ABBREVIATIONS
IBD
UC
ROM
TNBS
TNF-α
MDA
MPO
NO
GSH
EIE
QGC
EIQ
CMC-Na
5-AS
HETAB
BSA
TBARS
TCA
GST
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Animals
Induction of colitis and treatments
Assessment of colitis
Assessment of leukocyte involvement
Assessment of nitric oxide production
Assessment of total GSH levels
TBARS assay
Protein determination
Data analysis
RESULTS
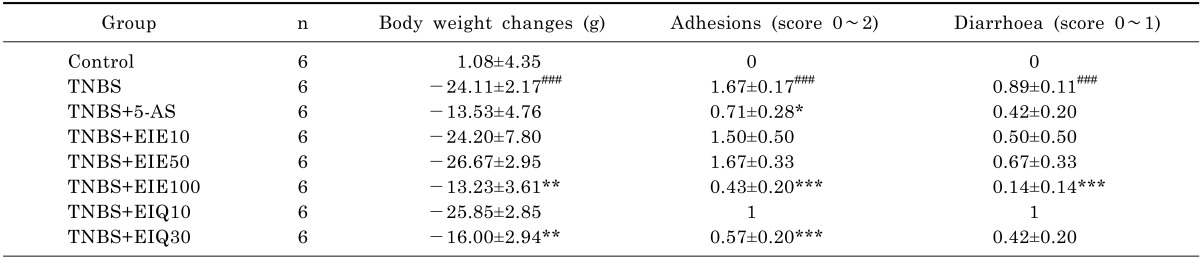
Therapeutic efficacy of EIE and EIQ in and experimental TNBS-induced colitis model
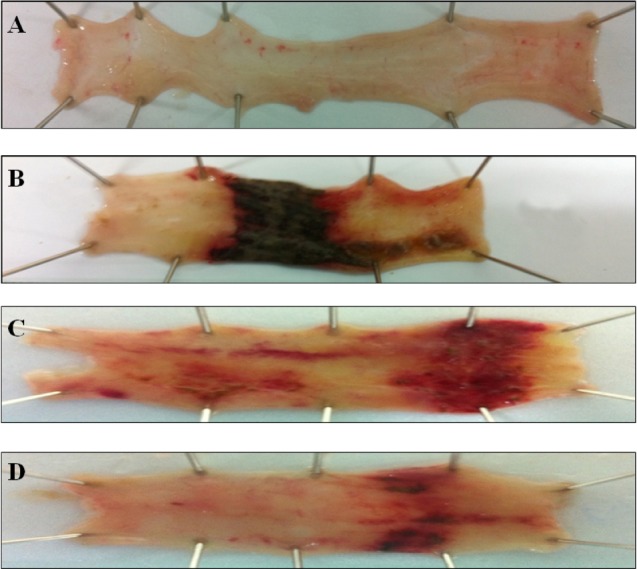 | Fig. 2Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on colonic injury in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. The image show representative colonic tissues from the in normal control group (A), TNBS and no treatment group (B), TNBS and EIE 100 mg/kg group (C), and TNBS and EIQ 30 mg/kg (D). TNBS lesions are characterized by focal ulceration, and treatment with the flavonoid glycosides EIE and EIQ reduced the severity of the lesions. |
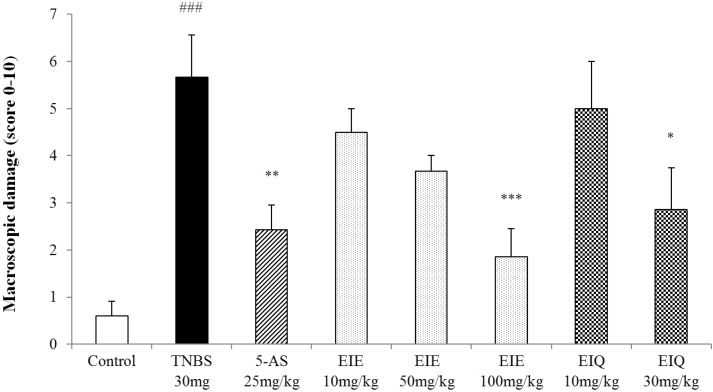 | Fig. 3Effect of acute administration of EIE, and EIQ on macroscopic colon damage in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. Macroscopic damage to the colon resulting from TNBS was scored on a scale of 0 to 10. EIE and EIQ dose-dependently diminished the macroscopic scores. The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
