INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Cell culture
Cell viability assay (MTS assay)
Caspase-3/7 activity assay
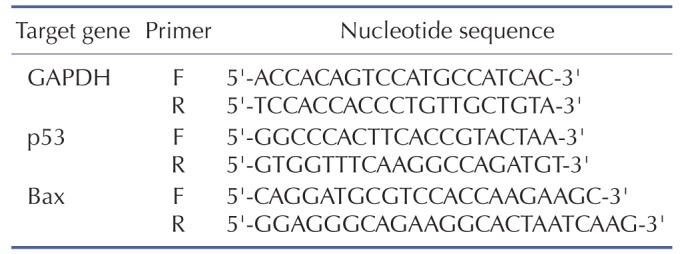
RNA isolation, reverse transcription (RT) and quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Preparation of cellular extracts and Western blot analysis
Transient transfection with small interfering RNA (siRNA)
Cell cycle analysis
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis
Preparation of Xenograft model
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Leptin increases expression of p53 in hepatic and breast cancer cells
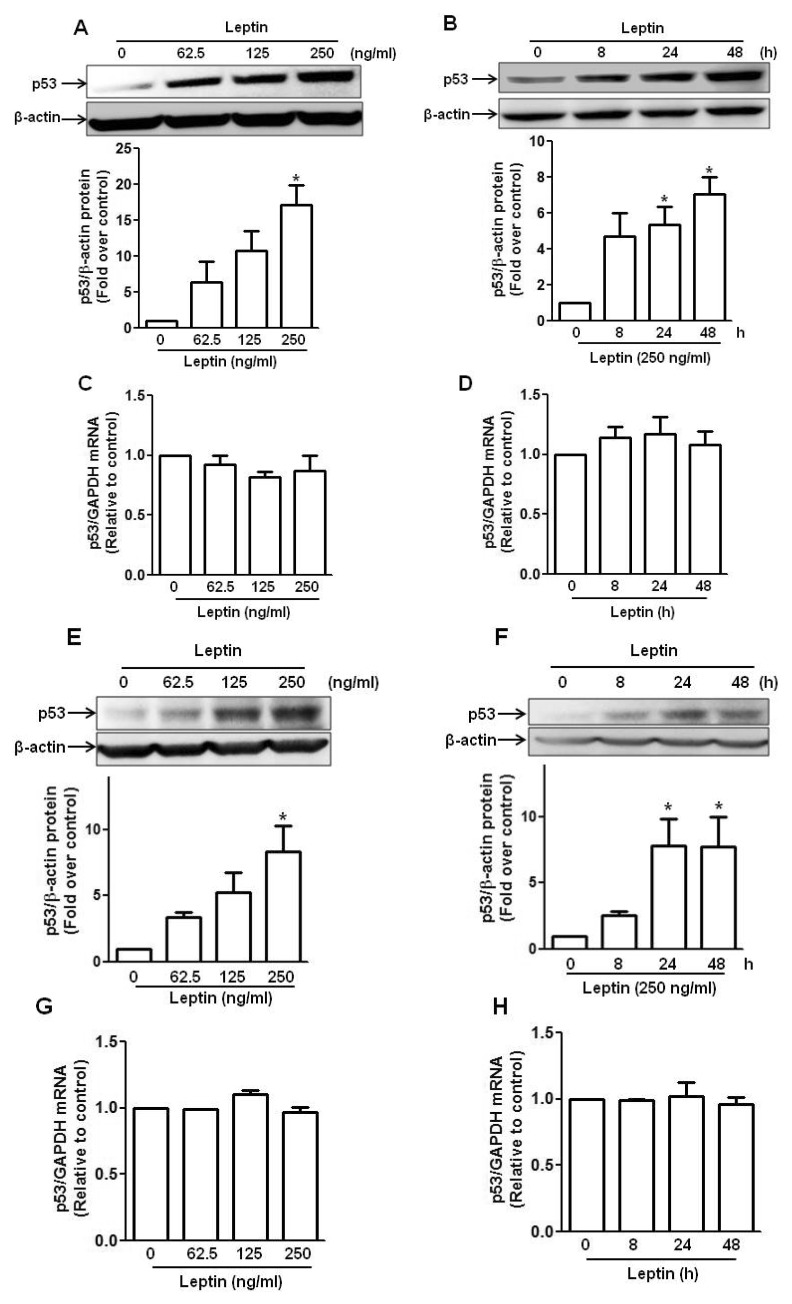 | Fig. 1Effect of leptin on the expression of p53 in hepatic and breast cancer cells.(A, B, C and D) HepG2 cells were treated with indicated concentration of leptin for 48 h (A and C) or 250 ng/ml of leptin for indicated time periods (B and D). (E, F, G and H) Similarly, MCF-7 cells were treated with indicated concentration of leptin for 48 h (E and G) or 250 ng/ml of leptin for indicated time periods (F and H). Protein expression level of p53 was determined by Western blot analysis as described in materials and methods (A, B, E and F). (Upper panel) Representative images of three independent experiments are shown along with β-actin as an internal loading control. (Lower panel) Quantitative analysis of p53 expression was performed by densitometric analysis and presented as mean±SEM (n=3). *p<0.05 compared with control group. (C, D, G and H) Messenger RNA level of p53 was determined by qRT-PCR analysis normalized to GAPDH. Data are expressed as mean±SEM of three to six independent experiments. *p<0.05 compared to the control group.
