INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
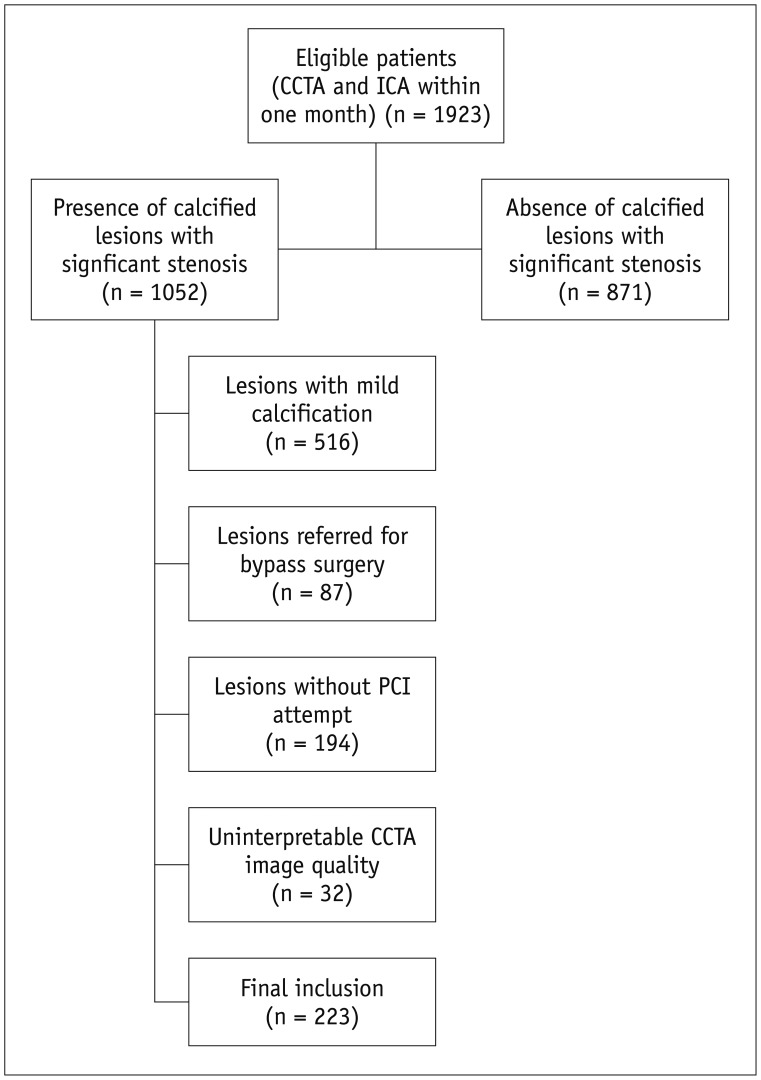
Patient Population
Scan Protocol of CCTA
CCTA Image Reconstruction and Analysis
ICA and RA Procedure
Statistical Analysis
RESULTS
Clinical Characteristics
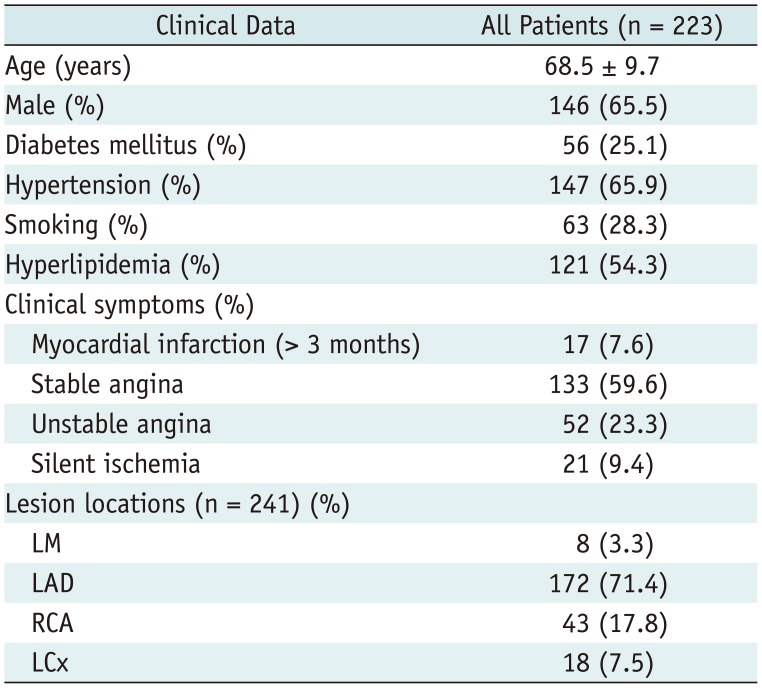
Table 1
