INTRODUCTION
Normal Anatomy
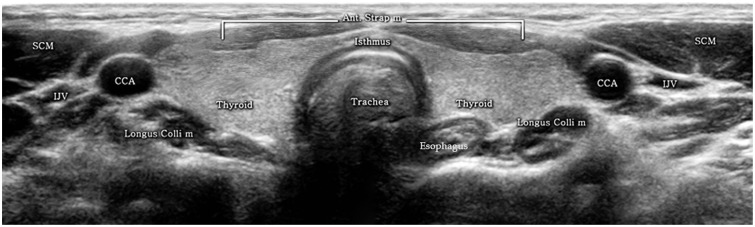 | Fig. 1
Normal transverse US of thyroid gland. Cross-sectional US shows normal thyroid glands and surrounding structures. Both thyroid glands show homogeneous parenchymal echogenicity higher than anterior strap muscles. Both CCAs run laterally adjacent to both thyroid lobes and infrahyoid strap muscles overlie thyroid gland. Both SCM muscles are located antero-laterally and longus colli muscles are seen posterolaterally to thyroid gland. US = ultrasonography, SCM = sternocleidomastoid muscle, CCA = common carotid artery, IJV = internal jugular vein, Ant. Strap m = anterior strap muscle, Longus Colli m = longus colli muscle |
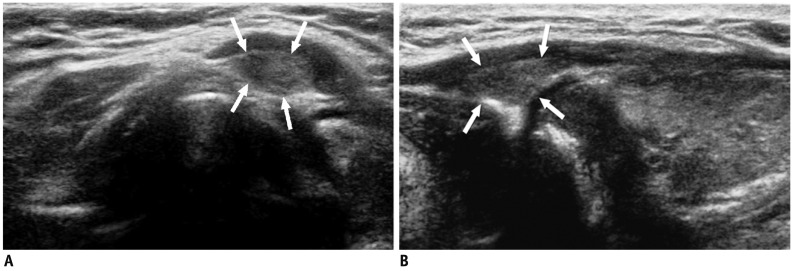 | Fig. 2Pyramidal lobe in 49-year-old woman with hypothyroidism.
A. On transverse ultrasonography small isoechoic mass (arrows) was seen at superior aspect of left thyroid lobe. B. Lesion (arrows) had same echogenicity as surrounding thyroid gland; thus, providing important diagnostic clue on longitudinal view.
|
Pitfalls Associated with Equipment
Pitfalls Associated with Examination Skills
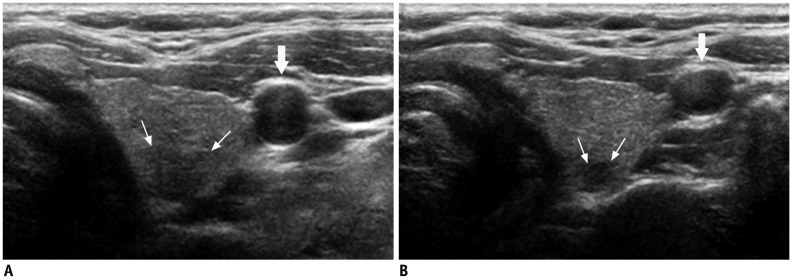 | Fig. 3Deep located lesion in left thyroid lobe in 35-year-old man.
A. Without compression, ill-defined, taller-than-wide hypoechoic nodule (small arrows) suggesting suspicious nodule is visible. B. Following compression, margin of nodule can be seen more easily and carotid artery (large arrows) is also compressed.
