INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals
Synthesis of MNP@m-SiO2
Synthesis of Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] and Organic Dye Incorporation
Trastuzumab (Her2/neu Expression Receptor Antibody) Conjugation with Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]-Her2Ab
Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Assay
Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES) Analysis
In Vitro Magnetic Resonance Imaging
RESULTS
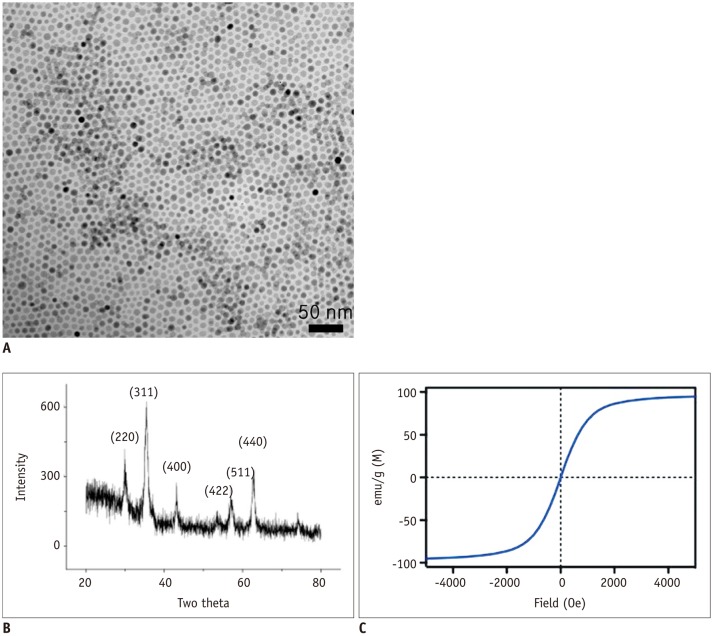 | Fig. 1Structural and magnetic characterization of prepared Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs).
A. Magnetic nanoparticles obtained by seed-mediated growth had narrow size distribution and consisted of single domain. B. X-ray powder diffractogram of 16-nm MNP. MNPs exhibited similar pattern, confirming their ferrite structure and crystal sizes, measured by fitting major peak (311), were in agreement with transmission electron microscopy estimation. C. Magnetic properties of MNP determined with vibrating sample magnetometer. Particles were superparamagnetic at 27℃. Relaxivity (r2) was measured at 0.47 T and 40℃. 16-nm MNP showed high r2 of 320 s-1·mM-1 (metal).
|
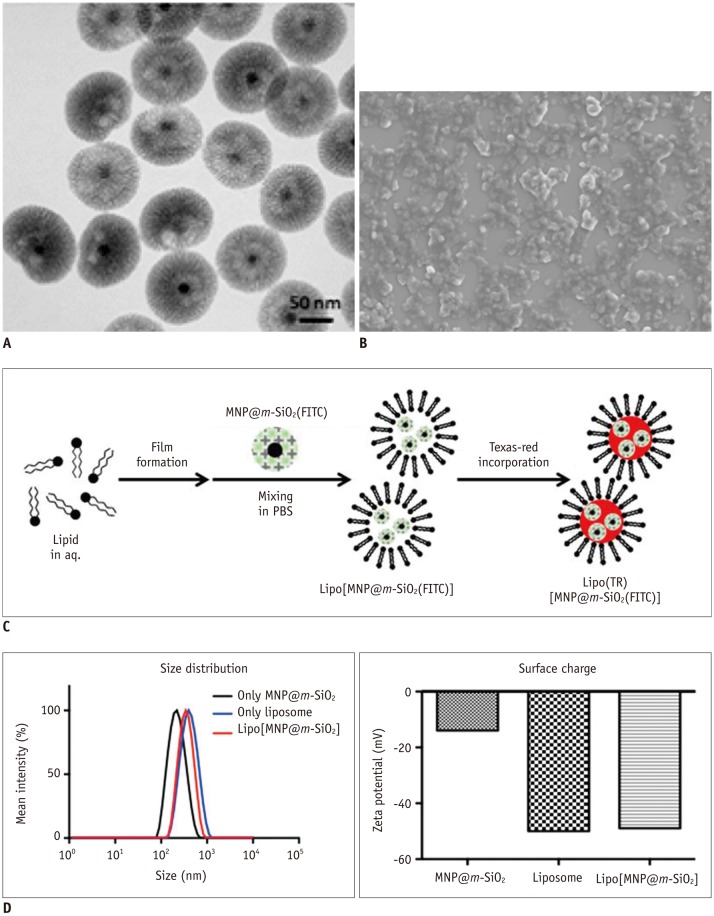 | Fig. 2Synthesis and characterization of Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] particle.
