Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Example of histogram analysis of MCA wall enhancement.Case with eccentric enhancement in source image (A) of 3D CE T1-TSE and corresponding region-of-interest (yellow circle in A) for enhancing middle cerebral artery including wall and its lumen. Left side of scheme (B) is scheme of sagittal M1 segment and matching voxel of 3D CE T1-TSE. Enhancing wall with variable degrees of thickness is presented in gray, and lumen of MCA and surrounding tissues are presented in black. Voxel intensity was decided from mean values of internal tissues, and depended on ratio of vessel wall, lumen and surrounding tissues. Voxel has mixed contents of enhancing wall and lumen with variable degrees (blue box). As result, voxels had variable degrees of signals from those of enhancing walls only (red box) to those of lumen only (green box). Example of histogram of normalized signal of VOI is located on right side of scheme. Shaded area under histogram represents relative signal intensities. Two histogram parameters, 90th percentile (solid arrow) and geometric mean (empty arrow) are marked. MCA = middle cerebral artery, VOI = volume of interest, 3D CE T1-TSE = 3-dimensional contrast-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin echo image
|
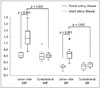 | Fig. 2Box and whisker plot of 90P and GM for lesion and contralateral side of M1 in both groups.Lesion side 90P was significantly higher in PAD group than in SAD group. Contralateral side 90P showed no significant difference between two groups. Lesion side 90P and GM of PAD group was significantly higher than that of SAD group. In PAD group, lesion side GM and 90P was significantly higher than contralateral side GM. GM = geometric means, PAD = parent artery disease, SAD = small artery disease, 90P = 90th percentile
|
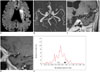 | Fig. 3Case of PAD.82-year-old woman visited emergency room for tendency to fall to right side. DWI showed patchy area of hyperintensity (arrow on A) of left frontal white matter and centrum semiovale. Mild stenosis (44%) was noted in distal M1 segment of left MCA (arrowheads on B). Note long segmental enhancement (arrowheads on C and D) along stenotic segment of left MCA on multiplanar reformatted image (C) and sagittal image (D) of 3D CE T1-TSE. On histogram analysis of lesion side (E), 90P (solid arrow on E) was 1.015, which was higher than our cut-off value of 0.73. Lesion side GM (empty arrow on E) was 0.738. Cut-off of GM was 0.346. DWI = diffusion-weighted images, GM = geometric means, MCA = middle cerebral artery, PAD = parent artery disease, 3D CE T1-TSE = 3-dimensional contrast-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin echo image, 90P = 90th percentile
|
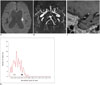 | Fig. 4Case of SAD.86-year-old woman visited emergency room for dysarthria. DWI showed small acute ischemic stroke lesion in left periventricular white matter (arrow on A). Minimal irregular contour (arrowheads) of M1 segment of left MCA was visible (B), and degree of stenosis was 20%. On sagittal image (C), enhancement score was 0. Histogram analysis of lesion side M1 (D) showed low 90P (solid arrow, 0.568) and low GM (empty arrow, 0.256) in lesion side M1. DWI = diffusion-weighted image, GM = geometric means, MCA = middle cerebral artery, SAD = small artery disease, 90P = 90th percentile
|
Table 1
Demographics and Risk Factors of Two Groups

Figures in parentheses are percentages. Age, NIHSS, interval between onset time to imaging were presented by median and inter-quartile ranges. Others were presented patient numbers in each category. *p < 0.05 by Wilcoxon's signed rank test. NIHSS = National Institute of Health Stroke Scale, PAD = parent artery disease, SAD = small artery disease
Table 2
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of M1 Segment of MCA

Volume of measured M1, stenosis, GM and 90P were presented in median and interquartile ranges. Visual enhancement score: grade 0, enhancement was similar to or less than that of intracranial arterial walls without plaque in same individual; grade 1, enhancement was greater than that of grade 0 but less than that of pituitary infundibulum; and grade 2, enhancement was similar to or greater than that of infundibulum. *Parameters were significantly different between lesion side and contralateral side in Mann-Whitney U test (p < 0.001), †Visual enhancement score, Stenosis, GM, and 90P were significantly different between lesion side and contralateral side in large vessel disease group in Wilcoxon signed rank test (p < 0.001). GM = geometric mean, MCA = middle cerebral artery, PAD = parent artery disease, SAD = small artery disease, VOI = volume of interest, 90P = 90th percentile of normalized signal of VOI of M1
Table 3
Receiver Operating Characteristic Analysis of Vessel Wall Enhancement and Stenosis for Discrimination of PAD versus SAD





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download