|
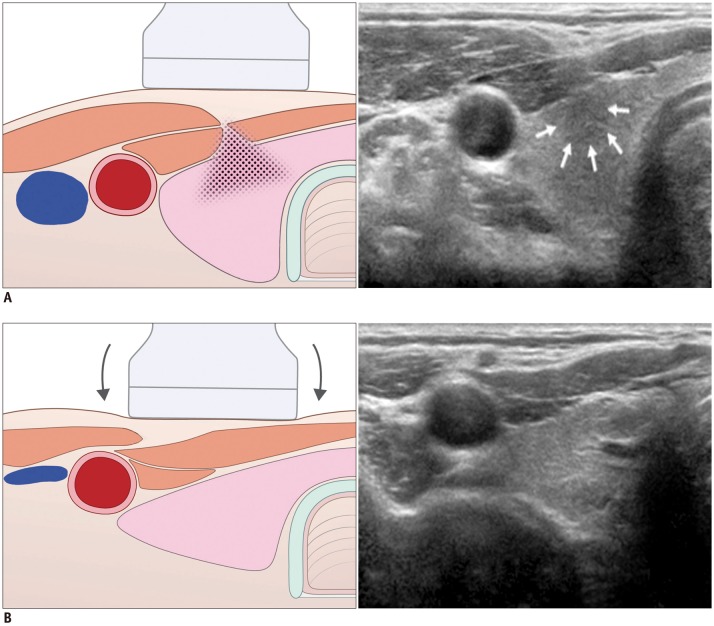 | Fig. 4Artifact related with muscle interface in 28-year-old man.
A. Before compression, hypoechoic lesion (arrows) is visible in anterior portion of right thyroid lobe. B. Following compression, lesion disappeared as it was pseudo-lesion caused by shadow (field with dots) from sternocleidomastoid muscle interface.
|
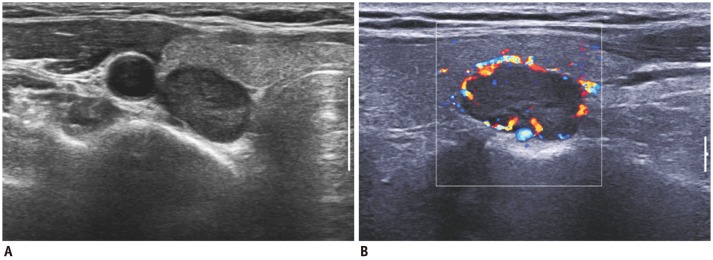
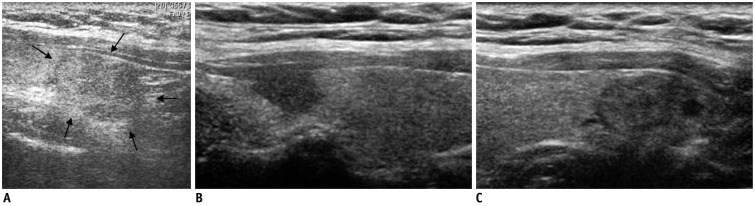 | Fig. 5Satisfaction of search in 51-year-old man with benign nodule.
A. Outside ultrasonography showed nodule (arrows) in right thyroid lobe. B, C. However, another suspicious nodule was detected at tip of right upper pole. Lesion in upper pole was surgically confirmed to be papillary carcinoma, but lesion in lower pole was confirmed to be adenomatous hyperplasia.
|
Pitfalls Associated with Anatomy
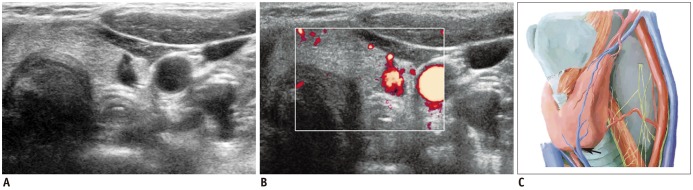
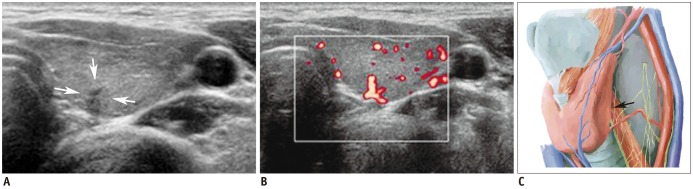 | Fig. 8Vascular structure mimicking thyroid nodule.
