difference in percentile between the intensity of PCSK9-LDLR in the presence of each chemical and that in the presence of the vehicle (DMSO), which was set as 100%, †Dil-LDL uptake denotes the factor of the mean fluorescence intensity in HepG2 cells treated with each chemical compared to that in cells treated with the vehicle, ‡The amount of LDLR or PCSK9 denotes the factor of the signal for the LDLR or PCSK9, respectively, from immunoblot data analyzed by ImageJ, §p<0.01 (bilateral), n=100.
Table 2
The Effect of CB_36 in Wild-Type and Pcsk9 Knock-Out Mice
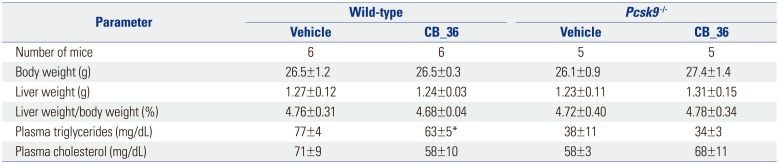
SEM, standard error of the mean.
Male mice, 10-12 weeks of age, were injected with CB_36 as described under "Materials and Methods." Each value represents the mean±SEM of the indicated number of mice.
*p<0.05 (Student's t-test) when compared with values in vehicle-injected mice. Similar results were obtained in one additional independent experiment.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download