Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
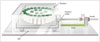 | Fig. 1Schematic figure of DCE-MRI phantom and moving platform.Moving platform consists of phantom holder with wheels, plastic cover box, handle, and rail; MR body coil (not illustrated) was placed on top of cover box. Well-trained researcher manually moved moving platform. DCE-MRI = dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging
|
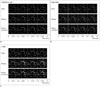 | Fig. 2Captured MRI images of dynamic scanning using each sequence according to motion mode.Each four-image set was arranged in horizontal axis along time points (6 seconds, 1 respiratory cycle in this study). We drew white dotted line below tube (asterisks) that contained highest concentrations of NiCl2 to clearly demonstrate movement.
A. MRI images using CAIPIRINHA-VIBE. For static mode (upper row), phantom showed stable location without any artifact. For moving mode (middle row), MR images obtained using CAIPIRINHA-VIBE showed vertical phantom displacement with mildly distorted tube shapes. After motion correction (lower row), phantom displacement had decreased markedly, with remaining ghosting artifacts around each tube. B. MRI images using radial-VIBE. For static mode (upper row), phantom also showed stable location without any artifact. For both moving (middle row) and motion-corrected (lower row) modes, MR images did not show significant displacement of phantom. However, round shape of each tube was significantly distorted due to streak artifacts on radial-VIBE, and these streak artifacts did not grossly improve after motion correction. C. MRI images using c-VIBE. For static mode (upper row), phantom also showed stable location without any artifact. For moving mode (middle row), MR images obtained using c-VIBE showed vertical phantom motion with related artifacts; true image of each tube overlapped with after-image of each tube, which disrupted original round shape. Neither displacement due to motion nor motion-related artifacts significantly improved after motion correction (lower row). c-VIBE = conventional VIBE, CAIPIRINHA = controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration, VIBE = volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination
|
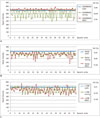 | Fig. 3Graphs and CoV (%) for signal stability of each MRI sequence.Signal intensities, which were obtained using each sequence, are plotted along dynamic series over six minutes. Each colored line indicates signal intensities according to motion mode, i.e., blue line, static mode; green line, moving mode; red line, motion-corrected mode. For all three sequences, signal intensities at static mode (blue lines) were stable without variation. Small CoVs, which are close to 0, indicate that variations in MRI signal intensities were negligible, thus suggesting better signal stability.
A. CAIPIRINHA-VIBE. Signal intensities for moving mode (green line) showed periodical vertical fluctuations. In motion-corrected mode (red line), variations in signal intensities observed in moving mode had decreased greatly. CoVs in static, moving, and motion-corrected modes were 0.09, 18.65, and 2.56, respectively. B. Radial-VIBE. Variations in signal intensities in radial-VIBE in moving mode (green line) were less prominent than those in CAIPIRINHA-VIBE or c-VIBE; however, these variations in signal intensities did not decrease after motion correction (red line). CoVs for static, moving, and motion-corrected modes were 0.03, 8.90, and 15.84, respectively. C. c-VIBE. Signal intensities in moving mode (green line) fluctuated up and down over time, and with motion correction (red line), variations in signal intensities observed in moving mode did not significantly decrease. CoVs in static, moving, and motion-corrected modes were 0.21, 12.91, and 12.50, respectively. c-VIBE = conventional VIBE, CAIPIRINHA = controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration, CoV = coefficients of variation, MOCO = motion correction, VIBE = volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination
|
Table 1
MR Parameters for Dynamic Scanning

CAIPIRINHA = controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration, GRAPPA = generalized auto-calibrating partially parallel acquisition, KWIC = k-space-weighted image contrast, NA = not applicable, PAT = parallel acquisition technique, VIBE = volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination
Table 2
Effect of Breathing Motion to Signal Intensity, Noise and SNR of DCE-MRI Images

*Analysis of variance was used to compare Mean SI, SD, and SNR between three groups, †Post-hoc t test with Bonferroni correction was used to compare Mean SI, SD, and SNR between two groups, and Levene's test was used to compare CoV between two groups.
c-VIBE = conventional VIBE, CAIPIRINHA = controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration, CoV = coefficients of variation, DCE-MRI = dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging, MOCO = motion correction, SD = standard deviation, SI = signal intensity, SNR = signal-to-noise ratio, VIBE = volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download