INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Vitro Study
Patient Population
CT Examinations
Image Analyses
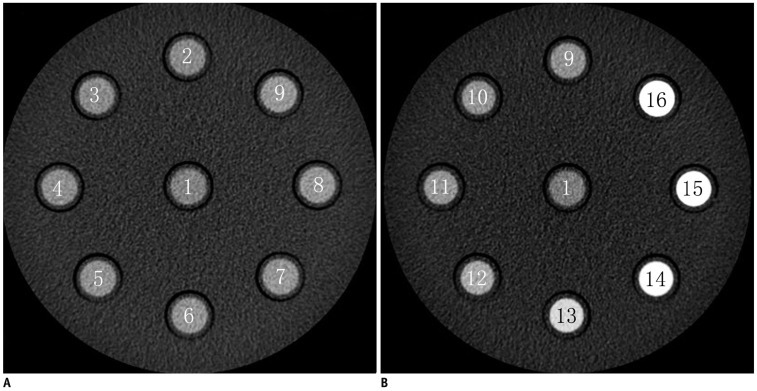
Vitro Study
Clinical Study
Statistical Analyses
RESULTS
Vitro Study
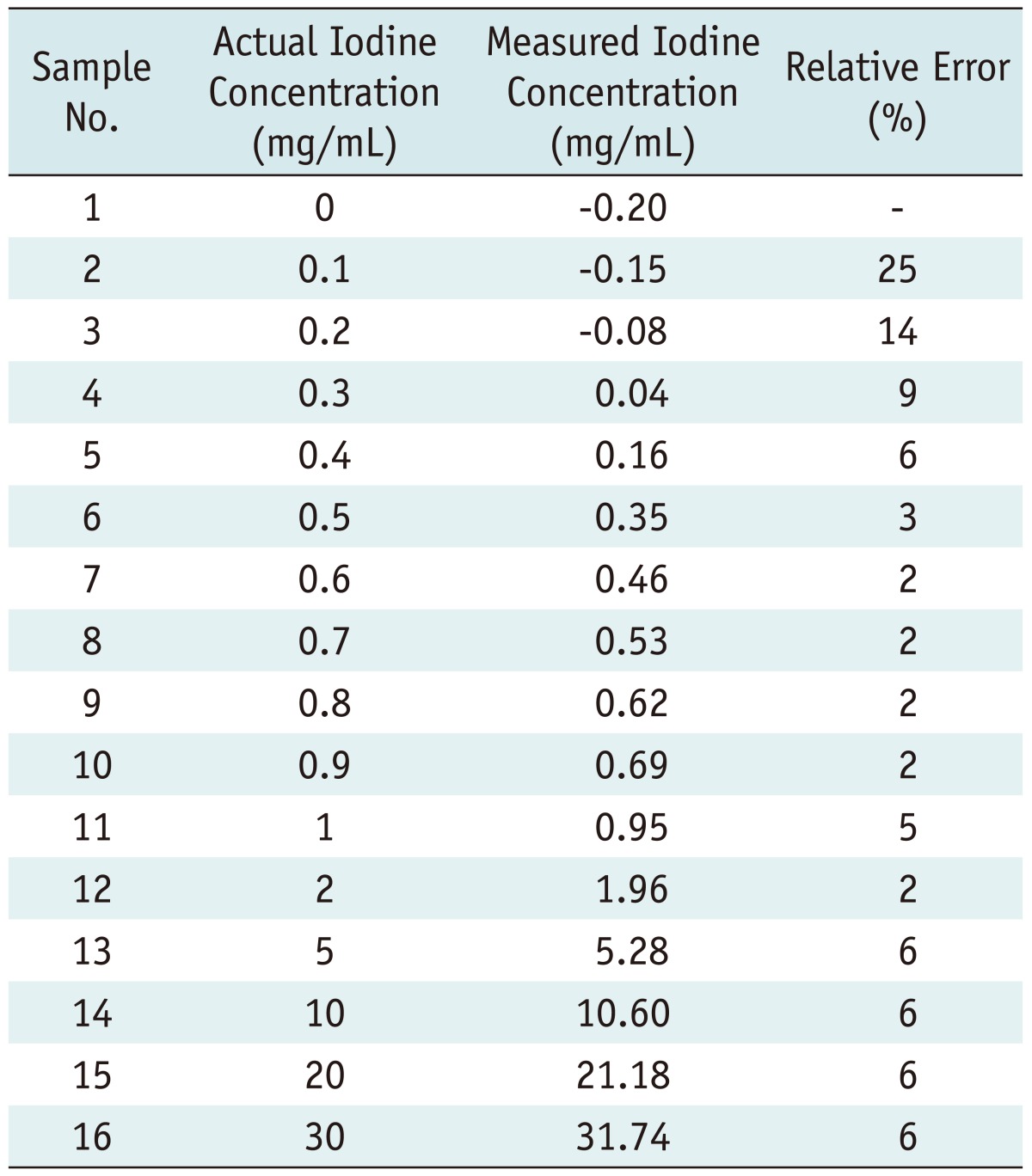
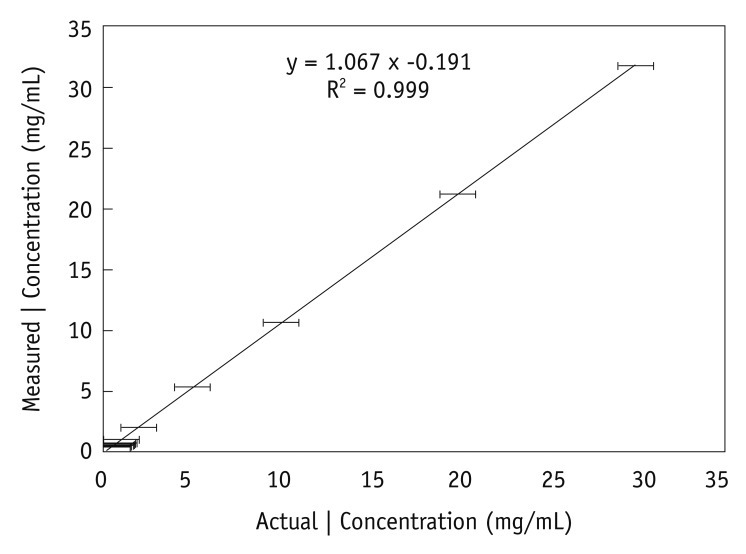 | Fig. 2Graph illustrates relationship between actual (x-axis) and measured (y-axis) iodine (I) concentrations in in vitro experiment. Test tubes filled with known iodine concentrations