Abstract
The aim of this study is to develop a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model in intra-abdominal infected rats, and extrapolate it to human to predict moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics profiles in various tissues in intra-abdominal infected human. 12 male rats with intra-abdominal infections, induced by Escherichia coli, received a single dose of 40 mg/kg body weight of moxifloxacin. Blood plasma was collected at 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 120, 240, 480, 1440 min after drug injection. A PBPK model was developed in rats and extrapolated to human using GastroPlus software. The predictions were assessed by comparing predictions and observations. In the plasma concentration versus time profile of moxifloxcinin rats, Cmax was 11.151 µg/mL at 5 min after the intravenous injection and t1/2 was 2.936 h. Plasma concentration and kinetics in human were predicted and compared with observed datas. Moxifloxacin penetrated and accumulated with high concentrations in redmarrow, lung, skin, heart, liver, kidney, spleen, muscle tissues in human with intra-abdominal infection. The predicted tissue to plasma concentration ratios in abdominal viscera were between 1.1 and 2.2. When rat plasma concentrations were known, extrapolation of a PBPK model was a method to predict drug pharmacokinetics and penetration in human. Moxifloxacin has a good penetration into liver, kidney, spleen, as well as other tissues in intra-abdominal infected human. Close monitoring are necessary when using moxifloxacin due to its high concentration distribution. This pathological model extrapolation may provide reference to the PK/PD study of antibacterial agents.
Go to : 
Moxifloxacin is an 8-methoxyquinolone with enhanced activity against Gram-positive pathogens and maintenance of activity against Gram-negative organisms. It is a broad-spectrum fluroquinolone used to treat a variety of infections, including complicated intra-abdominal infections (approved in the USA) [1]. It is mainly metabolized to the N-sulfate (metabolite M1) and the acylglucuronide (metabolite M2) [2].
Tissue distribution is an important component for understanding anti-infective efficacy, since target sites are commonly not located in the plasma [3]. Knowledge on pharmacokinetics in plasma alone, therefore, is often not sufficient to estimate if certain bacterial pathogens can be killed at the infected site. Previous researches have studied the pharmacokinetics and penetration of moxifloxacin under different pathological state [4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Only Stass [11] and Rink [12] have studied the pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in abdominal infection and reported that it has a good penetration into peritoneal exudates and abscess fluid in peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscess patients, respectively. However, data on drug penetration into various tissues inhuman is rare, especially in the patients with intra-abdominal infection.
The primary purpose of this investigation was to extrapolate a pathological rat model to human to predict moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution and to provide tissue concentration versus time profiles in human with intra-abdominal infection. The extrapolation was based on the Physiologically-based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model.
