INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Animals
Slice preparation
Electrophysiological recordings
Data analysis
RESULTS
Echinacoside suppresses epileptiform activity induced by 4-AP
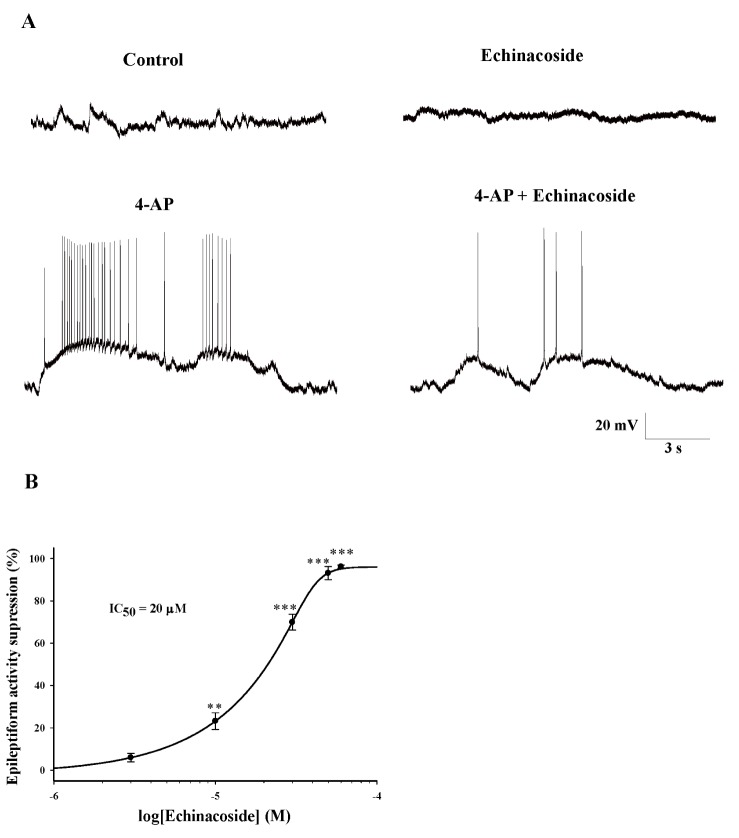 | Fig. 1Effect of echinacoside on the epileptiform activity induced by 4-AP in CA3 pyramidal neurons in rat hippocampal slices.(A) Representative current clamp recordings in control, echinacoside (20 µM), 4-AP (1 mM), and 4-AP (1 mM)+echinacoside (20 µM). 4-AP was applied for 10 min to induce epileptiform activity. Echinacoside was added 10 min after the application of 4-AP. (B) Normalized dose-response relationship of the effect of echinacoside on epileptiform activity induced by 4-AP (n=3-6). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. control group.
|
Echinacoside decreases the frequency but not the amplitude of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents induced by 4-AP
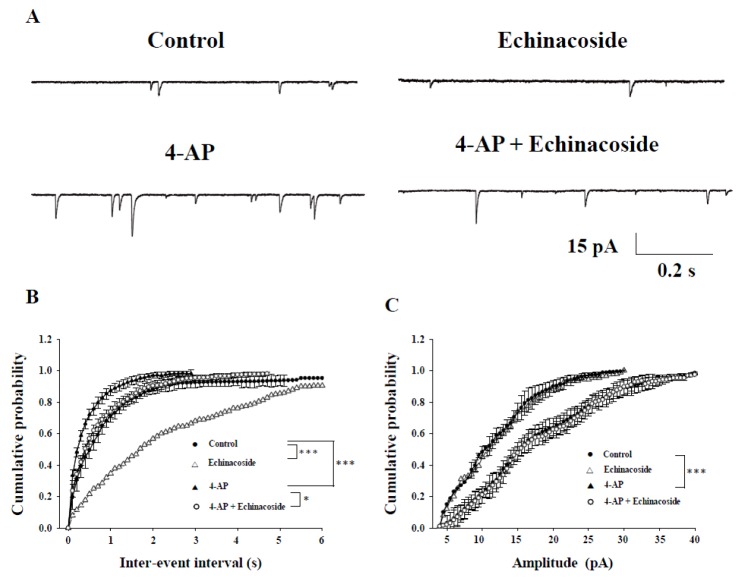 | Fig. 2Effect of echinacoside on spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials (sEPSCs) induced by 4-AP in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons.(A) Representative voltage clamp recordings in control, echinacoside (20 µM), 4-AP (1 mM), and 4-AP (1 mM)+echinacoside (20 µM). Echinacoside was added 10 min after the application of 4-AP. (B, C) Cumulative probability plots of sEPSCs frequency and amplitude, respectively. Each result represents mean values from 5 neurons. ***p<0.001 vs. control group. *p<0.05 vs. the 4-AP-treated group.