|
Leptin increases expression of p53 and USP2 in HepG2 tumor Xenograft model
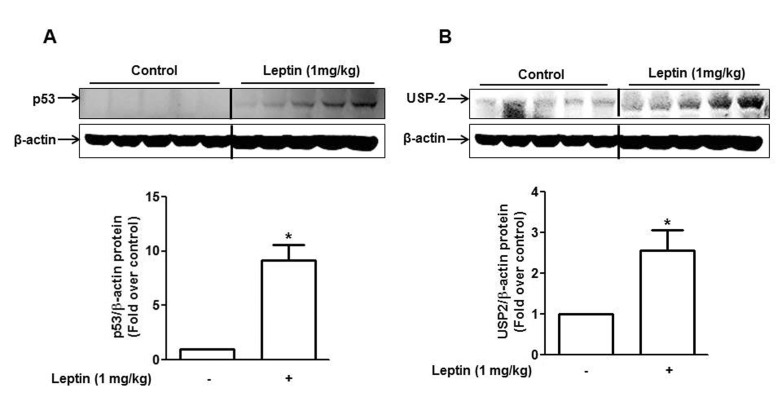 | Fig. 2Effect of leptin on the expression of p53 and USP2 in HepG2 Xenograft tumor model.BALB/c nude mice (4 weeks old male) were subcutaneously injected with HepG2 cells into the rear flanks. After two weeks of initial implantation, mice were randomly divided into two groups (control and leptin-treated group, n=5 per group). Leptin (1 mg/kg) was given intraperitoneally every 36 h for 4 weeks. p53 (A) and USP2 (B) protein expression were measured by Western blot analysis as described in materials and methods. Quantitative analysis of the p53 and USP2 expression was performed by densitometric analysis. Values are presented as mean±SEM (n=5). *p<0.05 compared to the mice not treated with leptin.
|
Leptin increases expression of p53 via suppression of ubiquitination in cancer cells
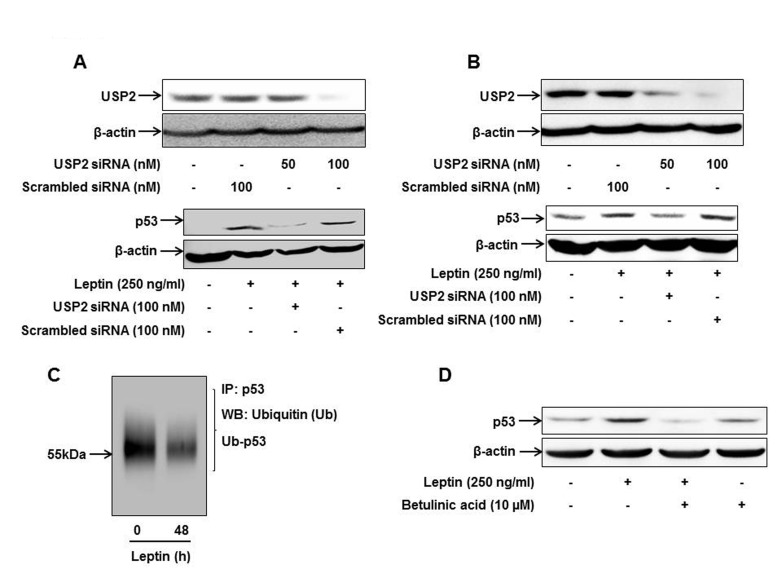 | Fig. 3Role of USP2 in leptin-induced p53 expression in cancer cells.HepG2 cells (A) and MCF-7 cells (B) were transfected with siRNA targeting USP2 or scrambled control siRNA followed by leptin treatment. (Upper panel) Transfection efficiency was determined after 48 h of transfection by Western blot analysis. (Lower panel) p53 protein expression was measured by Western blot analysis as described previously. (C) After treatment with leptin (250 ng/ml, 48 h), ubiquitinated p53 level was analyzed by immunoprecipitation using anti-p53 antibody and further immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin antibody as described in the materials and methods. (D) HepG2 cells were pretreated with betulinic acid; an activator of proteasome, for 2 h followed by treatment with leptin for additional 48 h. p53 expression level was determined by Western blot analysis. Images are representative of three independent experiments that showed similar results.
