Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
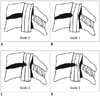 | Fig. 1Schematic diagrams of cervical canal stenosis grading system (adapted from reference 29).
A. Grade 0, normal. B. Grade 1, obliteration of > 50% of subarachnoid space with no sign of cord deformity. C. Grade 2, central canal stenosis with spinal cord deformity; cord is deformed but no signal change is noted in spinal cord. D. Grade 3, increased spinal cord signal intensity near compressed level on T2-weighted images.
|
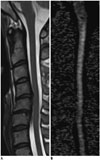 | Fig. 2Representative image used for diffusion tensor imaging parameter measurements.Gray-tone fractional anisotropy (FA) map was produced automatically by software. To measure FA and mean diffusivity values at most severe stenosis level, oval region of interest was drawn on FA map (B), excluding regions outside of spinal cord such as adjacent anatomical structures, and cord morphology was assessed with T2-weighted images (A) as reference.
|
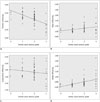 | Fig. 3Correlations between degree of central canal stenosis and diffusion tensor imaging parameters.
A. Fractional anisotropy values were negatively correlated with degree of central canal stenosis (rho = -0.545, p < 0.001). B. Mean diffusivity was not correlated with degree of central canal stenosis (rho = 0.156, p < 0.217). C. Longitudinal diffusivity was not correlated with degree of central canal stenosis (rho = -0.149, p < 0.238). D. Radial diffusivity was positively correlated with degree of central canal stenosis (rho = 0.399, p < 0.001). Diffusivity units are 1 × 10-3 mm2/sec.
|
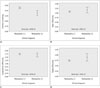 | Fig. 4Statistical comparison of diffusion tensor imaging values of patients with and without cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM).
A. Mean fractional anisotropy values were lower (p < 0.001) in patients with CSM [myelopathy (+)] (0.36 ± 0.08; range, 0.23-0.50) than in those without it [myelopathy (-)] (0.46 ± 0.06; range, 0.30-0.57). B. Mean diffusivity values did not differ (p = 0.318) between patients with CSM (1.16 ± 0.27; range, 0.79-1.85) and those without it (1.09 ± 0.12; range, 0.93-1.53). C. Mean longitudinal diffusivity values did not differ (p = 0.227) between patients with CSM (1.68 ± 0.26; range, 1.23-2.15) and those without it (1.76 ± 0.19; range, 1.32-2.17). D. Mean radial diffusivity values did not different (p = 0.082) between patients with CSM (0.90 ± 0.30; range, 0.56-1.70) and those without it (0.74 ± 0.12; range, 0.60-1.26). Diffusivity units are 1 × 10-3 mm2/sec. CI = confidence interval
|
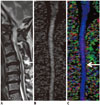 | Fig. 5Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) detected using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters in patient whose T2-weighted image was designated as showing as grade 2 stenosis.Off-center sagittal T2-weighted image (A) of patient showed deformed spinal cord without definite signal change at C4-5 disc level, which was most stenotic level (arrow); thus, stenosis was designated as grade 2. DTI parameters were measured at that level on mid-sagittal gray-tone fractional anisotropy (FA) map (B). FA, mean diffusivity, longitudinal diffusivity, and radial diffusivity values of this patient were 0.349, 1.198 × 10-3 mm2/sec, 1.728 × 10-3 mm2/sec, and 0.933 × 10-3 mm2/sec, respectively. All values were compatible with diagnosis of CSM considering cut-off value of each parameter. Color-coded map (C) based on principal eigenvalues in sagittal plane revealed subtle dark color (arrow), suggesting changes in eigenvalues at most stenotic level. Blue coloring represents principal eigenvector aligned in head-foot direction.
|
Table 1
Diagnostic Performance of Each Parameter and Their Combinations Determined through Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve in Patients with Grade 2 Stenosis

Numbers in parenthesis are counts used for calculations and their 95% confidence intervals. *Means positive in both MD and FA based on ideal cut-off value for each parameter, †Means positive in both LD and FA based on ideal cut-off value for each parameter, ‡Means positive in both RD and FA based on ideal cut-off value for each parameter, §Significant differences were observed between FA and MD∩FA (p = 0.003), FA and LD∩FA (p < 0.001), FA and RD∩FA (p < 0.001), MD and LD∩FA (p = 0.024), and MD and RD∩FA (p = 0.024) in post-hoc analysis. FA = fractional anisotropy, LD = longitudinal diffusivity, MD = mean diffusivity, NPV = negative predictive value, PPV = positive predictive value, RD = radial diffusivity




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download