1. Muoio DM, Newgard CB. Mechanisms of disease: molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 9:193–205. PMID:
18200017.
2. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(Suppl 1):S62–S69. PMID:
20042775.
3. Karlsson HK, Zierath JR. Insulin signaling and glucose transport in insulin resistant human skeletal muscle. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007; 48:103–113. PMID:
17709880.

4. DeFronzo RA, Tripathy D. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32(Suppl 2):S157–S163. PMID:
19875544.

5. Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and possible links with inflammation. Hypertension. 2005; 45:828–833. PMID:
15824195.

6. Ye J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front Med. 2013; 7:14–24. PMID:
23471659.

7. Vaag A, Henriksen JE, Beck-Nielsen H. Decreased insulin activation of glycogen synthase in skeletal muscles in young nonobese Caucasian first-degree relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992; 89:782–788. PMID:
1541672.

8. Huang S, Czech MP. The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab. 2007; 5:237–252. PMID:
17403369.

9. Petersen KF, Dufour S, Savage DB, Bilz S, Solomon G, Yonemitsu S, Cline GW, Befroy D, Zemany L, Kahn BB, Papademetris X, Rothman DL, Shulman GI. The role of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of the metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:12587–12594. PMID:
17640906.

10. Dresner A, Laurent D, Marcucci M, Griffin ME, Dufour S, Cline GW, Slezak LA, Andersen DK, Hundal RS, Rothman DL, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Effects of free fatty acids on glucose transport and IRS-1-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103:253–259. PMID:
9916137.

11. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory pathways and insulin action. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003; 27(Suppl 3):S53–S55. PMID:
14704746.

12. Storlien LH, Jenkins AB, Chisholm DJ, Pascoe WS, Khouri S, Kraegen EW. Influence of dietary fat composition on development of insulin resistance in rats. Relationship to muscle triglyceride and omega-3 fatty acids in muscle phospholipid. Diabetes. 1991; 40:280–289. PMID:
1991575.

13. Riccardi G, Giacco R, Rivellese AA. Dietary fat, insulin sensitivity and the metabolic syndrome. Clin Nutr. 2004; 23:447–456. PMID:
15297079.

14. Due A, Larsen TM, Hermansen K, Stender S, Holst JJ, Toubro S, Martinussen T, Astrup A. Comparison of the effects on insulin resistance and glucose tolerance of 6-mo high-monounsaturated-fat, low-fat, and control diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008; 87:855–862. PMID:
18400707.

15. Gillingham LG, Harris-Janz S, Jones PJ. Dietary monounsaturated fatty acids are protective against metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Lipids. 2011; 46:209–228. PMID:
21308420.

16. Paniagua JA, de la Sacristana AG, Sánchez E, Romero I, Vidal-Puig A, Berral FJ, Escribano A, Moyano MJ, Peréz-Martinez P, López-Miranda J, Pérez-Jiménez F. A MUFA-rich diet improves posprandial glucose, lipid and GLP-1 responses in insulin-resistant subjects. J Am Coll Nutr. 2007; 26:434–444. PMID:
17914131.

17. Shah M, Adams-Huet B, Brinkley L, Grundy SM, Garg A. Lipid, glycemic, and insulin responses to meals rich in saturated, cis-monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated (n-3 and n-6) fatty acids in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:2993–2998. PMID:
17804680.

18. Moon JH, Lee JY, Kang SB, Park JS, Lee BW, Kang ES, Ahn CW, Lee HC, Cha BS. Dietary monounsaturated fatty acids but not saturated fatty acids preserve the insulin signaling pathway via IRS-1/PI3K in rat skeletal muscle. Lipids. 2010; 45:1109–1116. PMID:
20960069.

19. Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Takemura S, Hatanaka A. Dietary saury oil reduces hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic KKAy mice and in diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice by altering gene expression. Lipids. 2011; 46:425–434. PMID:
21465306.

20. Keapai W, Apichai S, Pongchaidecha A, Amonlerdpison D, Lailerd N. Enhancing of skeletal glucose uptake by fish oil-derived MUFAs through glucose transporter 4 translocation in rat diaphragm. In : Proceeding of the International Graduate Research Conference; 2014 Dec 12; Chiang Mai, Thailand. p. HS7–HS12.
21. Cruz-Teno C, Pérez-Martínez P, Delgado-Lista J, Yubero-Serrano EM, García-Ríos A, Marín C, Gómez P, Jiménez-Gómez Y, Camargo A, Rodríguez-Cantalejo F, Malagón MM, Pérez-Jiménez F, Roche HM, López-Miranda J. Dietary fat modifies the postprandial inflammatory state in subjects with metabolic syndrome: the LIPGENE study. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012; 56:854–865. PMID:
22707261.

