Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
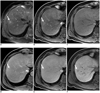 | Fig. 160-year-old man with gastric adenocarcinoma and focal eosinophilic infiltration (differential count of eosinophils was 18%) in liver.
A. T2-weighted image shows non-spherical hyperintense lesion (arrow) in segment VIII. B. Unenhanced T1-weighted image shows isointensity of lesion (arrow). C-E. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced dynamic images show heterogeneous enhancement with slight hyperintensity (arrow) during arterial phase (C) and faint hypointensity (arrow) during portal (D) and 3-minute late phases (E). F. Hepatobiliary phase image obtained 20 minutes after injection of contrast agent shows ill-defined hypointense lesion (arrow) with slight increase in size (13.6 mm on T2-weighted and 14.2 mm on hepatobiliary phase images) compared to A. Lesion spontaneously disappeared on follow-up CT (not shown) taken 6 months later. Lesion was correctly interpreted as focal eosinophilic infiltration on both sessions by all observers.
|
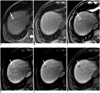 | Fig. 263-year-old man with colon adenocarcinoma and focal eosinophilic abscess, confirmed by biopsy (differential count of eosinophils in peripheral blood, 18%) in liver.
A. T2-weighted image shows spherical hyperintense lesion (arrow). B. Unenhanced T1-weighted image shows isointensity of lesion. C-E. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced dynamic images show rim enhancement (arrows) during arterial (C) portal phase (D) and 3-minute late phase (E). F. Hepatobiliary phase image obtained 20 minutes after injection of contrast agent shows well-defined hypointense lesion (arrow). Size difference between T2 (11.9 mm) and hepatobiliary phase (10.5 mm) was 1.4 mm. Slight decrease in size (11.9 mm on T2-weighted and 10.5 mm on hepatobiliary phase images) compared to A. Lesion was correctly interpreted as focal eosinophilic infiltration in session 2 after misinterpretation as metastasis in session 1 by all observers.
|
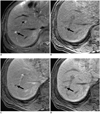 | Fig. 370-year-old man with rectal cancer and metastatic adenocarcinoma confirmed by intra-operative sonography-guided biopsy in liver (false-positive lesion).
A. T2-weighted MR image shows spherical hyperintense lesion (arrow). B. Unenhanced T1-weighted image shows hypointense lesion (arrow). C. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced dynamic image shows no enhancement with hypointensity (arrow) during portal phase or arterial and 3-minute late phases (not shown). D. Hepatobiliary phase image obtained 20 minutes after injection of contrast agent shows well-defined hypointense lesion (arrow) with no change in size compared to A. One of two observers misinterpreted it as focal eosinophilic infiltration in session 2, although it was correctly interpreted as metastasis in session 1.
|
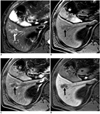 | Fig. 458-year-old man with colon cancer and focal eosinophilic abscess confirmed by percutaneous sonography-guided biopsy (differential count of eosinophils in peripheral blood, 2%) in liver (false-negative lesion).
A. T2-weighted image shows non-spherical hypointense lesion (arrow). B. Unenhanced T1-weighted image shows hypointense lesion (arrow). C. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced dynamic images show rim enhancement (arrow) during arterial phase only (C) with hypointensity during portal and 3-minute late phases, without rim enhancement (not shown). D. Hepatobiliary phase image obtained 20 minutes after injection of contrast agent shows well-defined hypointense lesion (arrow). Size difference between T2 (21.5 mm) and hepatobiliary phase (21.3 mm) was 0.2 mm, which is minimal change in size (21.5 mm on T2-weighted and 21.3 mm on hepatobiliary phase images) compared to A. Lesion was misinterpreted as metastasis on both sessions by all observers.
|
Table 1
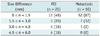
Table 2

Note.- Numbers in parentheses are percentages. AP = arterial phase, app. = appearance, E = enhancement, FEI = focal eosinophilic infiltration, HBP = hepatobiliary phase, LP = 3-minute late phase, n = number, PP = portal phase, SI = signal intensity, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image. †P values = univariate analysis, *On multivariate analysis, ill-defined margin (P = 0.0155) and isointensity on T1-weighted images (P = 0.0028) were statistically significant.
Table 3
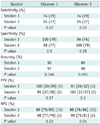
Note.- Numbers in parentheses in sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV are number of true positive, true negative, false positive and false negative lesions, respectively. For PPV, numbers in brackets are numbers of true-positive lesions divided by total number of lesions assigned confidence level of 4 or 5. For NPV, numbers in brackets are number of true-negative lesions divided by total number of lesions assigned confidence level of 1, 2 or 3. n = number, NPV = negative predictive values, PPV = positive predictive values




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download