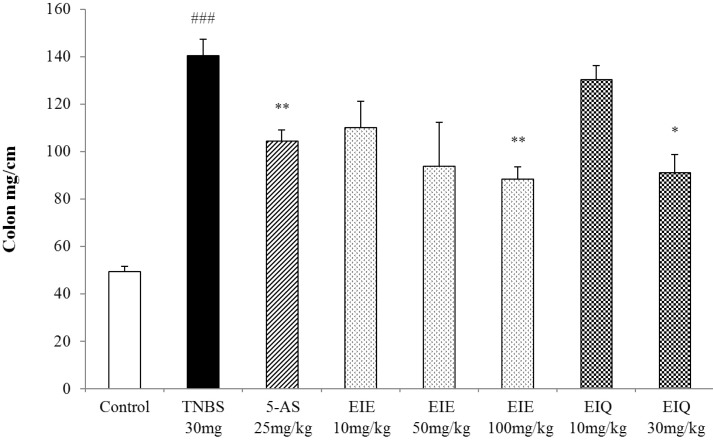 | Fig. 4Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on the colon weight to length ratio in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. Colon weight to length ratios were dose-dependently decreased by administration of EIE and EIQ. The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and *p<0.05 and ***p<0.01 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
The effects of EIE and EIQ on MPO activity in TNBS-induced colitis
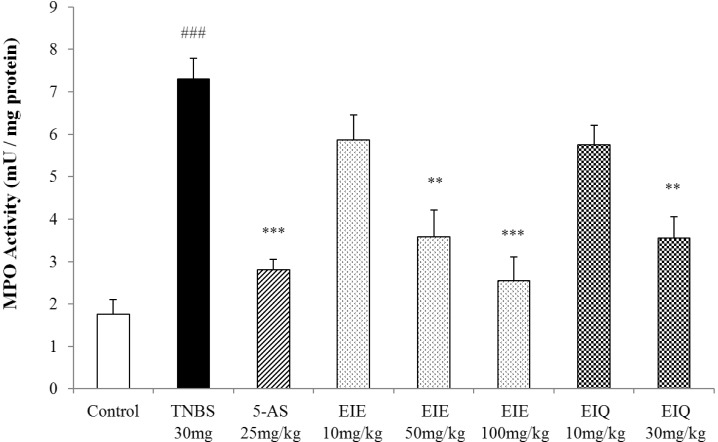 | Fig. 5Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on MPO activity in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. MPO activity was significantly increased by TNBS instillation compared with control group. However, MPO activity was significantly decreased by EIE (50 and 100 mg/kg) and EIQ (30 mg/kg). The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
The effects of EIE and EIQ on nitric oxide expression in TNBS-induced colitis
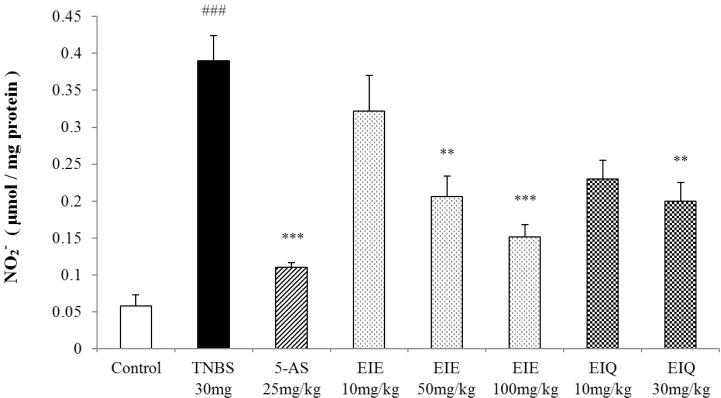 | Fig. 6Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on NO production with TNBS-induced colitis. After TNBS instillation, nitrite production was significantly increased compared with the control group. However, NO production was significantly decreased with EIE (50 and 100 mg/kg) or EIQ (30 mg/kg). The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
The effects of EIE and EIQ on colonic TNF-α expression in TNBS-induced colitis
