INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Solutions, materials, mutagenesis, and plasmid construction
Cell transfection
Measurement of intracellular pH
Co-immunoprecipitation and biotinylation
Densitometric quantification
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
NBCe1-B contains PP1-binding consensus residues
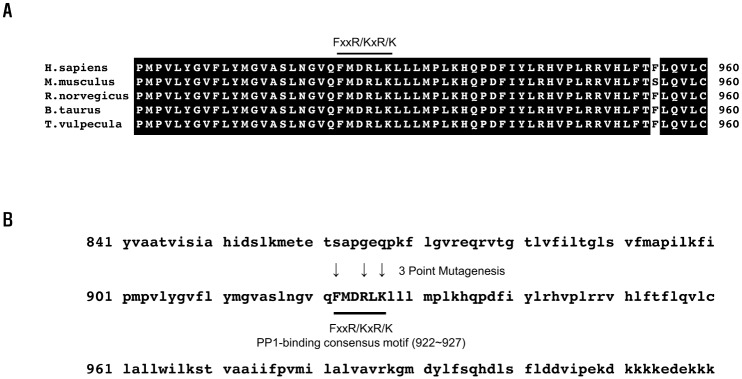 | Fig. 1Conservation of the PP1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B.(A) Sequence alignment analysis: the C-terminal part of the human NBCe1-B (Q9Y6R1.1) against the orthologous transporters of Mus musculus (O88343.2), Rattus norvegicus (Q9JI66.1), Bos taurus (NP_777030.1), and Trichosurus vulpecula (AEQ33587.1). (B) Amino acids (downward-pointing arrows) are critical in binding to PP1, and substituted by site-directed mutagenesis. (A, B) The PP1-binding consensus residues are indicated using bold bars.
|
PP1 directly interacts with PP1-binding consensus residues of NBCe1-B in vitro
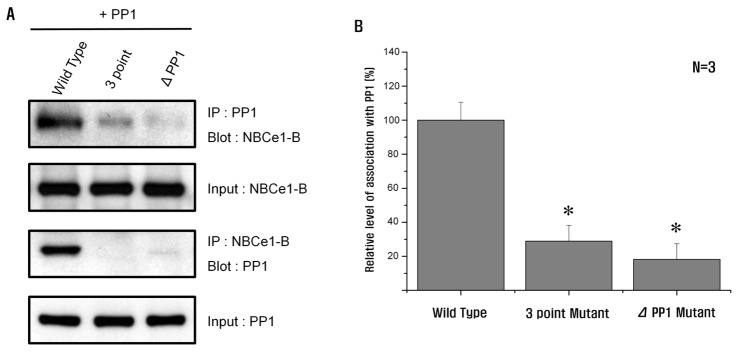 | Fig. 2PP1 interacts with the PP1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B.(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of NBCe1-B with PP1 in HEK293T cells transfected with PP1 co-expressing NBCe1-B, 3-point mutant, and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant. The cells were lysed with RIPA buffer. The extract was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP or anti-PP1. (B) HEK293T cells transfected with 3-point mutant or PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant showing a significant decrease of NBCe1-B activity via association with PP1 (28.9±9.3% and 18.2±9.1%; n=3; *p<0.05). *Significance was compared against the wild type value.
