Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Standard dose contrast enhanced-chest CT in 48-year-old woman (BMI: 23 kg/m2) with lung cancer in left upper lobe.
A-C. Transverse CT images with (A) full radiation dose FBP in B70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, (B) full radiation dose IRIS in I70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, and (C) half radiation dose IRIS in I70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness. Objective noise measured in saline bag was 66.1 HU, 37.5 HU and 53.8 HU, respectively (not shown). BMI = body mass index, HU = Hounsfield unit, FBP = filtered back projection, IRIS = iterative reconstruction in image space
|
 | Fig. 2Standard dose contrast enhanced-chest CT in 69-year-old man (BMI: 24 kg/m2) with mild emphysema.
A-C. Transverse CT images with (A) full radiation dose FBP in B70f kernel and 1 mm slice thickness, (B) full radiation dose IRIS in I70f kernel and 1 mm slice thickness, and (C) half radiation dose with IRIS in I70f kernel and 1 mm slice thickness. Objective noise measured in saline bag was 59.9 HU, 35.7 HU and 47.6 HU, respectively (not shown). BMI = body mass index, HU = Hounsfield unit, FBP = filtered back projection, IRIS = iterative reconstruction in image space
|
 | Fig. 3Low dose chest CT without enhancement in 37-year-old woman (BMI: 23 kg/m2) with small ground glass nodules.
A-C. Transverse CT images with (A) full radiation dose FBP in B70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, (B) full radiation dose IRIS in I70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, and (C) half radiation dose IRIS in I70f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness. Objective noise measured in saline bag was 67.8 HU, 41.5 HU and 58.2 HU, respectively (not shown). BMI = body mass index, HU = Hounsfield unit, FBP = filtered back projection, IRIS = iterative reconstruction in image space
|
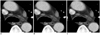 | Fig. 4Standard dose chest CT with enhancement in 75-year-old man (BMI: 21 kg/m2) with small lymph nodes in mediastinum.
A-C. Transverse CT images with (A) full radiation dose FBP in B30f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, (B) full radiation dose IRIS in I30f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness, and (C) half radiation dose IRIS in I30f kernel and 5 mm slice thickness. Objective noise measured in saline bag was 59.7 HU, 34.5 HU and 48.5 HU, respectively (not shown). Margins of mediastinal structures were slightly more blurred in (B) and (C) than in (A) due to excessive smoothing effect of IRIS image. BMI = body mass index, HU = Hounsfield unit, FBP = filtered back projection, IRIS = iterative reconstruction in image space
|
Table 2

Note.- *Comparison between F/FBP and H/IRIS. F/FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F/IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), H/FBP = half dose image with filtered back projection, H/IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), HU = Hounsfield unit, ROI = region of interest
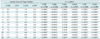
Table 3

Note.- Numbers in first column is related to Table 1. Numbers of 'average score of image quality' are means of total scores resulting from sum of subjective image quality scores by two radiologists. *Friedman test showed significant results in all assessed categories, †In post hoc comparisons, p value of < 0.0001 (adjusted by Bonferroni correction) indicates significant difference. F/FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F/IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), H/FBP = half dose image with filtered back projection, H/IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)
Table 4
Note.- Numbers in first column is related to Table 1. Numbers of 'average score of image quality' are means of total scores resulting from sum of subjective image quality scores by two radiologists. *Friedman test showed significant results in all assessed categories, †In post hoc comparisons, p value of < 0.0001 (adjusted by Bonferroni correction) indicates significant difference. F/FBP = full dose image with filtered back projection, F/IRIS = full dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen Germany), H/FBP = half dose image with filtered back projection, H/IRIS = half dose image with iterative reconstruction in image space (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download