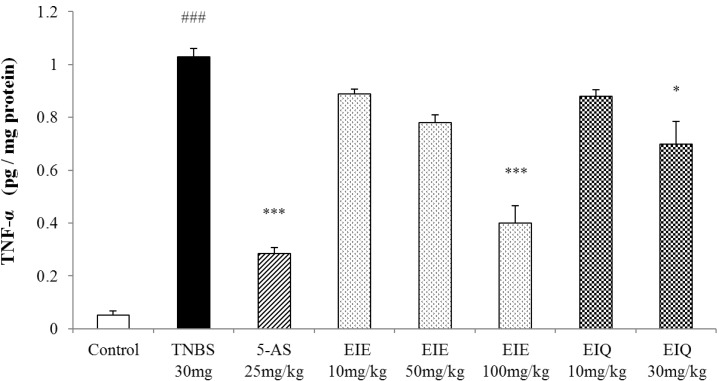 | Fig. 7Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on TNF-α expression in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. After TNBS instillation, TNF-α expression was significantly increased compared with the control group. However, TNF-α expression was significantly decreased by EIE (100 mg/kg) and EIQ (30 mg/kg). The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
The effect of EIE and EIQ on total GSH levels in TNBS-induced colitis
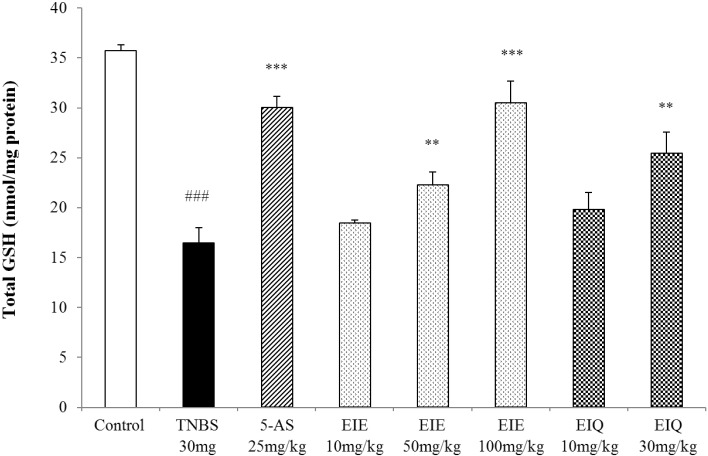 | Fig. 8Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on GSH levels in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. After TNBS instillation, total GSH levels were significantly decreased compared with the control group. However, GSH levels were significantly increased by administration of EIE (50 and 100 mg/kg) and EIQ (30 mg/kg). The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and **p<001 and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |
The effects of EIE and EIQ on MDA levels in TNBS-induced colitis
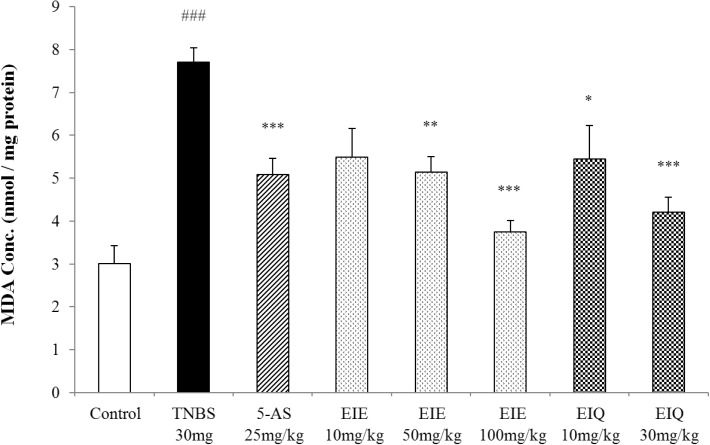 | Fig. 9Effect of EIE and EIQ administration on MDA levels in rats with TNBS-induced acute colitis. After TNBS instillation, MDA levels were significantly increased compared with control group. However, MDA was significantly decreased by administration of EIE (50 and 100 mg/kg) and EIQ (10 and 30 mg/kg). The data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. ###p<0.001 vs. the control group and *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 vs. the TNBS alone group. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download