Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Demonstration of slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry. The ultrasound probe is inserted into the Goldmann tonometry mount, and under joystick control, it can be softly and precisely used to touch the surface of the cornea. |
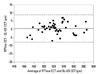 | Fig. 2Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the measurement of central corneal thickness between RTVue and slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry (SL-US). Mean difference of 0.5±4.3 (corrected SD) µm with limits of agreement between - 7.8 to 8.8 µm. For each subject, three consecutive measurements (repeatability data) with each instrument were averaged, and the difference was calculated. CCT, central corneal thickness; SD, standard deviation. |
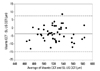 | Fig. 3Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the measurement of central corneal thickness between Visante and slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry (SL-US). Mean difference of - 3.6±5.7 (corrected SD) µm with limits of agreement between - 14.9 to 7.6 µm. For each subject, three consecutive measurements (repeatability data) with each instrument were averaged, and the difference was calculated. CCT, central corneal thickness; SD, standard deviation. |
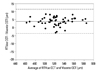 | Fig. 4Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the measurement of central corneal thickness between RTVue and Visante. Mean difference of 4.1±3.9 (corrected SD) µm with limits of agreement between - 3.5 to 11.8 µm. For each subject, three consecutive measurements (repeatability data) with each instrument were averaged, and the difference was calculated. CCT, central corneal thickness; SD, standard deviation. |
Table 1

CI, confidence interval; CV, coefficient of variation; ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; Rco, repeatability coefficient; SL-US, slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry; SD, standard deviation.
*One-way analysis of variance was used to compute Rco. Each subject's standard deviation was not correlated with each subject's mean (p=0.400, 0.188, 0.540 for RTVue, Visante, SL-US, respectively, Kendall's tau correlation).
†Average thickness of the central zone (2 mm diameter) was used. The corneal thickness was calculated by automated image processing software.
Table 2

CI, confidence interval; CV, coefficient of variation; ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; Rco, reproducibility coefficient; SL-US, slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry; SD, standard deviation.
*One-way analysis of variance was used to compute Rco. Each subject's standard deviation was not correlated with each subject's mean (p=0.230, 0.159, 0.115 for RTVue, Visante, SL-US, respectively, Kendall's tau correlation).
†Average thickness of the central zone (2 mm diameter) was used. The corneal thickness was calculated by automated image processing software.
Table 3

Table 4

CCT, central corneal thickness; CI, confidence interval; LoA, limit of agreement; NA, not available; SD, standard deviation.
*Repeatability and reproducibility were calculated by 2 repeated measurements.
†The mean of average value of the 2 repeated tests is not available.
‡To compare our results with others, we calculated coefficients again; repeatability or reproducibility coefficient=1.96×standard deviation of the difference between test 1 and test 2.95% CI of coefficient was estimated as explained in 'Details of statistical calculations'.
§The value is not clearly noted as the mean of average value of the 2 repeated tests.
∥Repeatability and reproducibility were calculated by 3 repeated measurements.
¶Measurement by pupil-centered RTVue was selected.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download