Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
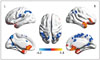 | Fig. 1ALFF maps show differences between pre-LT patients and HCs (p < 0.05, corrected by AlphaSim).Diffused ALFF decreases in bilateral calcarine, IPL, LG, PCu, PoCG, MCC, and right SMA and increases in bilateral LTC, PHG, right Hip, and SFG are observed in pre-LT patients relative to controls. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, HCs = healthy controls, Hip = hippocampus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LG = lingual gyrus, LT = liver transplantation, LTC = lateral temporal cortex, MCC = middle cingulate cortex, PCu = precuneus, PHG = parahippocampal gyrus, PoCG = postcentral gyrus, SFG = superior frontal gyrus, SMA = supplementary motor area
|
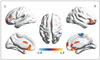 | Fig. 2ALFF maps show differences between post-LT patients and HCs (p < 0.05, corrected by AlphaSim).ALFF decreases in right IPL, calcarine, and SMA and increases in right SFG, IFG, left PHG, and MFG are detected in post-LT patients. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, HCs = healthy controls, IFG = inferior frontal gyrus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LT = liver transplantation, MFG = middle frontal gyrus, PHG = parahippocampal gyrus, SFG = superior frontal gyrus, SMA = supplementary motor area
|
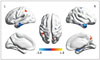 | Fig. 3ALFF maps show differences between post- and pre-LT patients (p < 0.05, corrected by AlphaSim).Paired t tests reveal ALFF increases in left IPL and right PCu and decreases in bilateral MTG, right PreCG, and Hip after LT. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, Hip = hippocampus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LT = liver transplantation, MTG = middle temporal gyrus, PCu = precuneus, PreCG = precentral gyrus
|
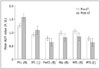 | Fig. 4Six brain regions were altered significantly in post-LT patients (p < 0.05, corrected by AlphaSim).A. U. = arbitrary unit, ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, Hip = hippocampus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LT = liver transplantation, MTG = middle temporal gyrus, PCu = precuneus, PreCG = precentral gyrus
|
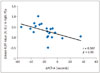 | Fig. 5Correlations between brain regions with altered ALFF and neuropsychological tests.ΔALFF in right PCu was negatively correlated with ΔNCT-A (r = 0.507, p < 0.05). Δrepresents differences before and after LT. A. U. = arbitrary unit, ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, LT = liver transplantation, NCT-A = number connection test-A, PCu = precuneus
|
Table 1
Demographics and Clinical Data of Pre- and Post-LT Groups and HCs

Table 2
Differences of ALFF between Pre-LT Patients and HCs
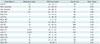
p<0.05, AlphaSim corrected. Negative t value represents decrease, and positive t value represents increase. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, HCs = healthy controls, Hip = hippocampus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LG = lingual gyrus, LT = liver transplantation, LTC = lateral temporal cortex, MCC = middle cingulate cortex, MNI = Montreal Neurological Institute, PCu = precuneus, PHG = parahippocampal gyrus, PoCG = postcentral gyrus, SFG = superior frontal gyrus, SMA = supplementary motor area
Table 3
Differences of ALFF between Post-LT Patients and HCs

p< 0.05, AlphaSim corrected. Negative t value represents decrease, and positive t value represents increase. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, HCs = healthy controls, IFG = inferior frontal gyrus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LT = liver transplantation, MFG = middle frontal gyrus, MNI = Montreal Neurological Institute, PHG = parahippocampal gyrus, SFG = superior frontal gyrus, SMA = supplementary motor area
Table 4
Differences of ALFF between Post- and Pre-LT Patients

p< 0.05, AlphaSim corrected. Negative t value represents decrease, and positive t value represents increase. ALFF = amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, Hip = hippocampus, IPL = inferior parietal lobule, LT = liver transplantation, MNI = Montreal Neurological Institute, MTG = middle temporal gyrus, PCu = precuneus, PreCG = precentral gyrus




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download