A PBPK model is a body composed of organ compartments, and each compartment contains mathematical descriptions of a chemical's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) [13]. Movement of a drug between the organ compartments, as well as the steadystate distribution of drug into each organ, can be defined by both the physicochemical parameters of the drug itself and the content of lipid, water and protein in each organ [3]. The difference lies in the PBPK models ability to substitute species-specific physiological and biochemical parameters into the model [13]. Therefore, moxifloxacin blood and tissue concentration predictions can be extrapolated from rats to humans by developing a PBPK model.
Go to : 
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride sodium chloride injection (BAY 12-8039; C21H24FN3O4·xHCL; 250 mL:0.4 g) was synthesized by Bayer HealthCare, Beijing, China.
Twelve healthy rats (breed SD), male, were included in the experiment, weighing 200~220 g. All the rats were obtained from the Laboratory Animal Center of Tianjin. The animals were housed under identical conditions (at room temperature), according to the requirements of the species. Standard particle feed and water were supplied.
Escherichia coli (E. coil, isolate 6857), used in our study, kindly supplied by Tianjin First Central Hospital. The organisms were stored at -65℃ before being subcultured on MH agar. Prior to use, the strains were grown, subcultured at 35℃ for 18 h and the fresh isolates were prepared as bacterial-liquid with sterile saline at the day of experiment.
Intra-abdominal infection model were induced by intraperitoneal injection of 10 ml/kg of E. coli bacteria liquid (2×109 CFU/ml) through left lower abdomen [14]. 2 h after bacteria liquid injection, the rats were clearly infected with the symptoms of erecting the fur and twisting the body. Then twelve rats were injected with a single dose of 40 mg/kg body weight of moxifloxacin through tail veins, which is equivalent to adult dose of 400 mg according to the conversion relation between human and rats. Blood samples were collected from the inter canthus at 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 120, 240, 480, 1440 min after drug treatment, respectively. The collection was performed in heparinized syringes. Plasma was obtained from centrifugation of blood samples. The separated plasma was stored at below -80℃ until further analysis. The study was performed in accordance with the "Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals" published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No. 8623, revised 1985), and was approved by the Experimental Animal Care and Use Committee of Tianjin Medical University.
