INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Animals and high-fat feed
Chemicals
Diabetic and brain ischemia/reperfusion model
Groups
Neurological evaluation
Evaluation of infarct volume by TTC staining
Histopathology
Immunohistochemistry
Measurement of superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on blood glucose
Table 1
Blood glucose (mM) levels and changes in MCAO/R rats in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=12)
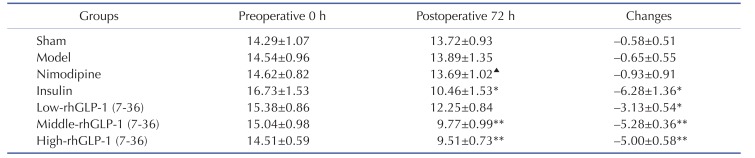
Tail vein blood samples were obtained to detect FBG levels with a blood glucose meter at preoperative 0 h and 72 h after administration in the morning, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly reduced blood glucoses compared with the Model group. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group; ▴p<0.05 vs. Insulin group.
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on neurological deficit scores of MCAO/R diabetic rats
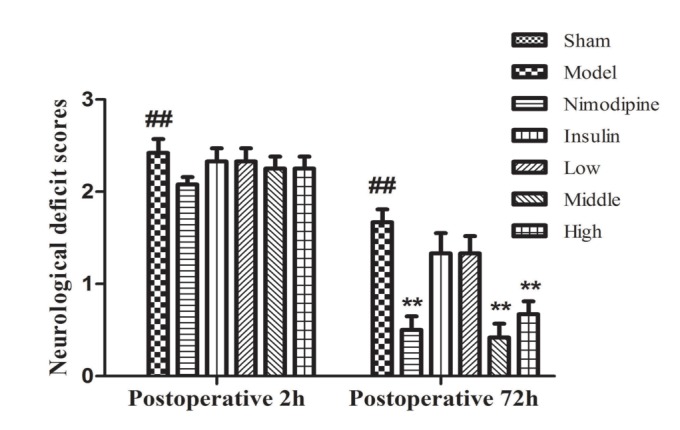 | Fig. 1Neurological deficit scores of MCAO/R rats in different groups.Neurological deficits were scored at 2 h after occlusion and 72 h after administration, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) can significantly reduced neurological deficit scores compared with the Model group. Columns represent the Mean±S.E.M (n=12). The intergroup variation was analyzed by nonparametric statistics with a Mann-Whitney U test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group; **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the infarction volumes of MCAO/R diabetic rats
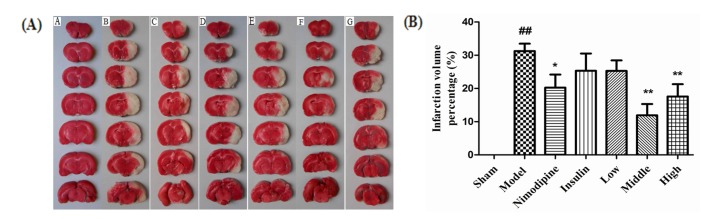 | Fig. 2Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the infarction volumes of MCAO/R diabetic rats.(A) Typical TTC stained brain slices of MCAO/R rats in different groups. The normal brain tissue is red and the cerebral ischemia and infarction tissues are white (n=6). A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) Infarction volume percentage of MCAO/R rats in different groups, columns represent the Mean±S.E.M (n=6). Infarction volumes were measured at 72h after administration, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) can significantly reduced Infarction volumes compared to the Model group. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the pathological changes in the brain