|
NBCe1-B activity is controlled by PP1
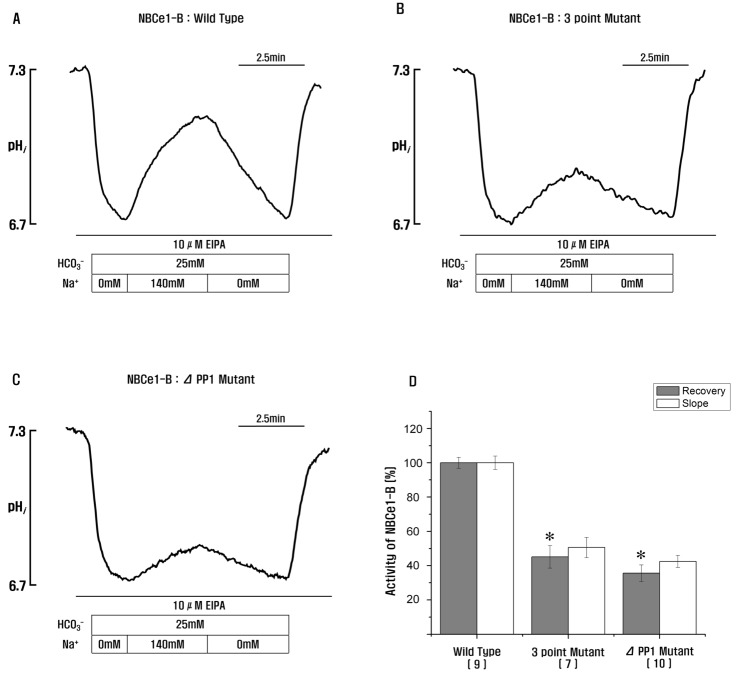 | Fig. 3Role of PP1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B.(A–C) Measurement of NBCe1-B activity in HeLa cells transfected with wild type, 3-point mutant, and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant by monitoring intracellular pH. (D) HeLa cells transfected with 3-point mutant or PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant showing a significant decrease of NBCe1-B activity (45.1±6.5% and 35.7±4.7%; *p<0.05). *Significance was compared against the wild type value. Number of experiments for each condition are shown below the X-axis. Recovery, the rates of Na+-dependent changes in pHi (Δ pHi (recovery)/Δ pHi (total)); Slope, the slopes of the first derivatives of pHi increase in HCO3−-buffered media containing 140 mM of Na+(Δ pHi/min).
|
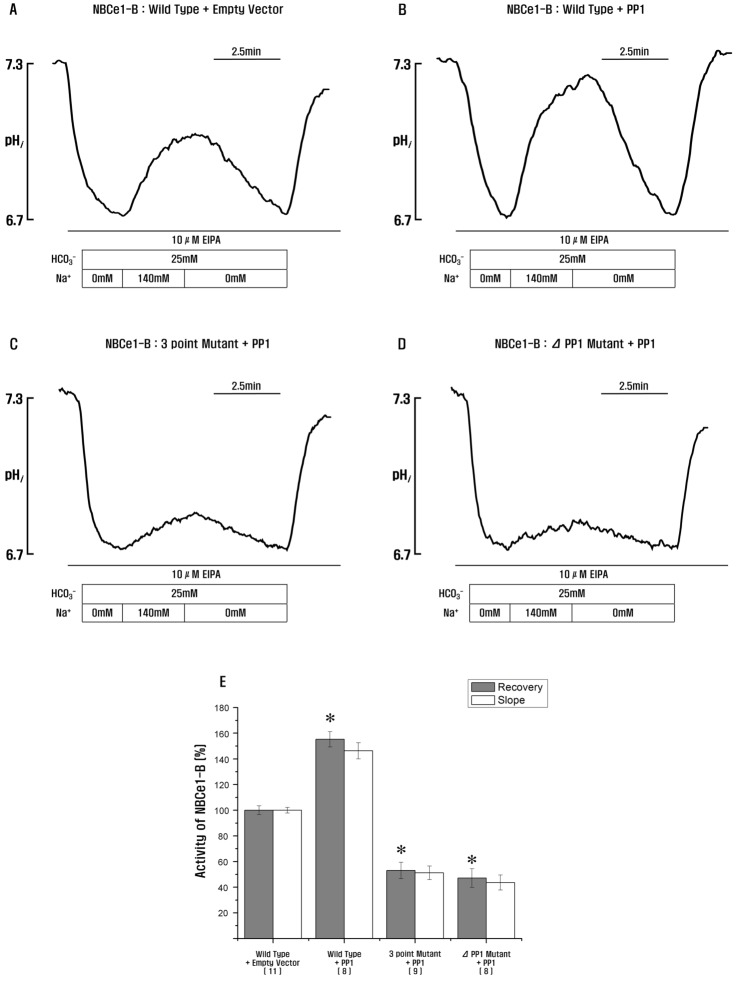 | Fig. 4PP1 stimulates NBCe1-B activity via PP1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B.(A–D) Measurement of NBCe1-B activity in HeLa cells transfected with wild type, 3-point mutant, and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant co-expressing PP1 by monitoring intracellular pH. (E) NBCe1-B with PP1 shows a significant increase in NBCe1-B activity, but 3-point mutant and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant co-expressing PP1 inhibit NBCe1-B activity (155.3±5.9%, 53.1±6.4% and 47.2±7.3%; *p<0.05). *Significance was compared against the wild type+empty vector value. Number of experiments for each condition are shown below the X-axis. Recovery, the rates of Na+-dependent changes in pHi (Δ pHi (recovery)/Δ pHi (total)); Slope, the slopes of the first derivatives of pHi increase in HCO3−-buffered media containing 140 mM of Na+(Δ pHi/min).