A. Transmission electron microscopy image of MNP@m-SiO2 particles. Black core dot represents 16-nm Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle and wrinkled
shell in grey represents m-SiO2. B. Scanning electron microscopy image of Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] showing monodispersed size and shape. C. Simple synthetic scheme for Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]. D. Size distribution and surface charge of prepared MNP@m-SiO2, liposome, and Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] were investigated by dynamic light scattering.
|
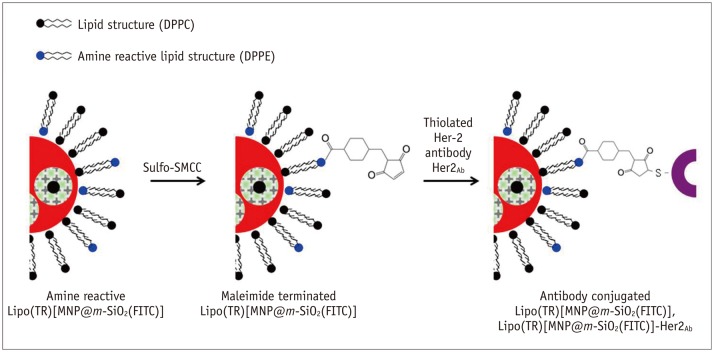 | Fig. 3Synthetic scheme for Her2/neu antibody conjugation onto prepared Lipo(TR)[MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)].
Synthesized Lipo(TR) [MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)] contained active amine site for DPPE lipid during preparatory steps. To terminate maleimide functional group on particle, commercially available Sulfo-SMCC was used and reacted with Lipo(TR)[MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)] by substitution reaction. Maleimide functional group could then be easily attached to thiol group of Her2/neu antibody after inducing thiolation of antibody with Traut's reagent. DPPC = 1,2-dipalmitory-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidycholine, DPPE = 1,2-dipalmitory-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, Sulfo-SMCC = Sulfo-succinimidyl-4-(N-maleimidomethyl) cyclohexane-1-carboxylate
|
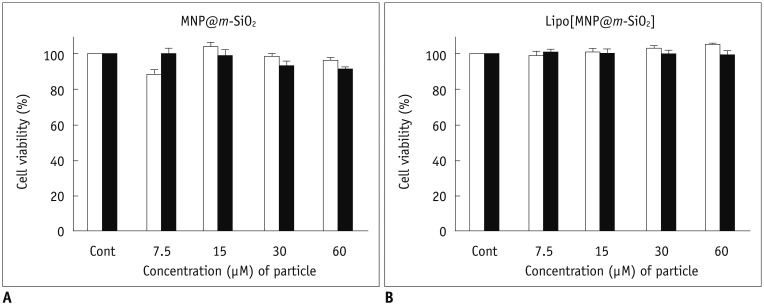 | Fig. 4Magnetic nanoparticle cytotoxicity assay.
Normal (3T3 fibroblast, white bar) and cancer (SKBR-3, black bar) cells were incubated for 24 hours in presence of varying amounts of particles. Cellular viability was then measured with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) bromide assay using [MNP@m-SiO2] (A) and Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]MNP@ (B).
