Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Flow chart of patients.Diagram showing inclusion of patients evaluated in study (n = number of patients). FDG = fluorodeoxyglucose, PET/MR = positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration
|
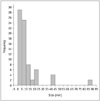 | Fig. 2Lesion size.Histogram showing frequency of lesion sizes for all 76 lesions found in 23 patients. Median lesion size was 6 mm; range was between 2 and 86 mm.
|
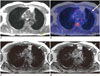
 | Fig. 367-year-old male patient with lung cancer.
A. CT in inspiration. B. VIBE sequence in inspiration. C. Dixon sequence in expiration. In left upper lobe, round atelectasis is shown (arrow), which could easily be identified in CT as well as in VIBE sequence due characteristic comet sign. In Dixon sequence, atelectasis was rated as potentially malignant lesion with confidence rating of 2 (= very likely) leading to false positive lesion. VIBE = volume interpolated breath-hold examination
|
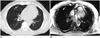
 | Fig. 462-year-old male patient with thyroid cancer.
A. Dixon sequence in expiration. B. Fused PET/Dixon. C. VIBEin. D. VIBEex. In fused images, focal uptake was observed in periphery of left lung (arrow), which was rated as lesion based on PET information. In Dixon sequence, there was no correlate to finding while in VIBEin and VIBEex small subpleural nodule was visible, which was rated as potentially malignant with confidence level of 1 (= highly likely). In follow-up imaging, lesion grew in size and was rated as metastasis in standard of reference. PET = positron emission tomography, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration
|
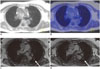
 | Fig. 562-year-old male patient with thyroid cancer.
A. CT in inspiration. B. VIBE in inspiration. In both modalities, lesion in right lung was identified (arrow). In MRI, lesion was assigned to middle lobe, in CT to upper lobe. This was attributed to non-visibility of pulmonary fissure in MRI, which may generally hamper lobe assignment in MRI especially in patients with accessory fissures or fissure distortions. In follow-up imaging, lesion grew in size and was rated as metastasis in standard of reference. VIBE = volume interpolated breath-hold examination
|
 | Fig. 676-year-old female patient with thyroid cancer.
A. Dixon sequence in expiration. B. Fused PET/Dixon. C. VIBEin. D. VIBEex. In VIBE images, pulmonary lesion was found both in inspiratory and expiratory scan (arrow). In Dixon sequence, lesion was not adequately visible and scan was rated as negative. Also in fused PET/Dixon images, lesion was not identifiable. Lesion was classified as malignant based on standard of reference due to growth in size in follow-up imaging. PET = positron emission tomography, VIBE = volume interpolated breath-hold examination, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration
|
Table 1
Parameters of T1-Weighted MR Sequences Used for Lung Imaging
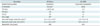
Table 2
Lesion-Based Analy

Values are given in percent together with 95% confidence interval in brackets. Specificity could not be calculated because there were no true negative pulmonary lesions. *Nodule size was measured in CT scan in inspiration (lung window setting). CTex = CT acquired in expiration, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration
Table 3
Lobe-Based Analysis

| CTex | VIBEin | VIBEex | Dixon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (CI) | 89.6 (77.8–95.5) | 58.3 (44.3–71.2) | 60.4 (46.3–73.0) | 31.3 (20.0–45.3) |
| Specificity (CI) | 100 (97.6–100) | 98.7 (95.5–99.7) | 99.4 (96.5–99.9) | 99.4 (96.5–99.9) |
Values are given in percent with the 95% confidence intervals (CI) in brackets. On right side of table, p values for pairwise comparisons between different imaging techniques are given. CTex = CT acquired in expiration, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration
Table 4
Comparison of Figures of Merit (FOM) Obtained by Different Imaging Techniques

FOM are given with 95% confidence intervals (CI) in brackets. P values for pairwise comparisons between different imaging techniques are given. CTex = CT acquired in expiration, VIBEex = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in expiration, VIBEin = volume interpolated breath-hold examination acquired in inspiration




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download