Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Figures and Tables
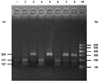 | Fig. 1The genotype analysis of SNP rs840088 by the PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method. rs840088G/A allele was genotyped by PCR-RFLP. PCR products were digested with MLY1 for 3 h at 37℃. After electrophoresis in 2.0% agarose gel and staining with ethidium bromide, the genotypes were determined. When the GG allele was present, MLY1 would cut the 304 bp PCR products into two fragments of 177 bp and 127 bp. The AA homozygous case showed a 304 p uncleavage product, while the GA heterozygous case showed 304 bp, 177 bp and 127 bp products. Lane M: DNA Marker; Lane1, 2, 4, 6: GG genotype; Lane3, 7, 8: GA genotype; Lane5: AA genotype. 90×66 mm (300×300 DPI). SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism. |
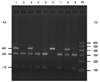 | Fig. 2The genotype analysis of SNP rs1438831 by the PCR-RFLP method. The SNP rs1438831G/A was also analyzed by PCR-RFLP using Taq1 enzyme. Taq1 digestion for 3 h at 65℃ cut the 402 bp PCR products into two fragments of 292 bp and 110 bp when the GG allele was present. The AA homozygous case showed 402 bp uncleavage product, while the GA heterozygous case showed 402 bp, 292 bp and 110 bp products. Lane M indicates the 100-bp molecular markers. Lanes 2, 3 and 6 indicate three kinds of genotypes: GG, GA, AA respectively. 81×58 mm (300×300 DPI). PCR-RFLP, PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism. |
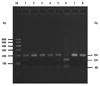 | Fig. 3The genotype analysis of rs3795879 by the PCR-RFLP method. In the case of rs3795879, MSC1 cleaved PCR products into 134 bp and 60 bp when GG allele was present. AA homozygous case showed 194 bp uncleavage product, while the GA heterozygous case showed 194 bp, 134 bp and 60 bp products. Lane M was loaded with 100-bp molecular markers. Lanes 1, 2 and 6 indicate three kinds of genotypes: GA, AA, GG respectively. 81×60 mm (300×300 DPI). PCR-RFLP, PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism. |
 | Fig. 4The DNA sequencing of rs840088. Direct sequencing of a subgroup of samples with the same primers for PCR-RFLP was performed using the BigDye Terminator v1.1 Cycle Sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems), and analyzed on an ABI PRISM 3100 DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA). (A) GG genotype. (B) GA genotype. (C) AA genotype. 82×48 mm (300×300 DPI). |
 | Fig. 5The DNA sequencing of rs1438831. DNA sequencing was performed as described in Fig. 4. (A) GG genotype. (B) GA genotype. (C) AA genotype. 82×48 mm (300×300 DPI). |
 | Fig. 6The DNA sequencing of rs3795879. DNA sequencing was performed as described in Fig. 4. (A) GG genotype. (B) GA genotype. (C) AA genotype. 82×48 mm (300×300 DPI). |
Table 1

COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Four hundred and nine patients with clinical diagnosis of COPD and 411 unrelated healthy controls without any respiratory system diseases, all of Chinese Han nationality, were selected for study. COPD was diagnosed according to the guidelines of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) consensus statement. Pulmonary function tests were performed to determine FVC, FEV1, FEV1% predicted, FEV1/FVC and post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC.
*Data are presented as No. or mean SD.
†p values were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U-test.
Table 2

The genotype distributions of rs840088, rs1438831, rs3795879 in controls and COPD patients were calculated. Each variation for deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) was evaluated by means of an χ2 test.
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
*p values were calculated using the χ2 test.
†Data are presented as No. (%).
‡Odds ratios were calculated using logistic regression to measure the ORs for COPD of specific genotypes.
Table 3

Table 4

Three SNPs were used to construct haplotypes. Using SHEsis software, four haplotypes were constructed (frequency >0.05). There is no significant association of haplotype frequencies of four haplotypes with COPD patients and controls (p>0.05).
SNPs, single nucleotide polymorphisms; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
*The global p-value was calculated with haplotype frequencies greater than 0.03 by the online software.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download