|
PP1 regulates surface expression of NBCe1-B
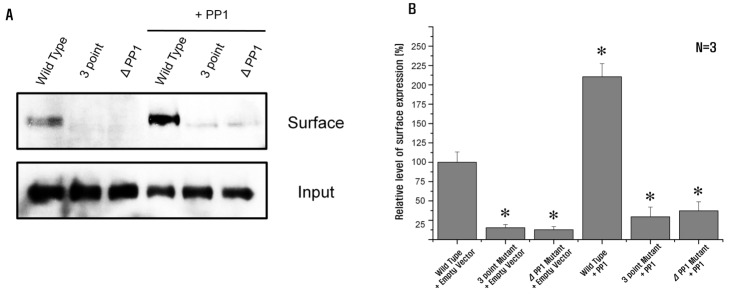 | Fig. 5NBCe1-B surface expression is associated with PP1.(A) Biotinylation of NBCe1-B with or without PP1 in HEK293T cells transfected with or without PP1 co-expressing NBCe1-B, 3-point mutant, and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant. Cells were incubated with biotin. Biotinylated NBCe1-B was isolated and recovered. Input corresponds to 5% of the total NBCe1-B used for the avidin pull-down step. (B) NBCe1-B with PP1 shows an approximate 2-fold increase of NBCe1-B surface expression level (210.5±16.9%). However, 3-point mutant and PP1-binding consensus residue deletion mutant with or without PP1 significantly inhibit NBCe1-B surface expression level (29.5±12.6%, 37.2±11.8%, 15.3±4.2% and 12.6±4.3%, respectively). Significant differences (*p<0.05) between wild type and each experimental group were statistically determined by one-way ANOVA.
|
DISCUSSION
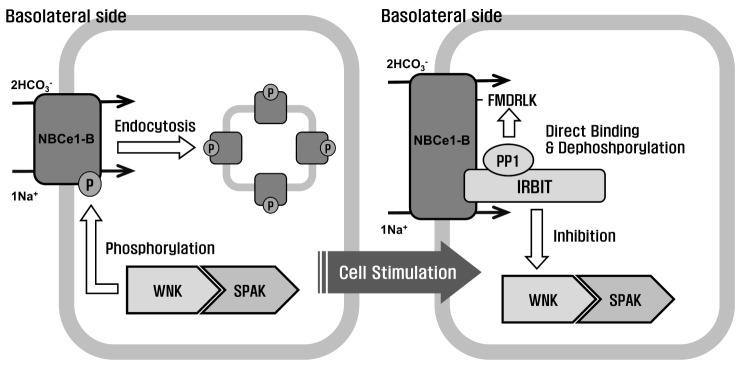 | Fig. 6Regulation of NBCe1-B via the IRBIT/PP1 and WNK/SPAK pathways.The WNK/SPAK pathway keeps the epithelial ductal cells in a steady state by decreasing the surface expression of NBCe1-B. The WNKs directly bind to SPAK, which phosphorylates NBCe1-B. After cell stimulation, IRBIT inhibits the WNK/SPAK pathway and activates NBCe1-B. IRBIT interacts with PP1 and PP1 is recruited to NBCe1-B by IRBIT. Thus, PP1 specifically docks with the PP1-binding consensus residue in NBCe1-B and dephosphorylates it, thereby restoring its surface expression.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download