The moxifloxacin concentrations were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultraviolet detection via a method validated in our laboratory. Plasma was mixed with ciprofloxacin solution (internal standard) and deproteinized with acetonitrile. The chromatography was done at room temperature on a reversed-phase Kromasil C18 column (150×4.6 mm, 5 µm) with an injection volume of 20 µL. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% (v/v) triethylamine, at PH 2.8 (adjusted with dilute phosphoric acid) and methanol (38:62 v/v) at a flow rate of 1 mL·min-1. Detection was performed at 296 nm using UV detector. Under these conditions, rentention times of moxifloxacin and the internal standard were 14.1 and 5.9 min, respectively. The bioanalytical method was validated according to the FDA guidelines (USDHHS, FKA, CDER, 2001). The linearity of the calibration curve was prepared with seven concentrations and determined using linear regression analysis. The lower-limit of quantification was 0.2 µg/mL. The method showed acceptable linearity with correlation coefficients, r2>0.9991, as well as high precision (RSD%<5%), recovery (93.3~115.8%), intra- and inter-day accuracy (RSD%<5.42%) and selectivity.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of moxifloxacin in rat plasma were calculated by non-compartmental method with WinNonlin software (Version 5.2.1, Pharsight Corporation, US).
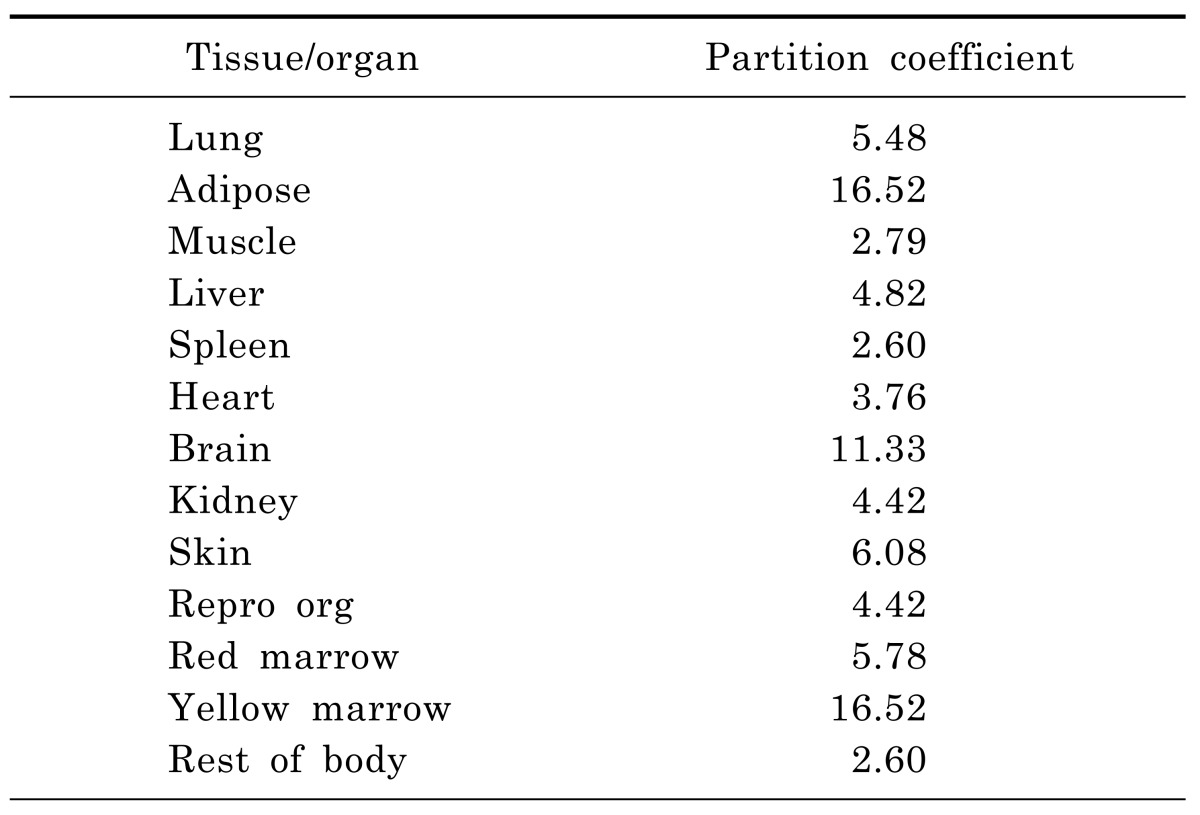
The PBPK model of moxifloxacin was built by GastroPlus version 8.0 (Simulations Plus, Inc, Lancaster, CA, USA). In summary, this model was composed of 14 tissue compartments, including the heart, lung, brain, adipose, muscle, skin, spleen, reproductive, gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidney, yellow marrow, red marrow and rest of the body. These compartments were linked together by venous and arterial blood circulation. All of the tissues were considered to be well-stirred compartments, and drug distribution into these compartments was driven by perfusion-limited kinetics. Each compartment was defined by an associated tissue blood flow rate, volume and a tissue-to-plasma partition coefficient (Kp). And the Kps (Table 1) were predicted using established tissue-composition based models [15,16,17] and they roughly followed the order shown in previous paper [3]. They depended on compound biopharmaceutical properties such as lipophilicity (log P), pKa, and fraction of free drug in plasma as well as the composition of lipids, water and proteins in each tissue compartment.
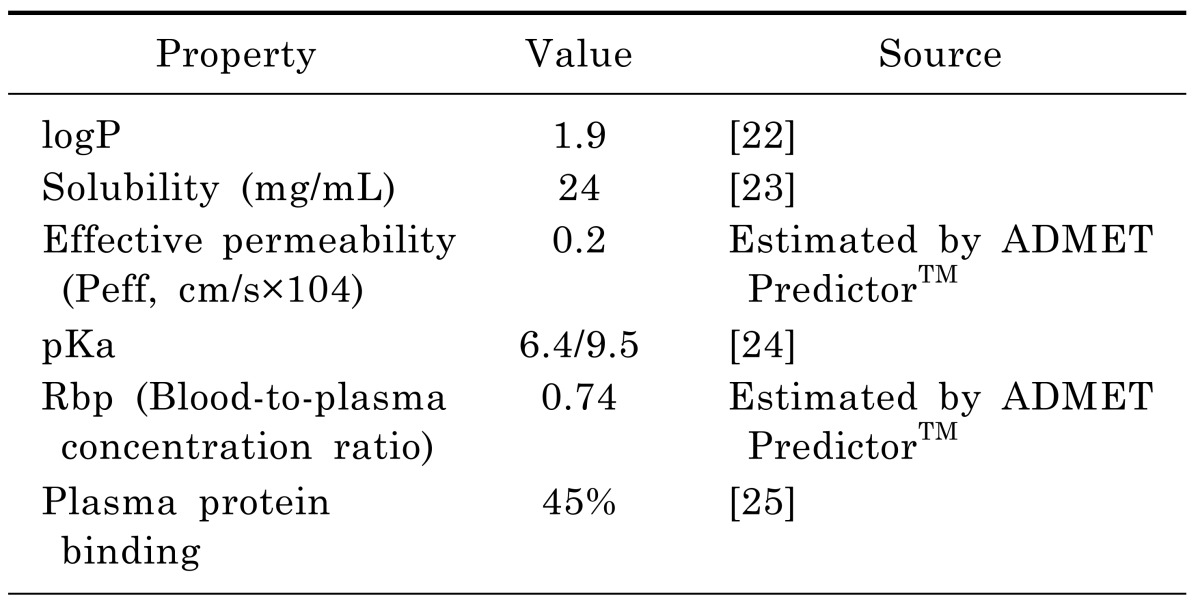
In the rat PBPK model, the physicochemical properties required as input information were depicted in Table 2. The logP, solubility, and pKa were obtained from the literatures. The effective permeability, plasma protein binding and blood-to-plasma concentration ratio were obtained using the ADMET Predictor™ module of GastroPlus, which has been consistently ranked as the most accurate predictive software in quantitative structure-pharmacokinetic relationship models (OSPKR models) of biopharmaceutical properties [18,19,20]. A PBPK model would be built in rats, plus the software defaulted rat physiologic parameters, the above physicochemical properties and moxifloxacin plasma concentration data in rats. And then human physiological and the metabolic parameters were substituted into the model. Km and Vmax values of moxifloxacin used in the human model were taken from Senggunprai et al. [21]. And then moxifloxacin concentrations in different tissues in man could be predicted based on the established model. Thus, the model would be extrapolated to human.