Demographic Data
ICA and PCI Characteristics
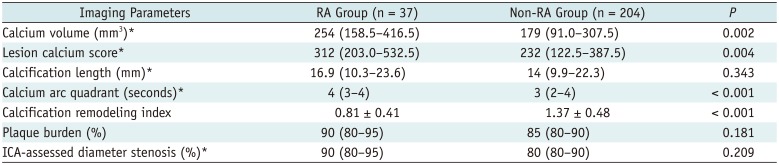
Table 2
Comparison of Various Parameters in Patients with or without RA
CCTA Characteristics
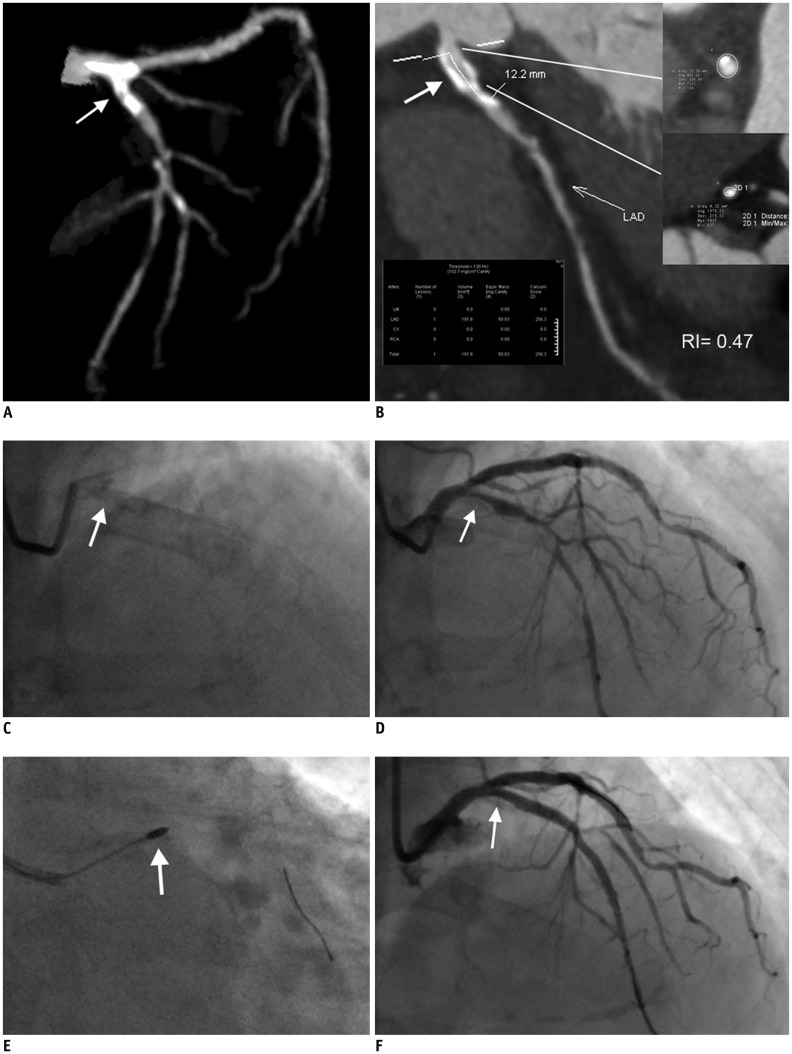 | Fig. 3Representative case of calcified coronary stenosis treated with RA and PCI.