|
 | Fig. 3Effect of echinacoside on miniature excitatory postsynaptic potentials (mEPSCs) in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons.(A) Representative voltage clamp recordings from neurons before (control) and after echinacoside (20 µM) application for 10 min. mEPSCs recorded in the presence of TTX. (B, C) Cumulative probability plots of mEPSCs frequency and amplitude, respectively. Each result represents mean values from 5 neurons. ***p<0.001 vs. control group.
|
Echinacoside does not affect postsynaptic glutamate receptor sensitivity
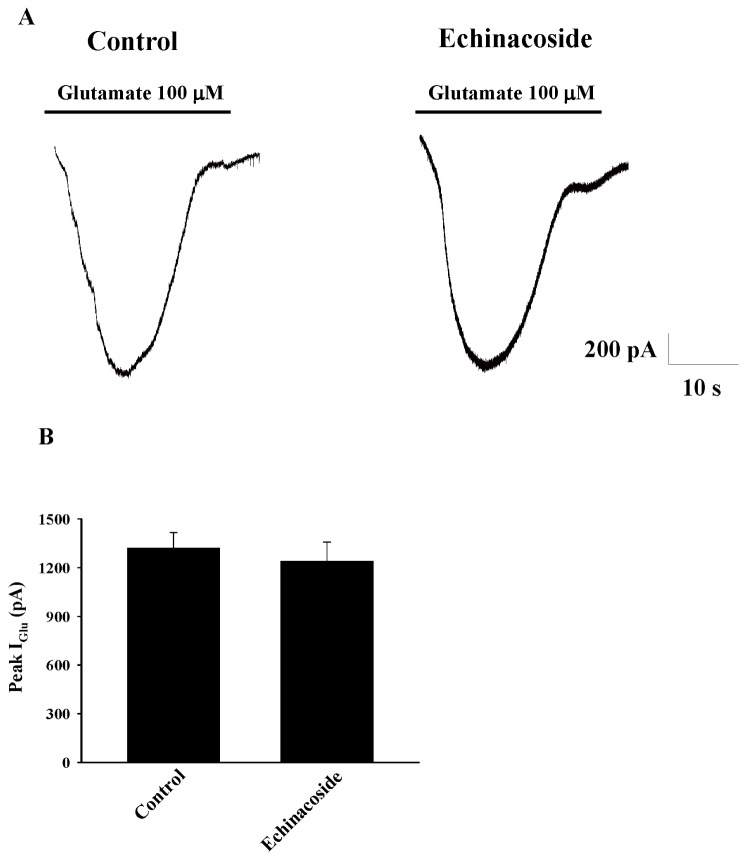 | Fig. 4Effect of echinacoside on glutamate-evoked postsynaptic currents (IGlu) in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons.Superfusion of 100 µM glutamate for 10 s evoked an inward current. (A) Typical IGlu traces recorded from a CA3 pyramidal neuron before (control) and after echinacoside (20 µM) application for 10 min. (B) Summary data (n=5) showing mean values of peak IGlu in the absence (control) and presence of 20 µM echinacoside.
|
Echinacoside reduces the number of sustained repetitive action potentials
 | Fig. 5Effect of echinacoside on sustained repetitive firing in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons.(A) Representative current clamp recordings of action potential induced by depolarizing current pulses (500 ms; 1 nA) from neurons before (control) and after echinacoside (20 µM) application for 10 min. (B) Summary data (n=7) showing mean values of action potential frequency in the absence (control) and presence of 20 µM echinacoside. ***p<0.001 vs. control group.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download