Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Standard dose contrast enhanced-chest CT in 77-year-old man (BMI 22 kg/m2) with sequalae of previous inflammation in right upper lobe.
A-C. Transverse CT images at 5 mm thickness with full radiation dose reconstructed with (A) filtered back projection (FBP) and (B) image reconstruction in image space (IRIS), and (C) with half radiation dose reconstructed with IRIS. When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and F-IRIS (B) images as reconstruction effect, their preference scores were 5 and 4 for lung 5 mm images, 2 and 3 for mediastinum, 5 and 3 for lung 1 mm images, and 5 and 4 for overall images (not shown). When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and H-IRIS (C) images as reconstruction effect and radiation dose effect, readers' preference scores were 4 and 3 for lung 5 mm images, 3 and 3 for mediastinum, 4 and 4 for lung 1 mm images, and 4 and 3 for overall images (not shown). BMI = body mass index, F-FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F-IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space, H-IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space
|
 | Fig. 2Standard dose contrast enhanced-chest CT in 19-year-old man (BMI, 21 kg/m2) with pulmonary hypertension.
A-C. Transverse CT images at 1 mm thickness with full radiation dose reconstructed with (A) FBP and (B) IRIS, and (C) with half radiation dose reconstructed with IRIS. When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and F-IRIS (B) images, reconstruction effect, they both had preference scores of 4 and 4 for lung 5 mm images, 3 and 3 for mediastinum, 4 and 3 for lung 1 mm images and 3 and 4 for overall (not shown). When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and H-IRIS (C) images, as reconstruction effect and radiation dose effect, readers' preference scores were 4 and each for lung 5 mm images, 3 and 2 each for mediastinum, 4 and 3 for lung 1 mm images and 4 and 3 for overall (not shown). BMI = body mass index, F-FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F-IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space, H-IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space
|
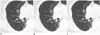 | Fig. 3Low dose chest CT in 62-year-old woman (BMI, 27 kg/m2) with postoperative lung cancer.
Transverse CT images at 5 mm thickness with full radiation dose reconstructed with (A) FBP and (B) IRIS, and (C) with half radiation dose reconstructed with IRIS. When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and F-IRIS (B) images as reconstruction effect, readers' preference scores of 4 and 4 for lung 5 mm images, 3 and 2 for mediastinum, 5 and 4 for lung 1 mm images, and 4 and 4 for overall (not shown). When they compared F-FBP (A) and H-IRIS (C) as reconstruction effect and radiation dose effect, two readers had preference scores of 4 and 4 each for lung 5 mm images, 2 and 3 for mediastinum, 5 and 4 for lung 1 mm images, and 4 and 4 overall (not shown). BMI = body mass index, F-FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F-IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space, H-IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space
|
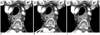 | Fig. 4Standard dose contrast enhanced-chest CT in 77-year-old man (BMI, 22 kg/m2) with esophageal cancer.
Transverse CT image at 5 mm thickness with full radiation dose reconstructed with (A) FBP and (B) IRIS, and (C) with half radiation dose reconstructed with IRIS. When two readers compared F-FBP (A) and F-IRIS (B) images, as reconstruction effect, readers' preference scores were 2 and 2 each for mediastinum, 4 and 3 for lung 5 mm images, 4 and 3 for lung 1 mm images and 4 and 3 for overall (not shown). When they compared F-FBP (A) and H-IRIS (C) as reconstruction effect and radiation dose effect, readers had preference scores of 2 and 2 each for mediastinum, 4 and 4 for lung 5 mm/1 mm images, and 3 overall (not shown). BMI = body mass index, F-FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F-IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space, H-IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space
|
Table 2

Note.- Combined data from two observers. 1 = strongly preferred F-FBP image, 2 = somewhat preferred F-FBP image, 3 = no preference, 4 = somewhat preferred H-IRIS image, 5 = strongly preferred H-IRIS image. In Wilcoxon's rank sum test, p < 0.05 indicates significant difference. F-FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, H-IRIS = half dose image with interative reconstruction in image space (IRIS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)
Table 3

Note.- Combined data from two observers. 1 = strongly preferred F-FBP image, 2 = somewhat preferred F-FBP image, 3 = no preference, 4 = somewhat preferred F-IRIS image, 5 = strongly preferred F-IRIS image. In Wilcoxon's rank sum test, p < 0.05 indicates significant difference. F/FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F/IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (IRIS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)
Table 4

Note.- Combined data from two observers. 1 = strongly preferred H-FBP image, 2 = somewhat preferred H-FBP image, 3 = no preference, 4 = somewhat preferred H-IRIS image, 5 = strongly preferred H-IRIS image. H/FBP = half dose image with filtered back projection, H/IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (IRIS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)
Table 5

Note.- Combined data from two observers. 1 = strongly preferred F-IRIS image, 2 = somewhat preferred F-IRIS image, 3 = no preference, 4 = somewhat preferred H-IRIS image, 5 = strongly preferred H-IRIS image. F/IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (IRIS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), H/IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (IRIS, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download