Experimental rat study was used to establish and validate the rat PBPK model. The same chemical specific and physiological parameters that used in the rat model were also employed in the human model. After the model extrapolated to human, the predicted plasma concentrations were validated by the data from an experimental human study, in which volunteers intravenously received a single of 400 mg moxifloxacin after complicated intra-abdominal infected [11]. The overall accuracy of the predicted pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed from the fold-error (difference between predicted and observed in vivo values), and the prediction was considered successful if the fold-error was less than two [26,27]. Validation of the predicted tissue concentrations (except plasma concentration) was problematic, due to the limited human data available and inconsistent units between prediction and observed data. But some tissue-to-plasma concentration ratios were available from the published literature. Thus, the model predictions in different tissues in human would be roughly validated by the ratios.
Go to : 
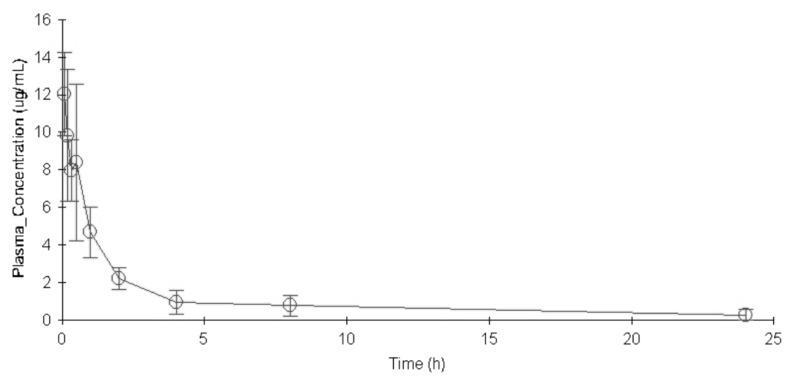
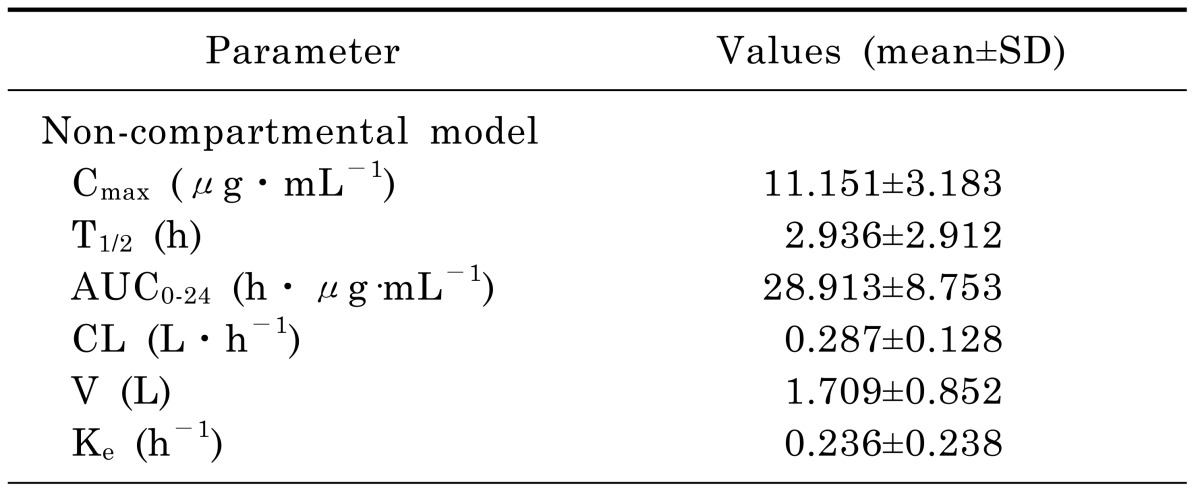
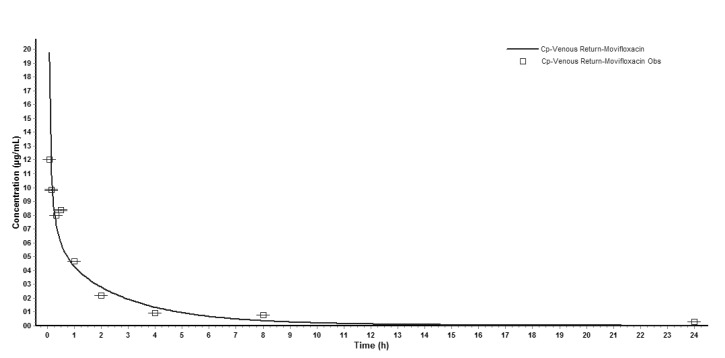
The concentration versus time profile of moxifloxacin (mean±SD) in rat plasma was shown in Fig. 1. The main PK parameters were summarized in Table 3. Plasma concentration of moxifloxacin at 5min after the intravenous injection of moxifloxacin was 11.151 µg/mL, and decreased progressively during the sampling period, reaching a geometric mean of 0.275 µg/mL at 24 h.
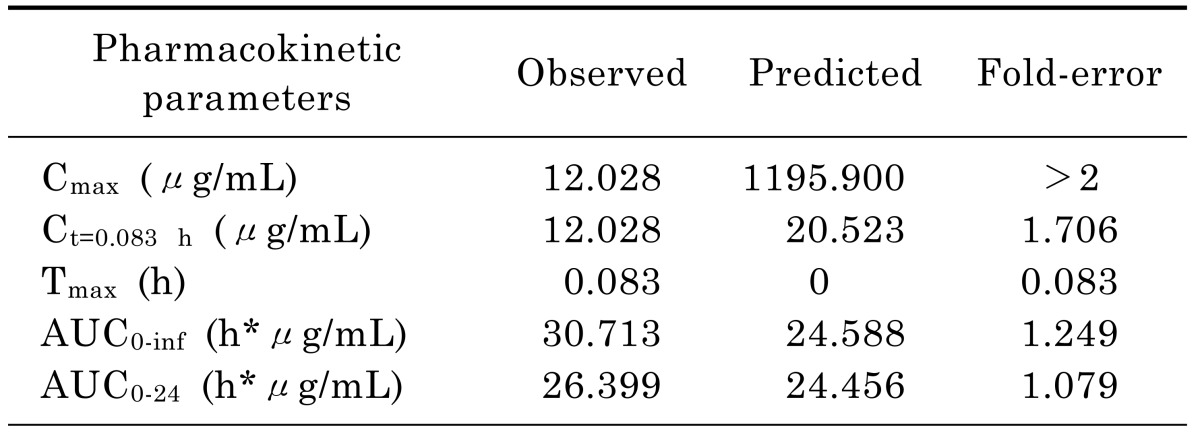
Input of moxifloxacin physicochemical parameters and plasma concentration data in rats into the WB-PBPK model produced a plasma concentration-time curve (Fig. 2). The predicted and observed pharmacokinetic parameters with prediction accuracy were summarized in Table 4. The simulated intravenous plasma concentration time profile of moxifloxacin by PBPK modeling corresponded well with the observed profile. Most of the predicted pharmacokinetic parameters were reasonably consistent (<2-fold error) with the observed values. Therefore, the PBPK model was established in rats.
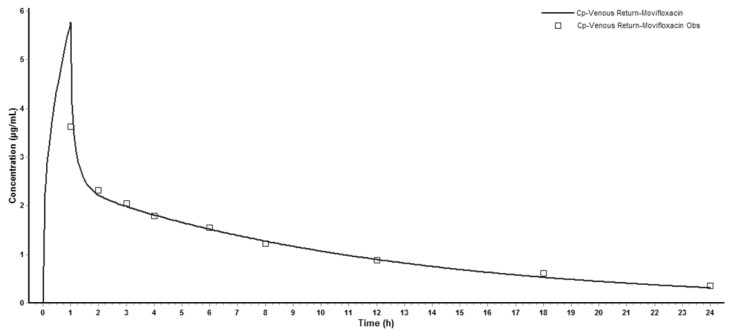
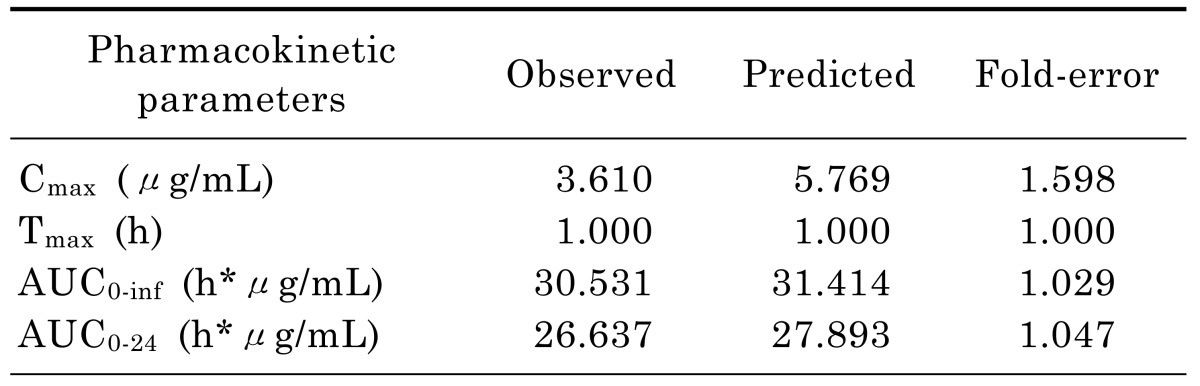
Successfully established PBPK model in rats was extrapolated to human and created a plasma concentration versus time profile (Fig. 3). The predicted plasma concentration data was validated by the data from paper of a single intravenous infusion of 400mg moxifloxacin in human with complicated intra-abdominal infections [11]. Fig. 3 showed that the simulated moxifloxacin concentration-time profile was qualitatively similar to the observed data, although the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was overestimated. All the fold-errors of the predicted and observed pharmacokinetic parameters were less than two (Table 5) which indicated that the human model extrapolated from rat was successful and the model was able to accurately simulate the plasma concentration-time profile.
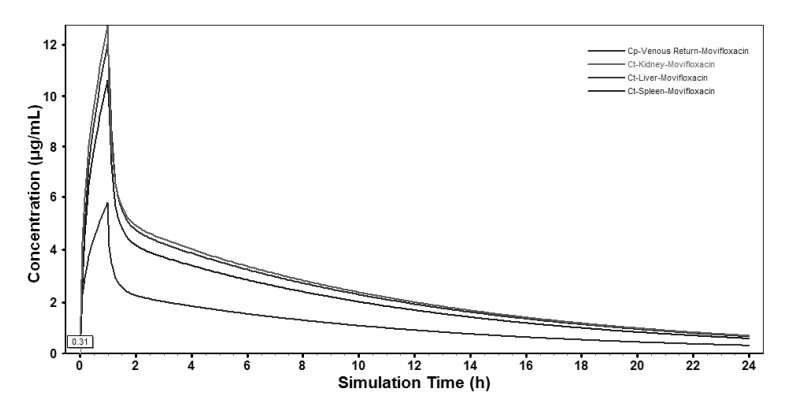
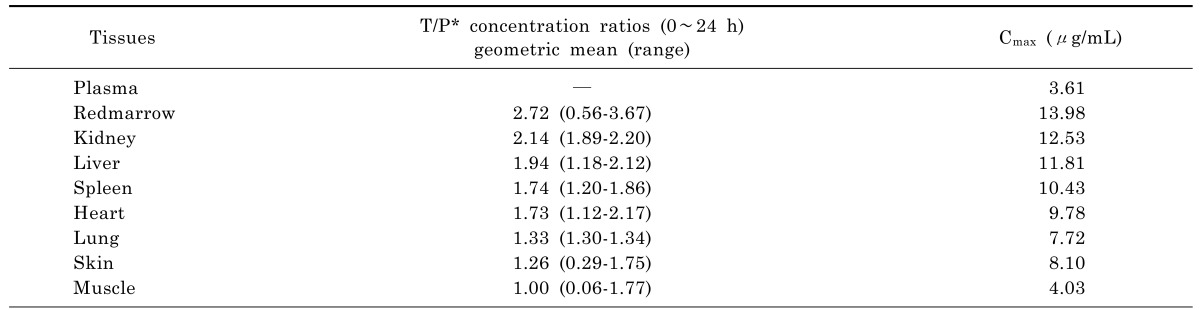
Based on the extrapolated PBPK model, moxifloxacin concentration-time profiles in various tissues were also simulated and the profiles in the main abdominal organs were showed in Fig. 4. The predicted moxifloxacin tissue-to-plasma concentration ratios and Cmax in main tissues were shown in Table 6.
