ABBREVIATIONS
HO-1
HUVECs
SnPP
Nrf2
ARE
OX1R
OX2R
VEGF
bFGF
EBM-2
EGM-2
ARE
SOD1
HIF-1α
mTOR
eIF-4E
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Reagents
Cell culture
RNA isolation and real-time PCR analysis
Western blot analysis
HO-1 activity
In vivo Matrigel plug assay
Aortic ring assay
Tube formation assay
Chemotactic migration assay
Transient transfection and reporter gene analysis
RNA interference
RESULTS
Orexin-A induces HO-1 expression and activity in human vascular endothelial cells
Fig. 1
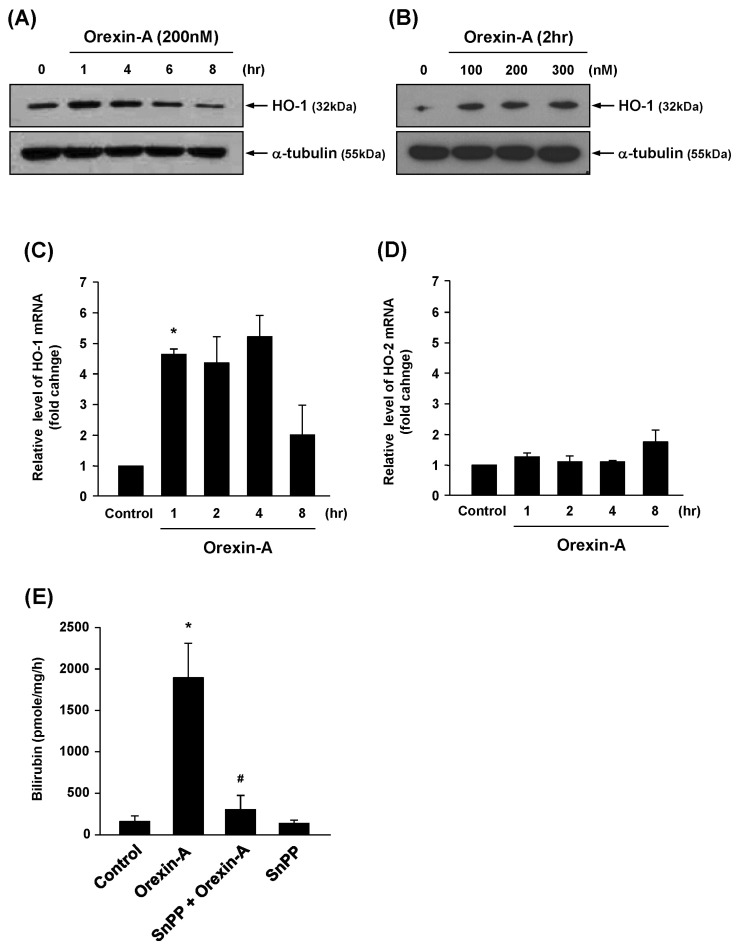
Upregulation of HO-1 expression and activity by orexin-A in vascular endothelial cells. (A and B) HUVECs were treated with orexin-A (200 nM) or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for the various times and concentrations shown. Expression of HO-1 was determined by western blot using HO-1 and α-tubulin antibodies (loading control). (C and D) Cells were incubated with orexin-A (200 nM) or PBS for the indicated times. Expression of HO-1 and HO-2 mRNA was analyzed by real-time PCR. These data represent the mean±SE of three experiments. *p<0.05 vs. control. (E) HUVECs were pretreated with SnPP (50 µM) for 15 min, followed by treatment with orexin-A for 4 hr. HO-1 enzyme activity was measured as described in the Materials and Methods. Three independent experiments were performed. *p<0.05 vs. control; #p<0.05 vs. orexin-A alone.
HO-1 plays a role in orexin-A-induced angiogenesis in vivo
Fig. 2
Involvement of HO-1 in orexin-A-induced angiogenesis in vivo. (A) Matrigel was treated with orexin-A (200 nM) or PBS in the presence or absence of SnPP (20 µM), and then subcutaneously injected into mice. After 7 days, the plugs were obtained from each mouse and photographed. (B) The level of vessel formation was quantified by measuring hemoglobin content. Each value represents the mean of at least three animals. *p<0.05 vs. control; #p<0.05 vs. orexin-A alone. (C) Matrigel plugs were stained using H&E and photographed. (D) Endothelial cells recruited into Matrigel plugs were immunostained with PECAM-1 antibody and observed using fluorescence microscopy.