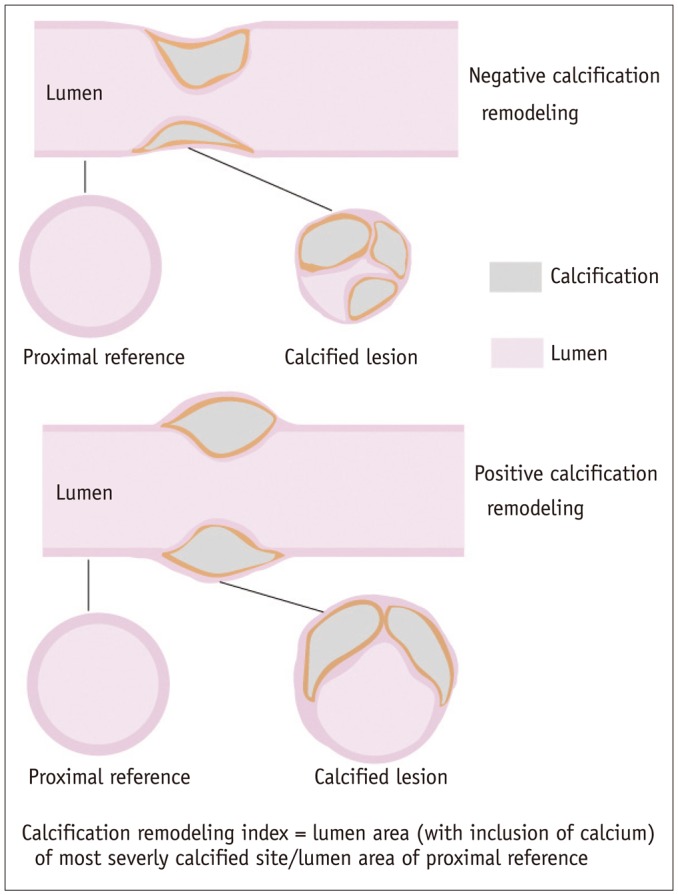
A. 3D-MIP image of left coronary artery showing calcified lesion located at LM and proximal LAD (white arrow). B. Calcification length measured on CPR image (white arrow) was 12.2 mm. Calcium volume and focal Agatston score were 191.8 mm3 and 256.3, respectively. Calcification remodeling index of this lesion was calculated to be 0.47. Involved calcium arc quadrant was 3 as identified on cross-sectional images. C. Fluoroscopy of left coronary artery revealing calcification of proximal LAD (white arrow). D. ICA of left coronary artery showing severe stenosis of proximal LAD (white arrow). E. Lesion was modified with RA (white arrow) prior to stent deployment. F. Lesion was successfully treated after stent implantation as confirmed by ICA (white arrow). CPR = curved planar reformation, LAD = left anterior descending, LM = left main, MIP = maximum intensity projection, RA = rotational atherectomy
|
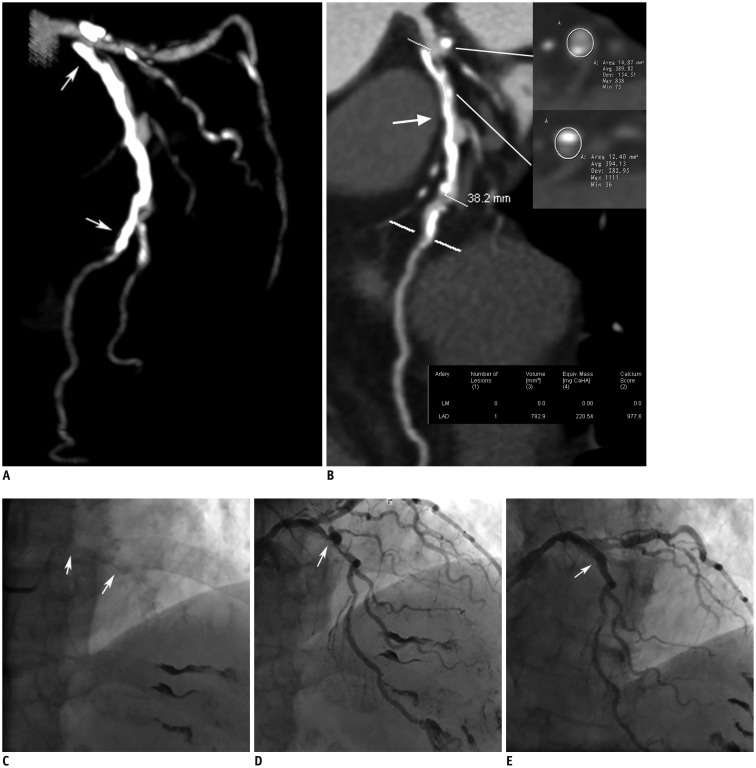 | Fig. 4Representative case of calcified coronary stenosis treated with PCI but without RA.
A. 3D-MIP image of left coronary artery showing long diffusely calcified lesion located at proximal to middle LAD (white arrows). B. Calcification length measured on CPR image (white arrow) was 38.2 mm. Calcium volume and focal Agatston score were 782.9 mm3 and 977.6, respectively. Calcification remodeling index of this lesion was calculated to be 0.91. Involved calcium arc quadrant was 2 as identified on cross-sectional images. C. Fluoroscopy of left coronary artery revealing calcification of proximal to middle LAD (white arrows). D. ICA of left coronary artery showing severe stenosis of proximal LAD (white arrow). E. Lesion was successfully treated after stent implantation without use of RA (white arrow).