Go to : 
The present study was the first attempt to predict moxifloxacin penetration into various tissues in human with intra-abdominal infections using a PBPK model, which was extrapolated from rat pathological model based on the plasma concentrations in rats and validated in both rats and human.
To assess whether an antimicrobial drug was likely to be of value in the therapy of infections in certain parts, it was important to determine the tissue concentrations of the agent, since drug concentrations in plasma do not reliably predict clinical efficacy [28]. Our research attempted to use model extrapolation method from rats to human to predict moxifloxacin tissue distribution in the model of intra-abdominal infection. Compared with classical pharmacokinetic models, there were several advantages offered by PBPK models including (1) the capacity to provide simultaneous time versus concentration curves for a compound in various tissues; (2) the incorporation of anatomical and physiologic information as well as chemical specific in vitro derived parameters; (3) the ability to predict the time versus concentration curve of chemicals across species by allometric scaling; (4) the resultant PBPK model has the potential for extrapolations from observed data to predicted situations [13].
In rat PBPK model, it was interesting to note that the predicted Cmax of moxifloxacin in rat plasma (1195.9 µg/mL) was much higher than that observed (12.028 µg/mL). Since there was no absorption phase when moxifloxacin was injected through the tail vein and rapidly distributed among the tissues. Maximum concentration in the plasma occurred as soon as moxifloxacin was intravenously injected.
Based on moxifloxacin physicochemical properties and low protein binding, it was expected that it would readily pass through membranes to exert its high antibacterial activity [29]. In our study, predictions for human tissues based on the PBPK model showed that the tissue/plasma concentration ratios were higher than 1.0 in most of the tissues (Table 6), indicating that moxifloxacin penetrated and accumulated well in the human body, which also validated the conclusion that moxifloxacin concentrations in most of the tissues were higher than that in blood [29,30]. It was reported that moxifloxacin could accumulate in uterine tissue, which located in abdomen, and the tissue to plasma ratios were between 1.7 and 2.1 [31]. That was close to the results of abdominal tissues in our study (1.7~2.2). The relatively short time period until reaching maximum concentrations in abdominal viscera (Fig. 4) indicated that relatively rapid drug penetration from plasma to soft tissues. Throughout 24 h simulation, the predicted concentration of moxifloacin in abdominal viscera exceeded the in vitro MICs of moxifloxacin for the pathogens commonly isolated in intra-abdominal infections, which have been reported as ≤1 µg/mL for a variety of Gram-negative and Gram-positive organisms [32]. In our study, moxifloxacin achieved high concentrations in abdominal viscera (liver 11.81 µg/mL; kidney 12.53 µg/mL; spleen 10.43 µg/mL), which indicated that it could play a good antibacterial activity in the abdominal cavity and that was in accordance with moxifloxacin clinical use in the treatment of intra-abdominal infection and was supported by the finding that moxifloxacin was effective in an in vitro pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model with mixed aerobic (E. coli) and anaerobic (B. fragilis) strains [33].