HO-1 activation regulates the angiogenic activity of orexin-A in vascular endothelial cells
Fig. 3
Effect of HO-1 inhibition on orexin-A-stimulated angiogenesis ex vivo and in vitro. (A) Rat aortic rings were embedded in Matrigel and cultured with orexin-A (200 nM) for 4 days in the presence or absence of SnPP (20 µM). The sprouted microvessels from aortic rings were photographed under a microscope (left). The newly formed sprouts of endothelial cells were counted (right). (B) HUVECs were seeded on growth factor-reduced Matrigel in the presence or absence of SnPP (20 µM) and treated with orexin-A (200 nM) for 4 hr. Cells were observed under a phase contrast microscope and the number of tube areas was counted. (C) HUVECs were seeded on gelatin-coated filters of transwell chambers. Cells were incubated with orexin-A (200 nM) and SnPP (20 µM) for 4 hr. The filter containing migrated cells was stained with H&E and photographed. The number of migrated cells was counted. All results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. *p<0.05 vs. control; #p<0.05 vs. orexin-A alone.

Orexin-A-induced expression of HO-1 and angiogenic activity is associated with activation of Nrf2
Fig. 4
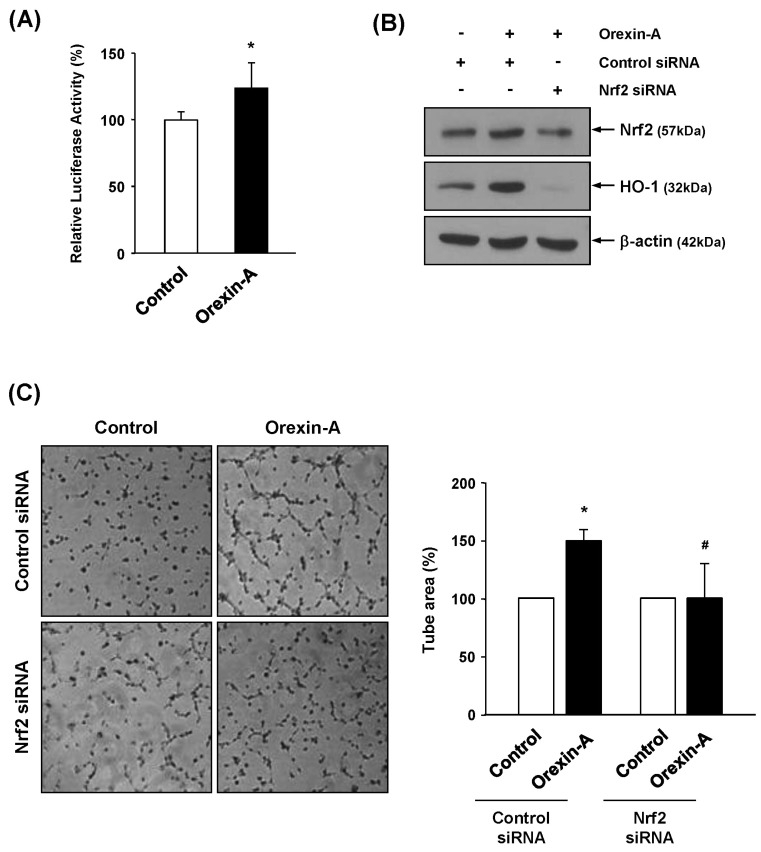
Influence of the ARE-Nrf2 pathway in orexin-A-mediated HO-1 induction and angiogenesis. (A) HMECs transfected with an ARE-luciferase construct were treated with orexin-A (200 nM) for 3 hr. The cell extracts were prepared and analyzed using a luminometer. Three independent experiments were performed. *p<0.05 vs. control. (B) HUVECs were transiently transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA (1 µM) by Amaxa nucleofector, followed by treatment with orexin-A for 2 hr. The expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 was determined by Western blot analysis. (C) For tube formation assays, Nrf2 siRNA-transfected cells were seeded on growth factor-reduced Matrigel. Cells were incubated with orexin-A (200 nM) for 4 hr. Newly formed tubes were photographed, and tube areas were quantified from at least three individual experiments. *p<0.05 vs. control; #p<0.05 vs. control siRNA with orexin-A.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download