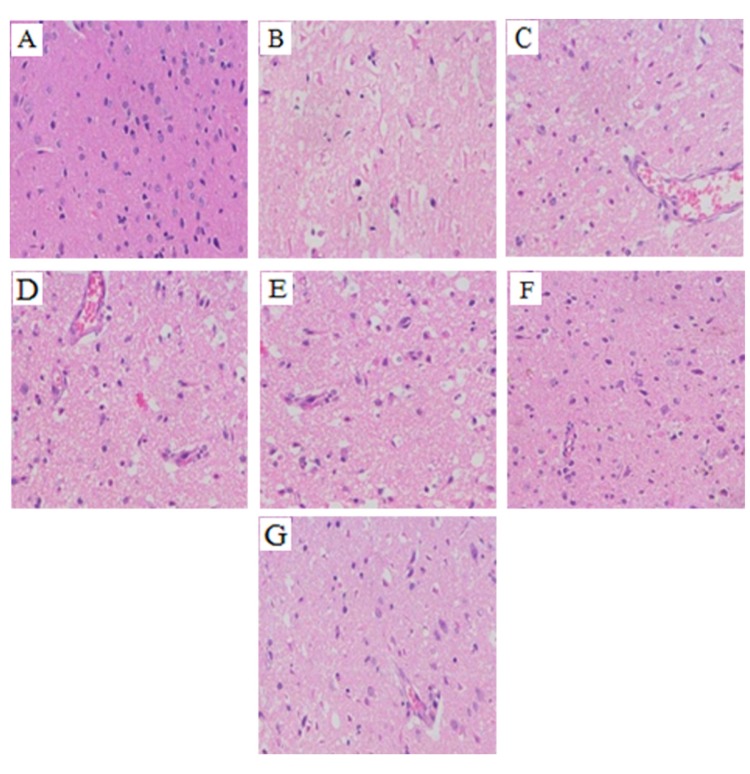 | Fig. 3Summary of typical pathological sections of MCAO/R rats in the different groups (HE, ×200, n=3).At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, the cavitation in each of the rhGLP-1, the nimodipine, and the insulin groups were alleviated, the number of surviving neurons increased and vascular proliferation was enhanced. (A) Sham group; (B) Model group; (C) Nimodipine group; (D) Insulin group; (E) Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; (F) Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; (G) High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group.
|
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the distribution and expression of Nrf2 in the cerebral cortex of the ischemia-reperfusion damage
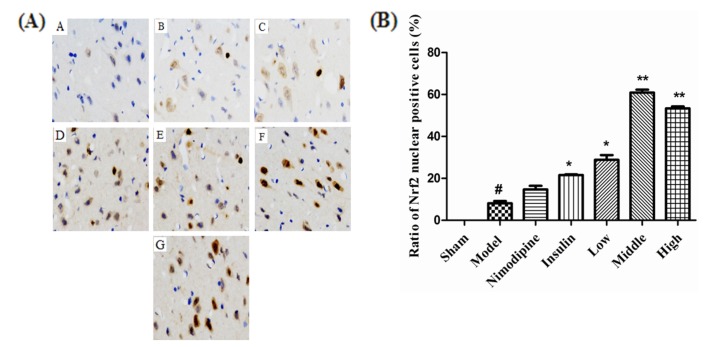 | Fig. 4Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the distribution and expression of Nrf2 in the cerebral cortex of the ischemia-reperfusion damage.(A) Immunohistochemistry of Nrf2 of MCAO/R rats in different groups (× 400, n=3), brown indicates Nrf2 positive. The expression of Nrf2 in cytoplasm and nuclear translocation increased after treatment with nimodipine, insulin, and rhGLP-1 (7-36). A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) Ratio of Nrf2 nuclear positive cells of MCAO/R rats in different groups, columns represent the Mean±S.E.M (n=3). The Nrf2 nuclear positive cells ratio significantly increased at 72 h after treated with rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) compared to the Model group. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by Dunnett's T3 test. #p<0.05 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|