Our results that moxifloxacin penetrated and accumulated with high concentrations in lung, skin, heart, liver, kidney, spleen, redmarrow, muscle tissues was considered as one of the cause of its indications and adverse drug reactions (ADRs). Moxifloacin was expected to be useful as an anti-infective agent for respiratory tract, skin, soft tissues and intra-abdominal infections, including biliary tract and uterine infection [4,5,6,11,12,31], which was accordance with our results. Meanwhile, drug abuse could cause organ damage both in human and animal [34,35]. The risks of ADRs, which was related to the high concentrations and long-term use, should be monitored, such as QT interval prolongation, tachycardia, palpitation, toxic epidermal necrolysis, rash, digestive system injury, etc [36,37]. Moxifloxacin was metabolized in liver [2]. Although no adjustment of dosage was needed for the patients with liver dysfunction [9], drug monitoring would be required to assess possible liver side effects caused by the higher concentration of moxifloxacin in liver in those population. Moreover, the tissue concentrations-time profiles and parameters simulated by the PBPK model were of great value in the further study of moxifloxacin tissue pharmacodynamics.
In conclusion, when plasma concentrations in rats are known, extrapolation of a PBPK model from rats to human is a method to predict plasma and local tissue concentrations in human, which may lead to a better understanding of PK/PD relationship of antimicrobial agents. In this study, the results indicate that moxifloxacin widely distributed in redmarrow, heart, lung, skin, muscle, etc. The tissue to plasma concentration ratios are all higher than 1.0. Moreover, moxifloxacin is especially applicable to the patients with intra-abdominal infection because of its higher concentration in intra-abdominal tissues, including kidney, liver and spleen. At the same time, adverse drug reactions caused by high concentration of moxifloxacin in these tissues should be carefully monitored while using the agent.
Go to : 
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been supported by the Science and Technology Project (Project No. 13KG108) of the Public Health Bureau, Tianjin, China.
Go to : 
ABBREVIATIONS
PBPK
physiologically-based pharmacokinetic
HPLC
high-performance liquid chromatography
Kp
tissue-to-plasma partition coefficient
log P
lipophilicity
Go to : 
References
1. Singh R, Ledesma KR, Chang KT, Hou JG, Prince RA, Tam VH. Pharmacodynamics of moxifloxacin against a high inoculum of Escherichia coli in an in vitro infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:556–562. PMID: 19589810.
2. Kern A, Kanhai W, Frohde R, et al. BAY 12-8039, a new 8-methoxy-quinolone: metabolism in rat, monkey and man [abstract no. F23]. In : 36th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 1996 Sep 15-18; New Orleans, Louisiana. p. 103.
3. Edginton AN, Ahr G, Willmann S, Stass H. Defining the role of macrophages in local moxifloxacin tissue concentrations using biopsy data and whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009; 48:181–187. PMID: 19385711.