22. Martín-Peláez S, Covas MI, Fitó M, Kušar A, Pravst I. Health effects of olive oil polyphenols: recent advances and possibilities for the use of health claims. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013; 57:760–771. PMID:
23450515.

23. AOAC. Official method 996.06: fat (total, saturated, and
unsaturated) in foods. 18th ed. AOAC International;2005. p. 20–25. Ch4.
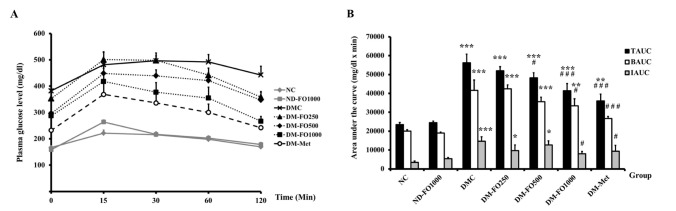
24. Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P. Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 2005; 52:313–320. PMID:
15979893.
25. Matthews JN, Altman DG, Campbell MJ, Royston P. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ. 1990; 300:230–235. PMID:
2106931.

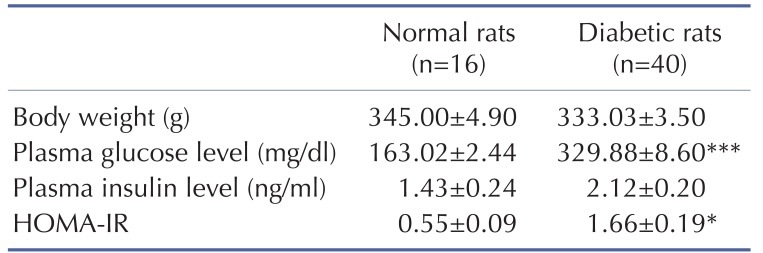
26. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419. PMID:
3899825.
27. Frayn KN, Maycock PF. Skeletal muscle triacylglycerol in the rat: methods for sampling and measurement, and studies of biological variability. J Lipid Res. 1980; 21:139–144. PMID:
7354251.

28. Mohammad A, Sharma V, McNeill JH. Vanadium increases GLUT4 in diabetic rat skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002; 233:139–143. PMID:
12083368.
29. Rhoads MG, Kandarian SC, Pacelli F, Doglietto GB, Bossola M. Expression of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins in skeletal muscle of gastric cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2010; 46:191–197. PMID:
19857958.
30. Musi N, Goodyear LJ. AMP-activated protein kinase and muscle glucose uptake. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003; 178:337–345. PMID:
12864738.

31. Hilder TL, Baer LA, Fuller PM, Fuller CA, Grindeland RE, Wade CE, Graves LM. Insulin-independent pathways mediating glucose uptake in hindlimb-suspended skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005; 99:2181–2188. PMID:
16099889.

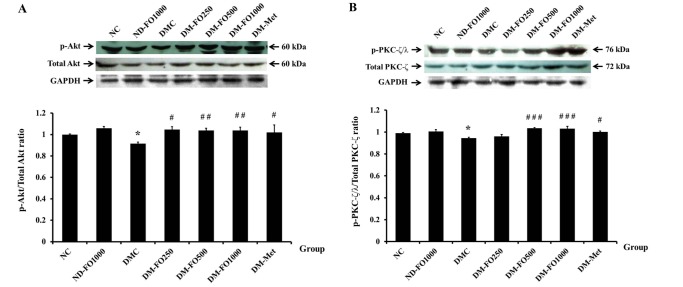
32. Itani SI, Ruderman NB, Schmieder F, Boden G. Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and IkappaB-alpha. Diabetes. 2002; 51:2005–2011. PMID:
12086926.
33. Jové M, Planavila A, Sánchez RM, Merlos M, Laguna JC, Vázquez-Carrera M. Palmitate induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells by a mechanism involving protein kinase C and nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Endocrinology. 2006; 147:552–561. PMID:
16223857.
34. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000; 20:1595–1599. PMID:
10845877.

