Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
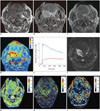 | Fig. 1Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging, color coded AUC60, TSI curve, D, D*, and f map of 65-year-old male patient with squamous cell carcinoma of right palatine tonsil.Pre-contrast and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging (A, B) showed mass in right palatine tonsil. Region of interest was drawn around entire tumor on dynamic contrast-enhanced source images (C). AUC60 (D) map derived from DCE-MRI showed fast visual increase in AUC in corresponding areas of contrast-enhancing lesion, and AUC60 value is 146.355. TSI curve (E) of entire enhancing lesion (blue curve) and normal muscle (red curve) showed wash out and plateau patterns, respectively. ROI was also drawn around entire tumor area on intravoxel incoherent motion MR source images (F), and D (G), D* (H), and f (I) maps demonstrated D, D*, and f values were 0.908 × 10-3 mm2/s, 184.075 × 10-3 mm2/s and 0.138, respectively. AUC60 = the initial 60-second area under curve, DCE-MRI = dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging, ROI = region of interest, SI = signal intensity, TSI = time-signal intensity
|
 | Fig. 2Correlation of difference between ADC and D values with f value from IVIM.Difference between D and ADC values correlated significantly with f value from IVIM in tumors (A) and normal muscle (B) (tumor, p = 0.017, r = 0.528; muscle, p = 0.003, r = 0.630). ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient, IVIM = intravoxel incoherent motion
|
Table 1
Summary of Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of All 20 Study Patients
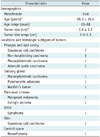
Table 2
Differences of Perfusion and Diffusion Parameters between Muscles and Tumors

For definitions of indicated parameters please refer to Imaging Processing section of Materials and Methods. Except p value, data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Unit for ADC, D and D* value is × 10-3 mm2/s. Unit for Tmax is second. ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient, AUCw = whole area under the curve, AUC60 = the initial 60-second area under the curve, Emax = the maximum amplitude of enhancement, Tmax = the time at which Emax occurs
Table 3
Correlation between Perfusion Parameters from IVIM and DCE-MRI in Tumors and Normal Muscles

For definitions of indicated parameters please refer to Imaging Processing section of Materials and Methods. Unit for D* value is × 10-3 mm2/s. Unit for Tmax is second. AUCw = whole area under the curve, AUC60 = the initial 60-second area under the curve, DCE-MRI = dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging, Emax = the maximum amplitude of enhancement, IVIM = intravoxel incoherent motion, Tmax = the time at which Emax occurs
Table 4
Correlation between Perfusion Parameters from IVIM and DCE-MRI in Tumors of Eight HNSCC Patients in Study Series

| f | D* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | |
| Wash-in | −0.147 | 0.728 | 0.094 | 0.824 |
| Emax | 0.039 | 0.927 | 0.533 | 0.174 |
| Tmax | 0.533 | 0.174 | 0.131 | 0.758 |
| AUC60 | −0.133 | 0.753 | 0.415 | 0.306 |
| AUCw | 0.005 | 0.990 | 0.600 | 0.116 |
For definitions of indicated parameters please refer to Imaging Processing section of Materials and Methods. Unit for D* value is × 10-3 mm2/s. Unit for Tmax is second. AUCw = whole area under the curve, AUC60 = the initial 60-second area under the curve, DCE-MRI = dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging, Emax = the maximum amplitude of enhancement, HNSCC = head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, IVIM = intravoxel incoherent motion, Tmax = the time at which Emax occurs




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download