|
p53 signaling is involved in leptin-induced cancer cell growth
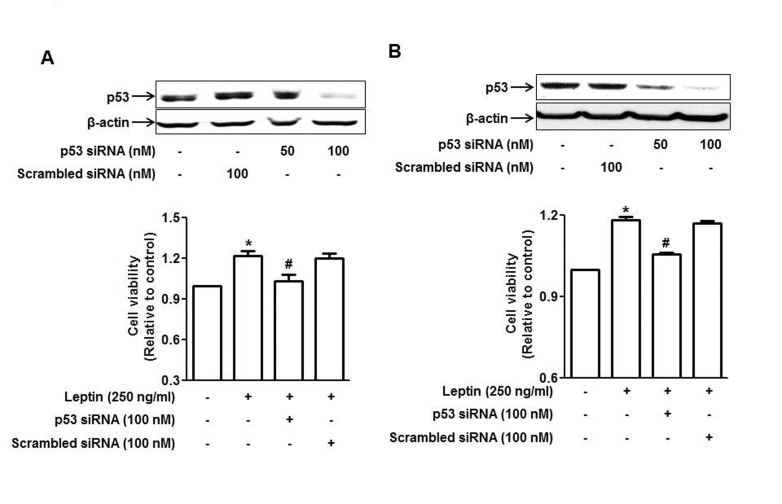 | Fig. 4Involvement of p53 signaling in leptin-induced growth of cancer cells.HepG2 cells (A) and MCF-7 cells (B) were transfected with siRNA targeting p53 or scrambled control siRNA followed by incubation with leptin for 48 h. (Upper panel) Transfection efficiency was determined after 48 h of transfection by Western blot analysis. (Lower panel) Cell viability was assessed by MTS assay as described in materials and methods. Values presented are the results of three independent experiments and are expressed as mean±SEM. *p<0.05 compared to the control group; #p<0.05 compared to the cells treated with leptin, but not transfected.
|
p53 signaling is involved in the suppression of apoptosis induced by leptin in HepG2 cells
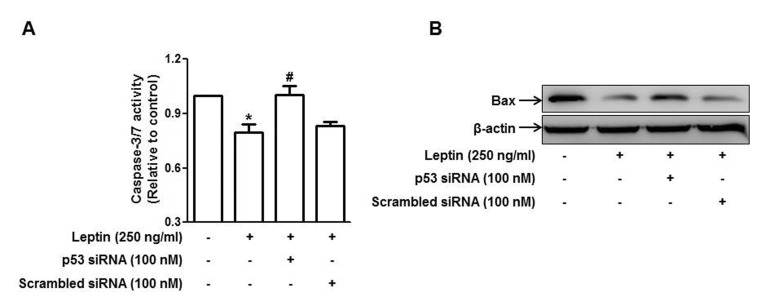 | Fig. 5Role of p53 signaling in leptin-induced suppression of apoptosis in HepG2 cells.Cells were transfected with siRNA targeting p53 or scrambled control siRNA followed by incubation with indicated concentration of leptin for 48 h. (A) Caspase-3/7 activity was assessed as described in materials and methods. Values are expressed as mean±SEM (n=3). *p<0.05 compared to the control group; #p<0.05 compared to the cells treated with leptin, but not transfected. (B) Bax protein expression was determined by Western blot analysis as described in materials and methods. Images are the representative of three independent experiments that showed similar results.
