MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
CT Imaging
Image Reading and Data Analysis
RESULTS
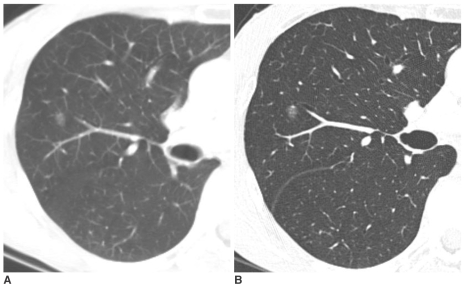 | Fig. 1Pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe confirmed as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia in a 62-year-old woman.
A. Initial CT shows 8 mm pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe.
B. Thin-section CT after 10 months shows persistent pure nodular ground-glass opacity with the same size. The lesion was pathologically confirmed by right upper lobectomy. She had a history of curative resection of adenocarcinoma in the left upper lobe one year before.
|
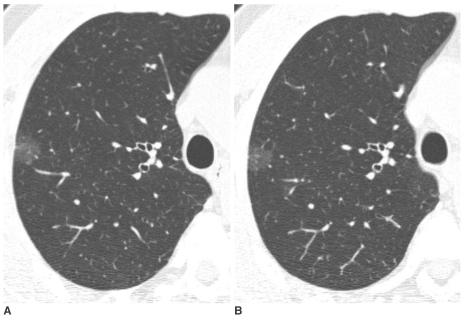 | Fig. 2Pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe confirmed as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia in a 58-year-old man.
A. Initial thin-section CT shows a 15 mm pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe.
B. On thin-section CT after 2 months, an interval change was not noted. An additional two pure nodular ground-glass opacities were found in the right upper lobe and one in the right middle lobe. All lesions were pathologically confirmed as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia by multifocal wedge resection.
|
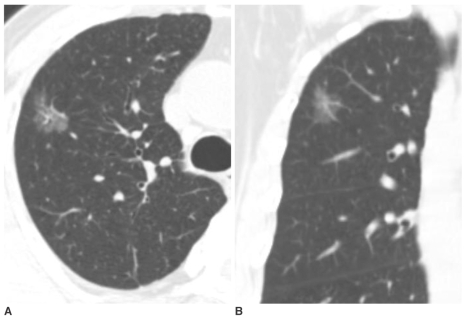 | Fig. 3Pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe confirmed as adenocarcinoma in a 67-year-old man.
A, B. Axial and coronal-reformatted images of thin-section CT shows 25 mm pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe. The lesion was pathologically confirmed by right upper lobectomy.
|
 | Fig. 4Pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe confirmed as focal interstitial fibrosis in a 61-year-old man.
A. Thin-section CT shows 30 mm pure nodular ground-glass opacity in the right upper lobe.
B. On follow-up CT scan after seven months, an interval change was not noted. The lesion was pathologically confirmed by right upper lobectomy. On pathologic slides, focal interstitial fibrosis with exuberant type II pneumocyte proliferation and alveolar macrophage collection were found. The cause of the focalinterstitial fibrosis was not confirmed.
|
 | Fig. 5Mixed nodular ground-glass opacity in the right lower lobe confirmed as adenocarcinoma in a 61-year-old man.
A, B. Axial and coronal-reformatted images of thin-section CT shows 21 mm mixed nodular ground-glass opacity in right upper lobe. An elongated shaped solid portion was noted in the lesion (arrows). The lesion was pathologically confirmed by right lower lobectomy.