of 0.3-30.0 mg/mm3 were scanned with CT spectral imaging, and iodine concentrations were measured from iodine-based material-decomposition images. Mean and standard deviations for three separate measurements for same iodine concentration in each test tube (n = 13) are shown. Fitted line shows linear relationship between measured and actual concentrations. |
Clinical Study
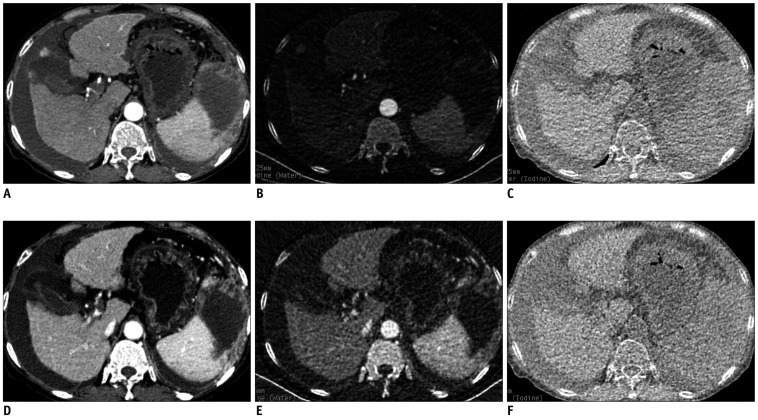 | Fig. 3Monochromatic and material decomposition images of cirrhosis.