|
Cell cycle progression by leptin is mediated by p53 signaling in HepG2 cells
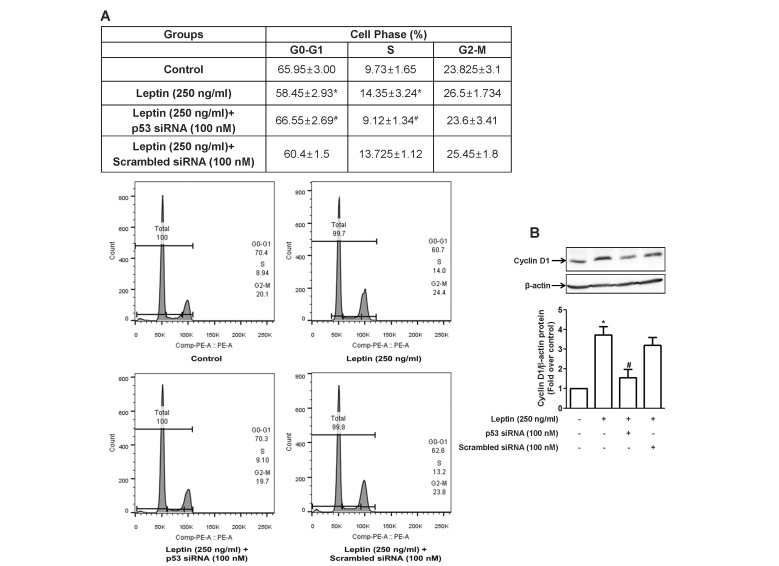 | Fig. 6Role of p53 signaling in leptin-induced cell cycle progression in HepG2 cells.Cells were transfected with siRNA targeting p53 or scrambled control siRNA followed by incubation with indicated concentration of leptin for 48 h. (A) Cell cycle was analyzed using flow cytometer as described in materials and methods. (Upper panel) Values are the percentage of the cells in each of the cell cycle phases and are expressed as mean±SEM (n=5). (Lower panel) Images are the representative image of the five independent experiments which showed similar results. (B) Cyclin D1 protein expression level was determined by Western blot analysis. (Upper panel) Representative images of three independent experiments are shown along with β-actin for internal loading control. (Lower panel) Quantitative analysis of p53 protein expression was performed by densitometric analysis and presented as mean±SEM (n=3). *p<0.05 compared to the control cells; #p<0.05 compared to the cells treated with leptin, but not transfected with siRNA.
|
p53 signaling is implicated in autophagy induction by leptin
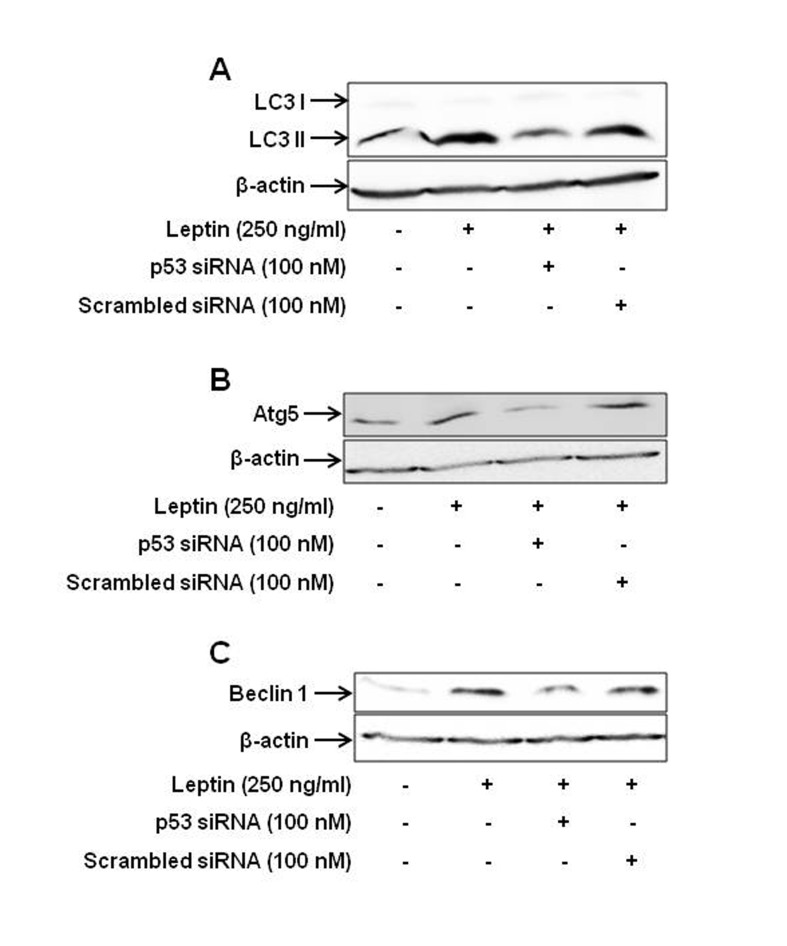 | Fig. 7Role of p53 signaling in leptin-induced increase in the expression of the genes related with autophagy.HepG2 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting p53 or scrambled control followed by incubation with leptin (250 ng/ml) for 48 h. Protein expression level of LC3 II (A), Atg5 (B) and Beclin-1 (C) was determined by Western blot analysis as indicated in the materials and methods. Images are the representative of three separate experiments that showed similar results.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download