Abstract
Objective
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
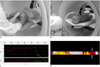 | Fig. 1Imaging techniques of xenon-enhanced dynamic dual-energy CT.
A. For young, sedated child (doll for demonstration), face mask is fitted with hands during CT examination. B. In older, cooperative child (5-year-old anthropomorphic phantom for demonstration), face mask with elastic straps is used. C. Diagram demonstrates dynamic dual-energy spiral CT scan protocol (D1-D7) during xenon wash-in (red) and wash-out (yellow) periods. Baseline scan (D1) is followed by wash-in (D2-D5) and wash-out scans (D6 and D7). Interscan delay of dynamic scans is set to 10-20 sec. Exhaled xenon concentration reaches 30% at end of wash-in period. Real-time monitoring of exhaled xenon and carbon dioxide concentrations (%) during CT examination is also shown. D. Dual-energy spiral scan is acquired in middle of lung lesion with shortest longitudinal coverage, approximately 2.6-3.0 cm, during free-breathing. Ventilation defect (arrows) is noted in left lung when right lung shows maximal xenon enhancement.
|
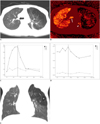 | Fig. 27-year-old boy with congenital pulmonary airway malformation (case 2).
A. Axial weighted-average CT image shows hyperlucent lesion in left upper lobe. B. 5th-phase axial xenon map acquired at end of xenon wash-in period demonstrates low xenon values in lung lesion similar to baseline level and high xenon values in normal right lung, left lower lobe (arrowhead) and central airway (arrow). C. Time-xenon value graph demonstrates distinguishing dynamic changes of xenon values between normal right upper lobe (RUL) and abnormal left upper lobe (LUL). Typically, normal RUL shows rapid increase of xenon value during wash-in period followed by rapid decrease of xenon value during wash-out period with logarithmic function. Conversely, xenon values in LUL remain low and largely unchanged throughout dynamic phases. After correction of baseline xenon values, peak xenon values are approximately 22 in RUL and below five in LUL. End of wash-in period is indicated as vertical gray line (C, D). D. Time-attenuation graph shows zigzag pattern and particularly for normal right upper lobe (RUL) depending on different lung volumes during free breathing. This has been regarded as demerit of xenon-enhanced dynamic single-energy CT. E. Coronal reformatted CT image reveals cyst (asterisk) and accessory fissure (arrow), i.e., left minor fissure, in left lung lesion.
|
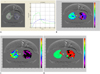 | Fig. 38-year-old boy with bronchial atresia (case 5).
A. Time-xenon value graph demonstrates normal curve (green) of right upper lobe as well as curve (blue) of left upper lobe with low-resistant collateral ventilation that is typical for bronchial atresia. As compared with normal curve of right upper lobe, peak of xenon value is lower and it arrived later as well as the wash-out of xenon is slower. B. A (amplitude of xenon enhancement) map reveals that A values in left upper lobe, approximately 10-15, are lower than those in right upper lobe, approximately 20-30. Of note, A values are quite heterogeneous in both regions. Black areas indicate areas with fitting error (B-D). C. K (rate of xenon enhancement) map shows that K values in left upper lobe, approximately below 0.03, are lower than those in right upper lobe. The same as for the A values, the K values are also heterogeneous in both regions. D. TOA (time of arrival of xenon gas) map demonstrates greater TOA values in left upper lobe, approximately 20, than those in right upper lobe, approximately 12. TOA values are notably more uniform than A and K values in both regions.
|
Table 1

Note.- *Two lesions were histologically proven to be type I (case 1) or type II (case 4) congenital pulmonary airway malformation. †Lung lesion might have component of CPAM as several cysts were identified on CT. CPAM = congenital pulmonary airway malformation, L = lung lesion, N = normal lung, NA = not applicable due to fitting error, TOA = time of arrival
Table 2

Note.- *Two lesions were histologically proven to be type I (case 1) or type II (case 4) congenital pulmonary airway malformation. †Lung lesion might have component of CPAM as several cysts were identified on CT. CPAM = congenital pulmonary airway malformation, LLL = the left lower lobe, LUL = the left upper lobe, RLL = the right lower lobe, RUL = the right upper lobe




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download