|
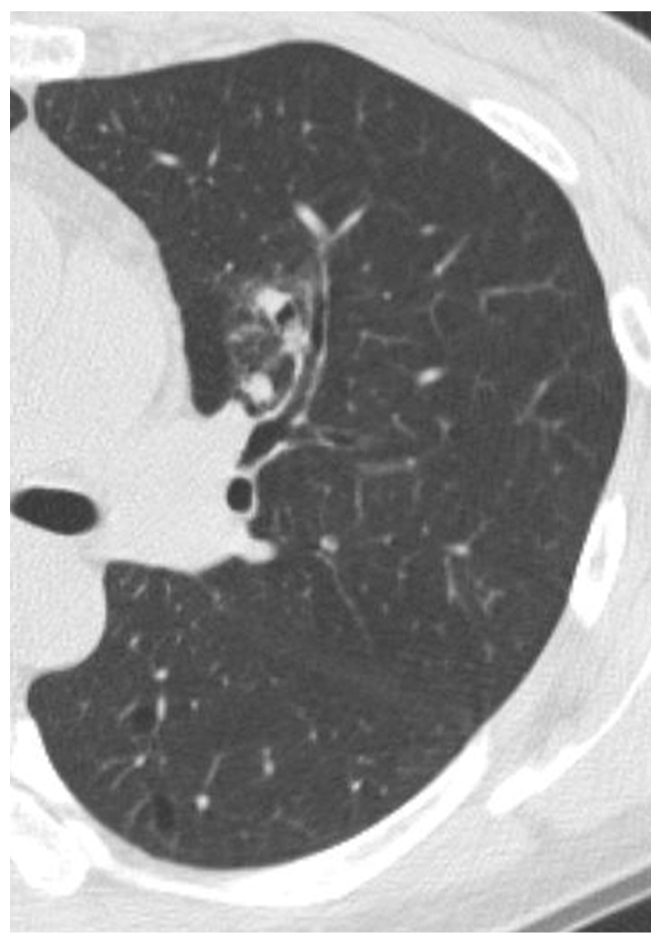 | Fig. 6Mixed nodular ground-glass opacity in the left upper lobe confirmed as aspergillosis in a 52-year-old woman. Thin-section CT shows 23 mm mixed nodular ground-glass opacity in the left upper lobe. Multifocal solid portions were seen in the lesion. The lesion was pathologically confirmed by CT-guided cutting needle biopsy. She also had fungal sinusitis in the right maxillary sinus. |
Table 2
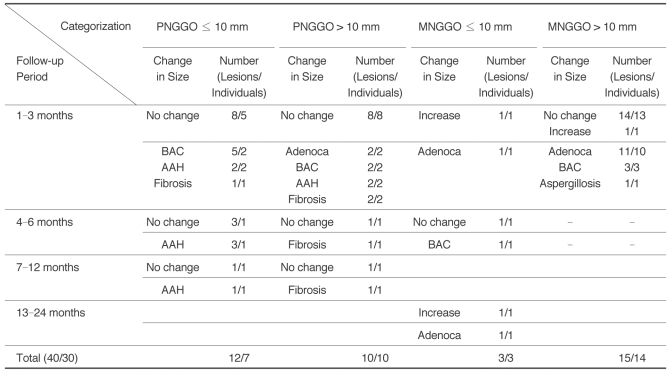
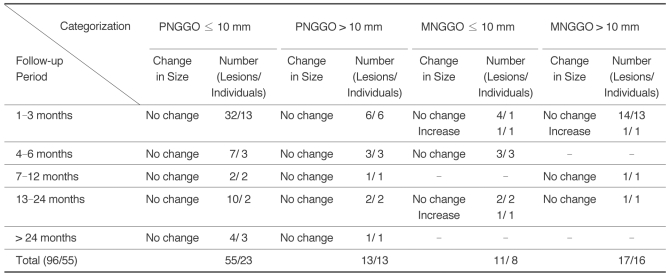
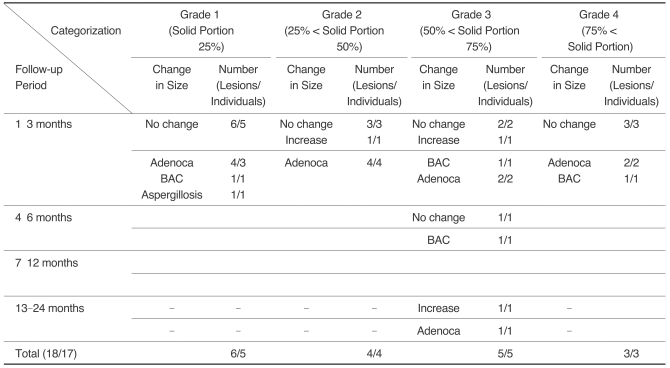
Note.-GGO = ground-glass opacity, PNGGO = pure nodular ground-glass opacity, MNGGO = mixed nodular ground-glass opacity, BAC = bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, AAH = atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, Adenoca = adenocarcinoma, Fibrosis = focal interstitial fibrosis
The sum of patient number is not matched with total number because of the patients with multiple lesions.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download