4. Yoshida K, Okimoto N, Kishimoto M, Fukano H, Hara H, Yoneyama H, Moriya O, Kawanishi M, Kimura M, Matsushima T, Niki Y. Efficacy and safety of moxifloxacin for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia based on pharmacokinetic analysis. J Infect Chemother. 2011; 17:678–685. PMID: 21847518.

5. Ober MC, Hoppe-Tichy T, Köninger J, Schunter O, Sonntag HG, Weigand MA, Encke J, Gutt C, Swoboda S. Tissue penetration of moxifloxacin into human gallbladder wall in patients with biliary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:1091–1095. PMID: 19734170.

6. Majcher-Peszynska J, Sass M, Schipper S, Czaika V, Gussmann A, Lobmann R, Mundkowski RG, Luebbert C, Kujath P, Ruf BR, Koch H, Schareck W, Klar E, Drewelow B. Moxifloxacin-DFI Study Group. Pharmacokinetics and penetration of moxifloxacin into infected diabetic foot tissue in a large diabetic patient cohort. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 67:135–142. PMID: 20871984.

7. Kees MG, Weber S, Kees F, Horbach T. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in plasma and tissue of morbidly obese patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:2330–2335. PMID: 21729931.

8. Stass H, Kubitza D, Halabi A, Delesen H. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin, a novel 8-methoxy-quinolone, in patients with renal dysfunction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53:232–237. PMID: 11874385.

