Abbreviations
CSF
DTI
FA
FDR
FLAIR
FOV
FWE
FWHM
GM
GMC
MNI
mTLE
NEX
rCBF
SPGR
SPM
VBM
WCAT
WM
WMAT
WMC
WMV
Journal List > Korean J Radiol > v.11(1) > 1026429
CSF
DTI
FA
FDR
FLAIR
FOV
FWE
FWHM
GM
GMC
MNI
mTLE
NEX
rCBF
SPGR
SPM
VBM
WCAT
WM
WMAT
WMC
WMV
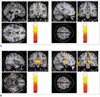 | Fig. 1Decreased gray matter concentration in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. (A) shows reduced gray matter concentrations in left hippocampus, bilateral thalami, precentral gyri, superior frontal gyri, and cingulate gyri in left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients, whereas (B) reveals a gray matter concentration reduction in right hippocampus, thalami, precentral gyri, and frontopolar gyri in right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients. These findings were significant at corrected false discovery rate of p < 0.05. |
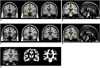
 | Fig. 2Decreased gray matter volume in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
A. MR images show reduced gray matter volumes in bilateral frontopolar gyri, cingulate gyri, caudate nuclei, left thalamus, hippocampi, left insular gyrus, pons, and cerebelli in left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients.
B. MR images show gray matter volume reduction in bilateral frontopolar gyri, left orbital gyrus, caudate nuclei, thalami, hippocampi, left superior/middle temporal gyri, and cerebelli in right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Volume reductions in ipsilateral whole temporal lobes were observed in left and right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy groups. These findings were significant at corrected false discovery rate of p < 0.05.
|
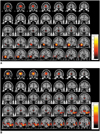
 | Fig. 3White matter concentration changes in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients. White matter concentrations reduced in internal capsules, temporal stem, and parahippocampal regions in left (A) and right (C) mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients, whereas white matter concentrations increased in precentral gyri, pons, and internal capsules in left (B) and right (D) mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Pons (arrow) was partitioned into white matter image using SPM2 segmentation (E). These findings were significant at uncorrected p < 0.001. |
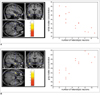 | Fig. 4Correlation between gray and white matter concentrations and heterotopic neuron counts in left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Negative correlation (r = -0.839, p = 0.00005) was found between white matter concentration and heterotopic neuron count in left anterior temporal lobe (A), whereas a positive correlation (r = 0.819, p = 0.00005) was observed between gray matter concentration and heterotopic neuron count in left anterior temporal lobe (B). Whole brain mask with uncorrected p < 0.001, and extent threshold of κE > 200 voxels were applied for statistical parametric mapping analysis. |

This study was supported by a Grant (2009K001257) from the Brain Research Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program, which was funded by a Ministry of Science, by the Samsung Biomedical Research Institute grant, #SBRI C-A7-226-3, and partly by a Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government [KRF-2008-359-E00009]
CSF
DTI
FA
FDR
FLAIR
FOV
FWE
FWHM
GM
GMC
MNI
mTLE
NEX
rCBF
SPGR
SPM
VBM
WCAT
WM
WMAT
WMC
WMV