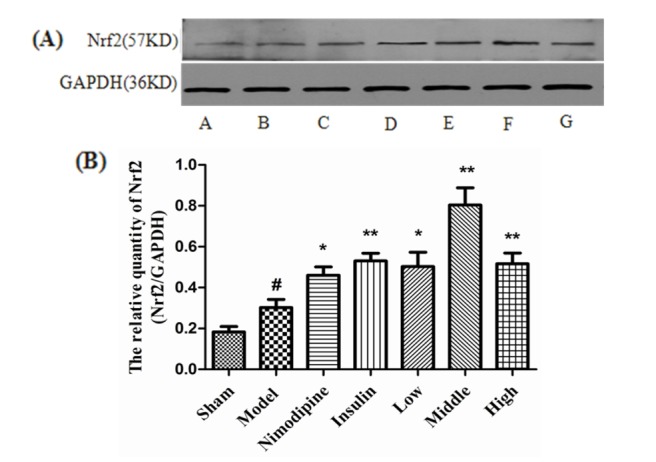 | Fig. 5Nrf2 expression in MCAO/R rats.(A) Expression of Nrf2 protein in MCAO/R rats in different groups (n=4) with GAPDH as a loading control. A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) Nrf2/GAPDH in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid), nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly enhance Nrf2 protein expression. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. #p<0.05 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|
Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the levels of HO-1 expression and P-PI3K/PI3K ratio in the cerebral cortex of the ischemia-reperfusion damage
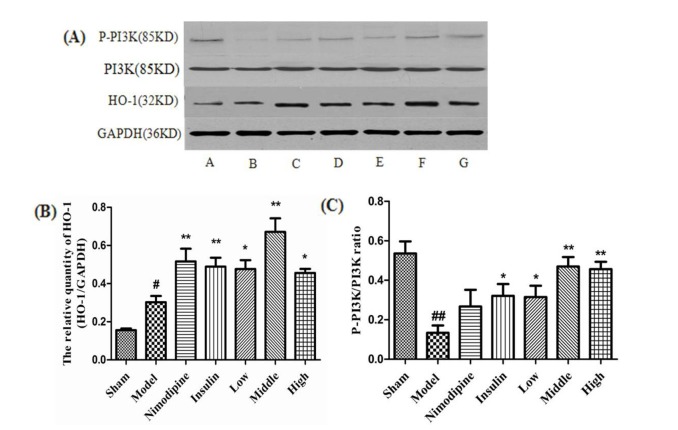 | Fig. 6Effect of rhGLP-1 on the levels of HO-1 expression and P-PI3K/PI3K ratio in the cerebral cortex of the ischemia-reperfusion damage.(A) Expressions of HO-1 and P-PI3K protein in MCAO/R rats in different groups (n=4) with GAPDH as a loading control. A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) HO-1/GAPDH in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid), nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly enhance HO-1 protein expression. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. #p<0.05 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group. (C) P-PI3K/PI3K ratio in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly enhance P-PI3K/PI3K ratio. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|
The effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the activities of SOD and the contents of MDA
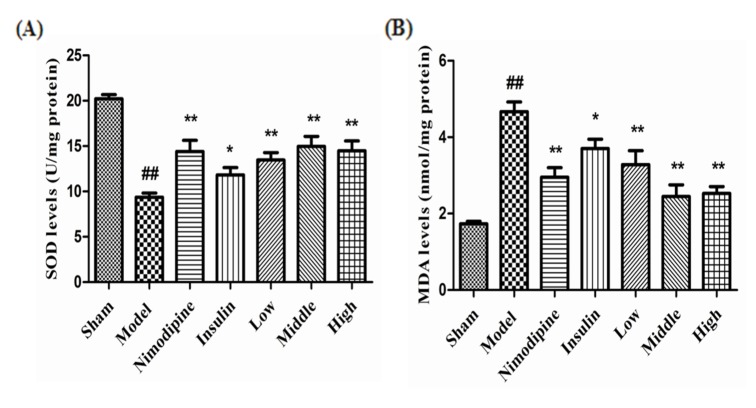 | Fig. 7The effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the activities of SOD and the contents of MDA.(A) SOD activities of MCAO/R rats in different groups. (B) MDA contents of MCAO/R rats in different groups. Columns represent the Mean±S. E.M (n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid), nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly improved the activities of SOD and decrease MDA contents. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group, *p<0.05; **p<0.01 vs. Model group.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download