|
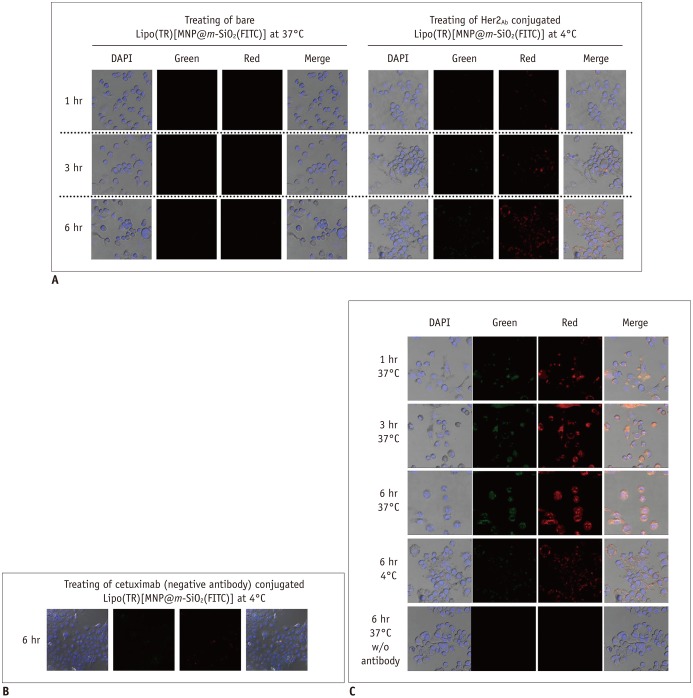 | Fig. 5Specific targeting of breast cancer cells using Her2/neu antibody conjugated magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs).
Dual fluorescent imaging using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) was performed on SKBR-3 breast cancer cells after treatment with bare Lipo(TR)[MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)] without antibody conjugation and Lipo(TR)[MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)]-Her2Ab
(A); negative control Lipo(TR)[MNP@m-SiO2(FITC)]-cetuximab (B) carrying green and red organic dyes were subjected to fluorescence imaging by using CLSM. Uptake of MNPs through endocytosis was hindered by decreasing incubation temperature for SKBR-3 cells from 37℃ to 4℃ (C). Green = FITC, Red = hydrophilic regions, Blue = DAPI/nuclei
|
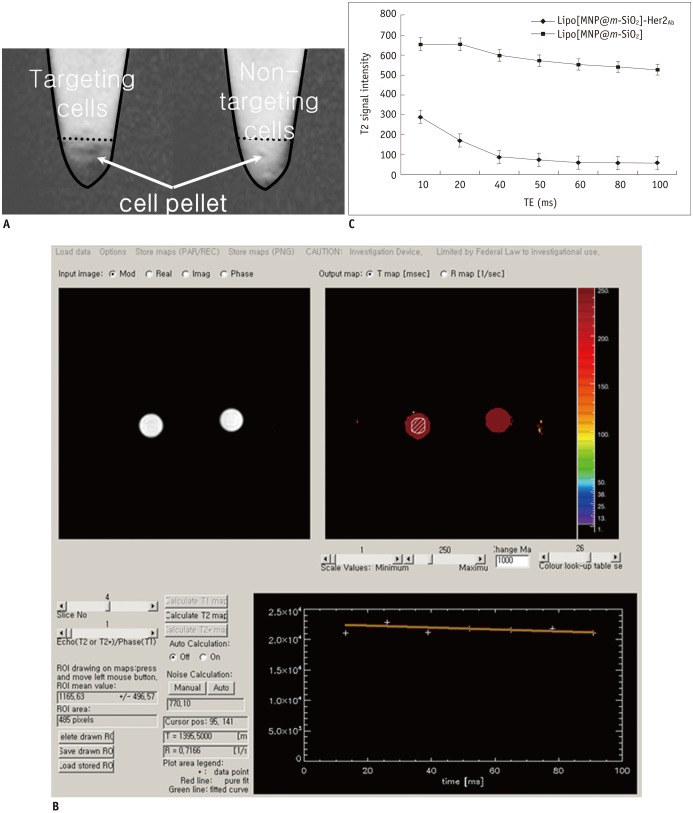 | Fig. 6MR imaging of breast cancer cells after targeting with Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]-Her2Ab.
T2 weighted images of SKBR-3 breast cancer cells after treatment with bare (Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]) and trastuzumab conjugated nanoparticles (Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2]-Her2Ab) (A) T2 relaxometry. T2 weighted images of Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] with and without trastuzumab conjugation. When regions of interest (ROI) was placed in cell pellet, T2 value can be automatically calculated (B). (C) Single-exponential fit of mean signal intensity versus echo time (TE) from Lipo[MNP@m-SiO2] with and without trastuzumab conjugation in different axial slices. Data as mean intensity with ROI with standard deviation in intensities of pixel.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download