A. Irregular, taller-than-wide, hypoechoic lesion (arrows) was seen at posterior aspect of left mid thyroid pole. B. Color Doppler scan revealed vascular structure. C. Vascular structure likely arose from inferior thyroid artery (arrow). Spectral wave form on Doppler scan would help confirmation.
|
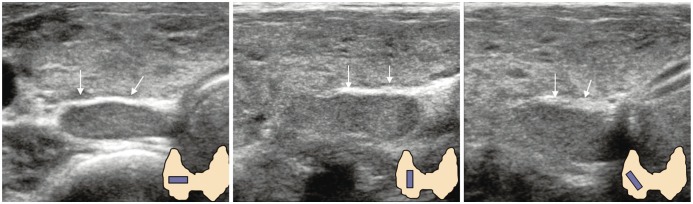
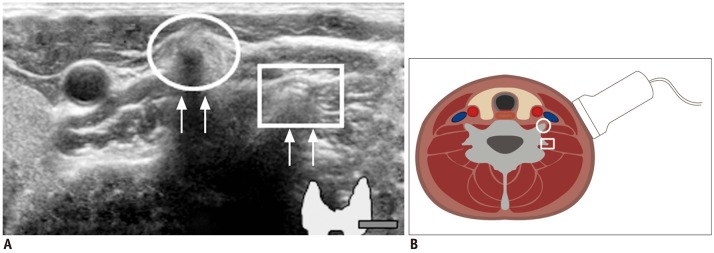 | Fig. 10Prominent vertebral transverse process mimicking calcified lymph nodes.
A. Circle indicates anterior tubercle of transverse process and square identifies posterior tubercle. Echogenic line (arrows) suggested vertebral cortex. B. Sectional diagram provides more detailed explanation.
|
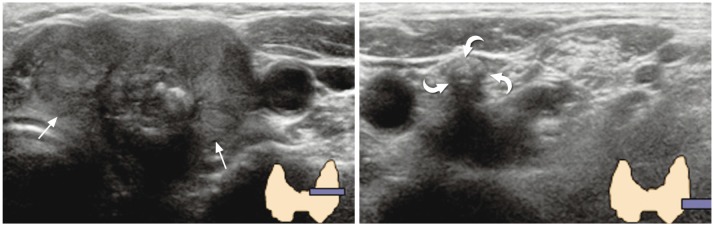 | Fig. 11
Dense calcified lymph node mimicking vertebral transverse process. 69-year-old woman was referred to our hospital for diagnosed thyroid cancer (arrows). During preoperative thyroid ultrasonography, dense calcification (curved arrows) was visible at left level IV region. It was initially confused with vertebral transverse process, but was finally determined to be metastatic lymph node. |
Pitfalls Associated with Interpretation
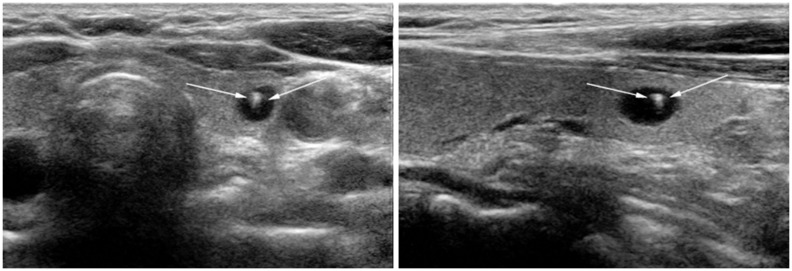 | Fig. 12
Typical comet-tail artifact in benign colloid cyst. 58-year-old woman who had undergone mastectomy for breast cancer was presented for screening thyroid ultrasonography. Small cyst containing echogenic spot with comet-tail (arrows) was identified. This is typical case of "comet-tail artifact" caused by colloid crystals. |
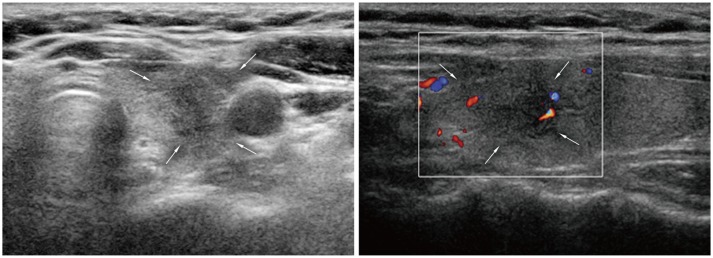 | Fig. 13