35. Al-Shoumer KA, Al-Asousi AA, Doi SA, Vasanthy BA. Serum leptin and its relationship with metabolic variables in Arabs with type 2 diabetes mellitusd. Ann Saudi Me. 2008; 28:367–370.
36. Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008; 14:741–751. PMID:
19009016.

37. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, Eto K, Akanuma Y, Froguel P, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Carling D, Kimura S, Nagai R, Kahn BB, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 2002; 8:1288–1295. PMID:
12368907.

38. Shehzad A, Iqbal W, Shehzad O, Lee YS. Adiponectin: regulation of its production and its role in human diseases. Hormones (Athens). 2012; 11:8–20. PMID:
22450341.

39. Paz-Filho G, Mastronardi C, Wong ML, Licinio J. Leptin therapy, insulin sensitivity, and glucose homeostasis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16(Suppl 3):S549–S555. PMID:
23565489.

40. Yadav A, Kataria MA, Saini V, Yadav A. Role of leptin and adiponectin in insulin resistance. Clin Chim Acta. 2013; 417:80–84. PMID:
23266767.

41. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:1930–1935. PMID:
11344187.

42. Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Li C, Jiang H. Expression of ghrelin and leptin during the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Mol Med Rep. 2013; 7:223–228. PMID:
23129112.

43. Watson RT, Pessin JE. Intracellular organization of insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001; 56:175–193. PMID:
11237212.

44. Michelle Furtado L, Poon V, Klip A. GLUT4 activation: thoughts on possible mechanisms. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003; 178:287–296. PMID:
12864733.

45. Dimopoulos N, Watson M, Sakamoto K, Hundal HS. Differential effects of palmitate and palmitoleate on insulin action and glucose utilization in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells. Biochem J. 2006; 399:473–481. PMID:
16822230.

46. Tavaré JM, Fletcher LM, Oatey PB, Tyas L, Wakefield JG, Welsh GI. Lighting up insulin action. Diabet Med. 2001; 18:253–260. PMID:
11437854.

47. Nardi F, Lipina C, Magill D, Hage Hassan R, Hajduch E, Gray A, Hundal HS. Enhanced insulin sensitivity associated with provision of mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids in skeletal muscle cells involves counter modulation of PP2A. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92255. PMID:
24632852.

48. Coll T, Eyre E, Rodríguez-Calvo R, Palomer X, Sánchez RM, Merlos M, Laguna JC, Vázquez-Carrera M. Oleate reverses palmitateinduced insulin resistance and inflammation in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:11107–11116. PMID:
18281277.

49. Friedrichsen M, Mortensen B, Pehmøller C, Birk JB, Wojtaszewski JF. Exercise-induced AMPK activity in skeletal muscle: role in glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013; 366:204–214. PMID:
22796442.

50. Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001; 414:799–806. PMID:
11742412.

51. Hardie DG. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the metabolic syndrome and in heart disease. FEBS Lett. 2008; 582:81–89. PMID:
18022388.

52. Bolsoni-Lopes A, Festuccia WT, Chimin P, Farias TS, Torres-Leal FL, Cruz MM, Andrade PB, Hirabara SM, Lima FB, Alonso-Vale MI1. Palmitoleic acid (n-7) increases white adipocytes GLUT4 content and glucose uptake in association with AMPK activation. Lipids Health Dis. 2014; 13:199. PMID:
25528561.

53. Chavez JA, Summers SA. Characterizing the effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling and ceramide and diacylglycerol accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003; 419:101–109. PMID:
14592453.

54. Griffin ME, Marcucci MJ, Cline GW, Bell K, Barucci N, Lee D, Goodyear LJ, Kraegen EW, White MF, Shulman GI. Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade. Diabetes. 1999; 48:1270–1274. PMID:
10342815.

55. Yu C, Chen Y, Cline GW, Zhang D, Zong H, Wang Y, Bergeron R, Kim JK, Cushman SW, Cooney GJ, Atcheson B, White MF, Kraegen EW, Shulman GI. Mechanism by which fatty acids inhibit insulin activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in muscle. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:50230–50236. PMID:
12006582.

56. Kanety H, Feinstein R, Papa MZ, Hemi R, Karasik A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:23780–23784. PMID:
7559552.
57. Green CJ, Pedersen M, Pedersen BK, Scheele C. Elevated NF-κB activation is conserved in human myocytes cultured from obese type 2 diabetic patients and attenuated by AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2810–2819. PMID:
21911750.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


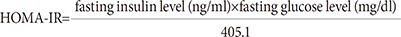
 XML Download
XML Download