Transverse (A, D) monochromatic CT image obtained at 70-keV energy level and (B, E) iodine-based and (C, F) water-based material-decomposition images obtained from single spectral CT acquisition (section thickness, 1.25 mm) in 63-year-old woman with cirrhosis B during AP and PVP respectively. AP = arterial phase, PVP = portal venous phase
|
Table 2
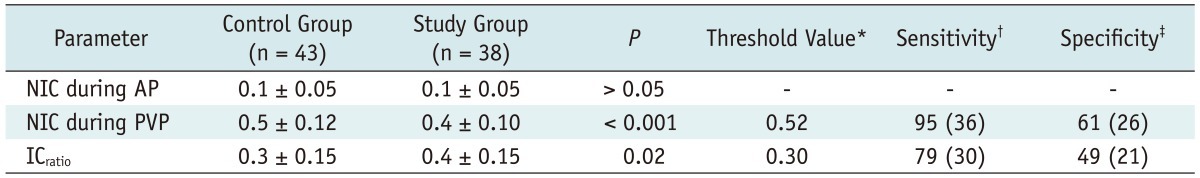
Note.- With exception of p values, data are mean values ± standard deviations. p values for comparisons between control group and study group. *Threshold NIC and ICratio are cited in milligrams per milliliter, †Sensitivity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent number of cirrhotic livers in study group (n = 38), ‡Specificity values are cited as percentages. Data are number of healthy livers in control group (n = 43). AP = arterial phase, ICratio = iodine concentration ratio, NIC = normalized iodine concentration, PVP = portal venous phase
Table 3
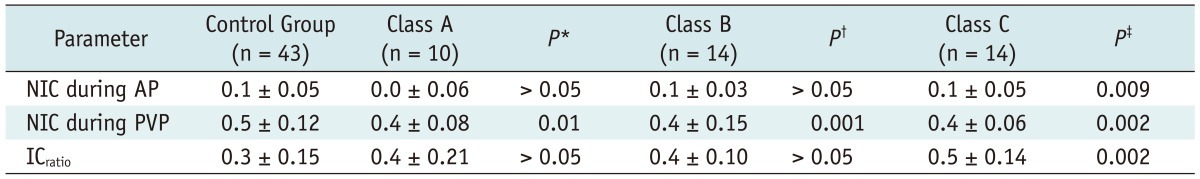
Note.- With exception of p values, data are mean values ± standard deviations. *p values for comparisons between control group and Class A group, †p values for comparisons between control group and Class B group, ‡p values for comparisons between control group and Class C group. AP = arterial phase, ICratio = iodine concentration ratio, NIC = normalized iodine concentration, PVP = portal venous phase
Table 4
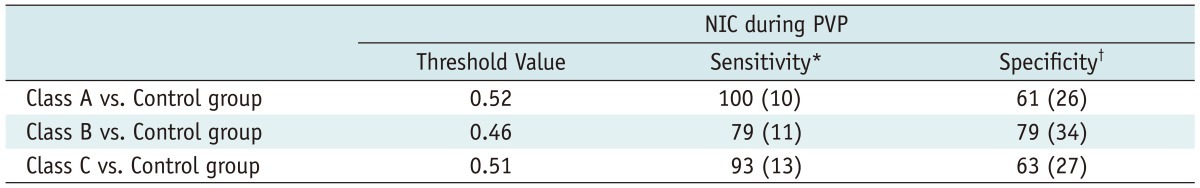
Note.- *Sensitivity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent, respectively, number of Class A liver cirrhosis (n = 10), Class B liver cirrhosis (n = 14) and Class C liver cirrhosis (n = 14) used to calculate percentages, †Specificity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent number of healthy livers in control group (n = 43) used to calculate percentages. NIC = normalized iodine concentration, PVP = portal venous phase
Table 5

Note.- *Sensitivity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent number of Class C liver cirrhosis (n = 14) used to calculate percentages, †Specificity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent number of healthy livers in control group (n = 43) used to calculate percentages. AP = arterial phase, ICratio = iodine concentration ratio, NIC = normalized iodine concentration
Table 6
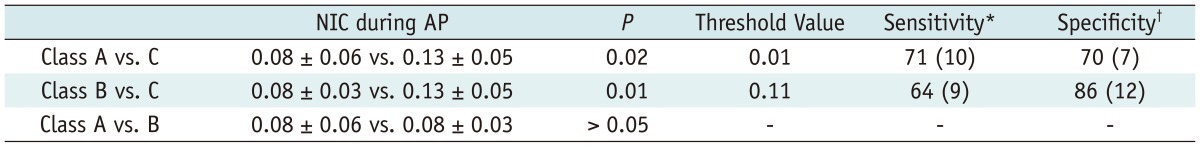
Note.- With exception of p values, data are mean values ± standard deviations. p values for comparisons among Class A, Class B and Class C groups. *Sensitivity values are cited as percentages. Between Class A-B and C, data in parentheses represent number of Class C liver cirrhosis (n = 14) used to calculate percentages, †Specificity values are cited as percentages. Data in parentheses represent number of Class A (n = 10) and Class B liver cirrhosis (n = 14) used to calculate percentages. AP = arterial phase, NIC = normalized iodine concentration




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download