|
ROC Curve Analysis and Multivariate Analysis
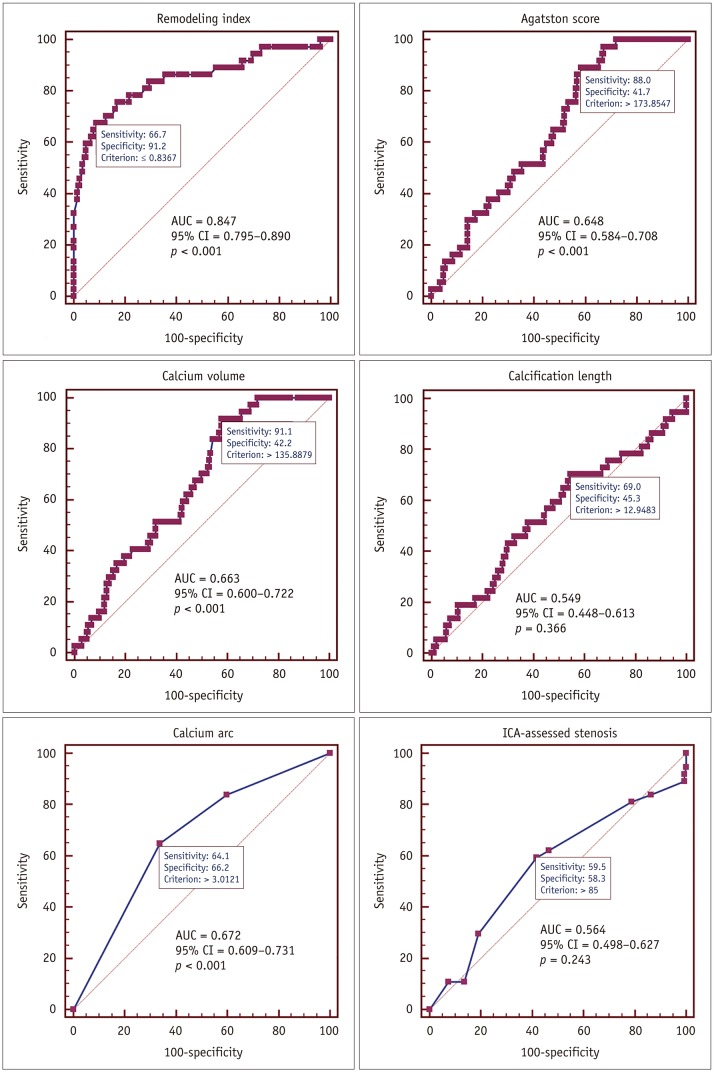 | Fig. 5ROC curve analysis of various parameters for identifying calcified lesions treated with RA.Calcification remodeling index showing largest AUC and best diagnostic performance over other parameters. AUC = area under curve, CI = confidence interval, ROC = receiver operating characteristic.
Calcification remodeling index showing largest AUC and best diagnostic performance over other parameters.
|
Table 3
ROC Curve Analysis of Various Parameters for Identifying Lesions with RA
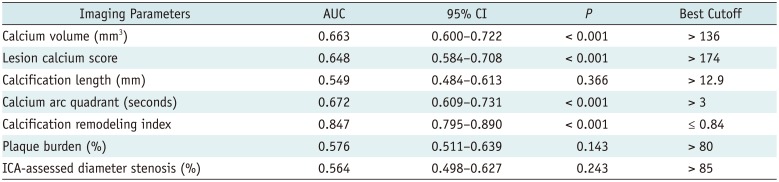
Table 4
Diagnostic Performance of Various Parameters for Identifying Lesions with RA
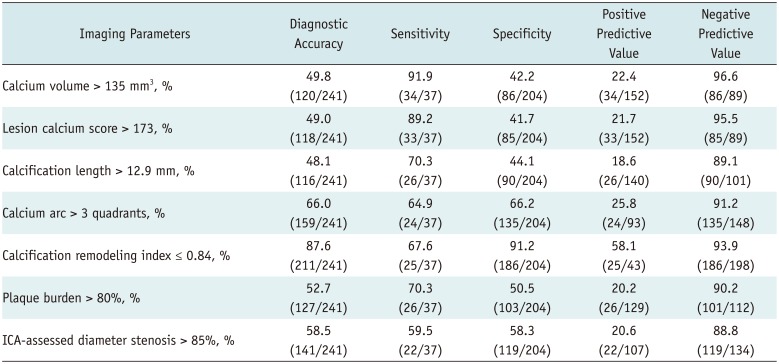
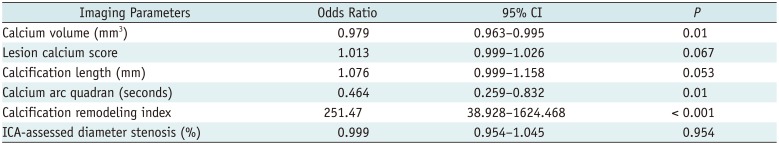
Table 5
Multivariate Analysis to Identify Predictors of RA Employment




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download