9. Barth J, Jäger D, Mundkowski R, Drewelow B, Welte T, Burkhardt O. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of intravenous moxifloxacin in patients with severe hepatic impairment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 62:575–578. PMID: 18515790.

10. Pletz MW, Bloos F, Burkhardt O, Brunkhorst FM, Bode-Böger SM, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Greer MW, Stass H, Welte T. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:979–983. PMID: 20336279.

11. Stass H, Rink AD, Delesen H, Kubitza D, Vestweber KH. Pharmacokinetics and peritoneal penetration of moxifloxacin in peritonitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 58:693–696. PMID: 16895940.

12. Rink AD, Stass H, Delesen H, Kubitza D, Vestweber KH. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of moxifloxacin in intervention therapy for intra-abdominal abscess. Clin Drug Investig. 2008; 28:71–79.
13. Campbell A. Development of PBPK model of molinate and molinate sulfoxide in rats and humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009; 53:195–204. PMID: 19545510.

14. Wenli Y, Naiqiang C, Qiang F, Donghua L. Immune imbalance of rats with severe abdominal infection. Chin J Surg Integr Tradit West Med. 2011; 17:276–279.
15. Poirier A, Funk C, Scherrmann JM, Lavé T. Mechanistic modeling of hepatic transport from cells to whole body: application to napsagatran and fexofenadine. Mol Pharm. 2009; 6:1716–1733. PMID: 19739673.

16. Rodgers T, Leahy D, Rowland M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling 1: predicting the tissue distribution of moderate-to-strong bases. J Pharm Sci. 2005; 94:1259–1276. PMID: 15858854.

17. Rodgers T, Rowland M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling 2: predicting the tissue distribution of acids, very weak bases, neutrals and zwitterions. J Pharm Sci. 2006; 95:1238–1257. PMID: 16639716.

18. Mannhold R, Poda GI, Ostermann C, Tetko IV. Calculation of molecular lipophilicity: State-of-the-art and comparison of log P methods on more than 96,000 compounds. J Pharm Sci. 2009; 98:861–893. PMID: 18683876.
19. De Buck SS, Sinha VK, Fenu LA, Gilissen RA, Mackie CE, Nijsen MJ. The prediction of drug metabolism, tissue distribution, and bioavailability of 50 structurally diverse compounds in rat using mechanism-based absorption, distribution, and metabolism prediction tools. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007; 35:649–659. PMID: 17267621.

21. Senggunprai L, Yoshinari K, Yamazoe Y. Selective role of sulfotransferase 2A1 (SULT2A1) in the N-sulfoconjugation of quinolone drugs in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009; 37:1711–1717. PMID: 19420132.
22. Lemaire S, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. Contrasting effects of acidic pH on the extracellular and intracellular activities of the anti-gram-positive fluoroquinolones moxifloxacin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:649–658. PMID: 21135179.
23. Beyer R, Pestova E, Millichap JJ, Stosor V, Noskin GA, Peterson LR. A convenient assay for estimating the possible involvement of efflux of fluoroquinolones by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for diminished moxifloxacin, sparfloxacin, and trovafloxacin efflux. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000; 44:798–801. PMID: 10681364.
24. MacGowan AP. Moxifloxacin (Bay 12-8039): a new methoxy quinolone antibacterial. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1999; 8:181–199.

25. Wise R. A review of the clinical pharmacology of moxifloxacin, a new 8-methoxyquinolone, and its potential relation to therapeutic efficacy. Clin Drug Investig. 1999; 17:365–387.
26. Li GF, Wang K, Chen R, Zhao HR, Yang J, Zheng QS. Simulation of the pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol in healthy adults and patients with impaired renal function using whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012; 33:1359–1371. PMID: 23085739.

27. Jones HM, Parrott N, Jorga K, Lavé T. A novel strategy for physiologically based predictions of human pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006; 45:511–542. PMID: 16640456.

28. Eichler HG, Müller M. Drug distribution. The forgotten relative in clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998; 34:95–99. PMID: 9515183.
29. Siefert HM, Kohlsdorfer C, Steinke W, Witt A. Pharmacokinetics of the 8-methoxyquinolone, moxifloxacin: tissue distribution in male rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999; 43(Suppl B):61–67. PMID: 10382877.
30. Stass H. Distribution and Tissue Penetration of Moxifloxacin. Drugs. 1999; 58(2):Suppl. 229–230.

31. Stass H, Kubitza D, Aydeniz B, Wallwiener D, Halabi A, Gleiter C. Penetration and accumulation of moxifloxacin in uterine tissue. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008; 102:132–136. PMID: 18501909.

32. Edmiston CE, Krepel CJ, Seabrook GR, Somberg LR, Nakeeb A, Cambria RA, Towne JB. In vitro activities of moxifloxacin against 900 aerobic and anaerobic surgical isolates from patients with intra-abdominal and diabetic foot infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1012–1016. PMID: 14982797.
33. Schaumann R, Goldstein EJ, Forberg J, Rodloff AC. Activity of moxifloxacin against Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia coli in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model employing pure and mixed cultures. J Med Microbiol. 2005; 54:749–753. PMID: 16014428.
34. Singh VP, Singh N, Jaggi AS. A review on renal toxicity profile of common abusive drugs. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013; 17:347–357. PMID: 23946695.

35. Randhawa PK, Singh K, Singh N, Jaggi AS. A review on chemical-induced inflammatory bowel disease models in rodents. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014; 18:279–288. PMID: 25177159.

36. Watson KJ, Gorczyca WP, Umland J, Zhang Y, Chen X, Sun SZ, Fermini B, Holbrook M, Van Der Graaf PH. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the effect of Moxifloxacin on QTc prolongation in telemetered cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2011; 63:304–313. PMID: 21419854.

37. Moxifloxacin. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2008; 88:127–131. PMID: 18486050.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download