Subacute thyroiditis. 48-year-old woman was referred for suspicious left thyroid lesion. Ultrasonography revealed irregular hypoechoic mass (arrows) in her left upper pole. Vascularity was noted at some peripheral areas on color Doppler imaging. Patient had experienced neck pain within past several weeks. Fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed and confirmed subacute thyroiditis. |
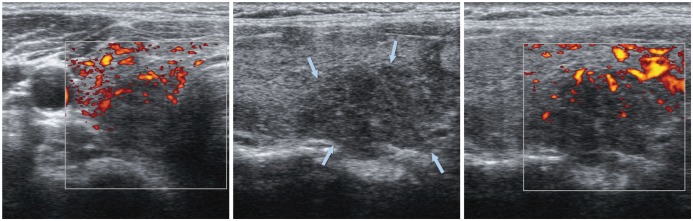 | Fig. 14
Focal lymphocytic thyroiditis. 40-year-old woman underwent thyroid US for evaluation of hypothyroidism. Suspicious hypoechoic lesion (arrows) was seen in mid pole of right thyroid lobe. However, lesion was confirmed to be lymphocytic thyroiditis by US-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy. US = ultrasonography |
Pitfalls Associated with Extrathyroidal Abnormalities
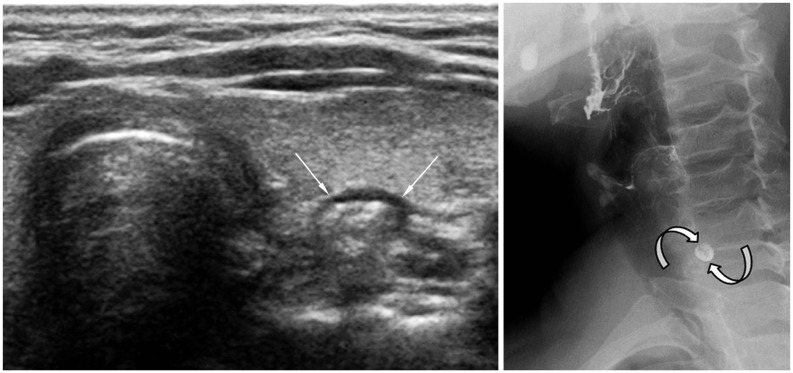 | Fig. 15
Pharyngoesophageal diverticulum. 63-year-old woman was referred for evaluation of left thyroid nodule. High-resolution ultrasonography revealed pharyngoesophageal diverticulum (arrows). Small barium collection (curved arrows) suggesting diverticulum was visible on esophagography. |
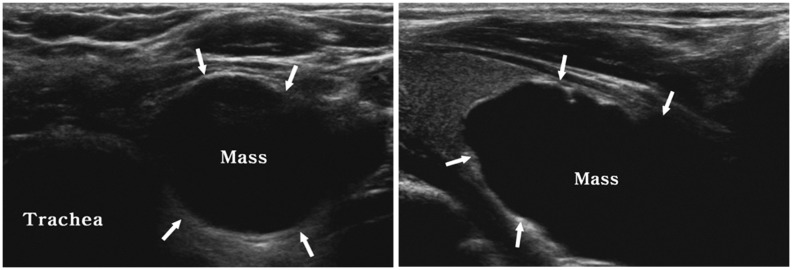
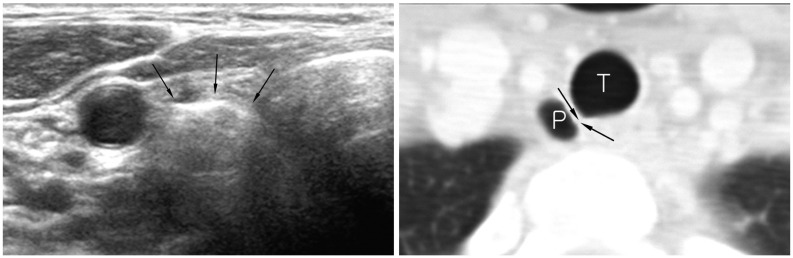 | Fig. 16
Right paratracheal air cyst in 47-year-old woman. Screening ultrasonography revealed echogenic mass (arrows) suggestive of air-containing mass in right paratracheal region. Neck CT scan was performed and confirmed presence of right paratracheal air cyst with slit-like communicating channel (arrows). P = paratracheal air cyst, T = trachea |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download