INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Experimental animals
Oral and intrathecal (i.t.) injection
Drugs
Measurement of blood glucose level
Treatment of drugs
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effect of hitamine receptor agonists and antagonists on the blood glucose level
 | Fig. 1Effect of 2-pyridylethylamine or cetirizine administered i.t. on the blood glucose level. Mice were intrathecally (i.t.) administered with 2-pyridylethylamine (from 0.1 to 1 µg) (A) or cetirizine (from 0.05 to 0.5 µg) (B). The 16 h fasted mice were pretreated i.t. with 2-pyridylethylamine (C) or cetirizine (D) for 10 min and then, D-glucose (2 g/kg body weight) administered orally once. The blood glucose level was measured at 30, 60 and 120 min after i.t. or oral administration. The blood was collected from tail-vein. The vertical bars indicate the standard error of mean. Each quantified result was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc test (C and D: **p<0.01, ***p<0.005; compared to D-Glucose+Saline group). The number of animals used for each group was 8~10. |
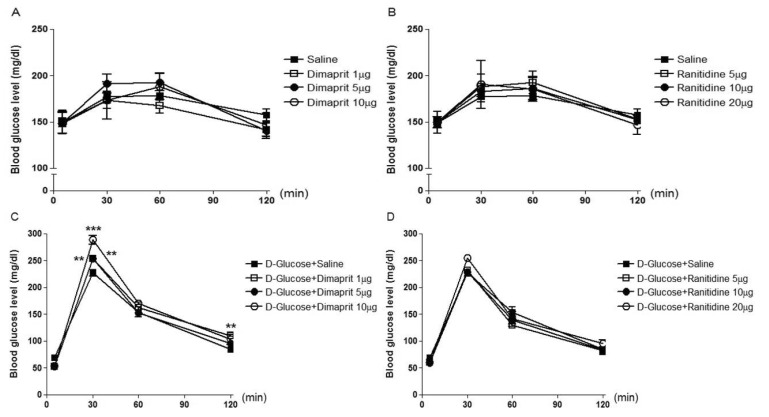 | Fig. 2Effect of dimaprit or ranitidine administered i.t. on the blood glucose level. Mice were intrathecally (i.t.) administered with dimaprit (from 1 to 10 µg) (A) or ranitidine (from 5 to 20 µg) (B). The 16 h fasted mice were pretreated i.t. with dimaprit (C) or ranitidine (D) for 10 min and then, D-glucose (2 g/kg body weight) administered orally once. The blood glucose level was measured at 30, 60 and 120 min after i.t. or oral administration. The blood was collected from tail-vein. The vertical bars indicate the standard error of mean. Each quantified result was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc test (C: **p<0.01, ***p<0.005; compared to D-Glucose+Saline group). The number of animals used for each group was 8~10. |
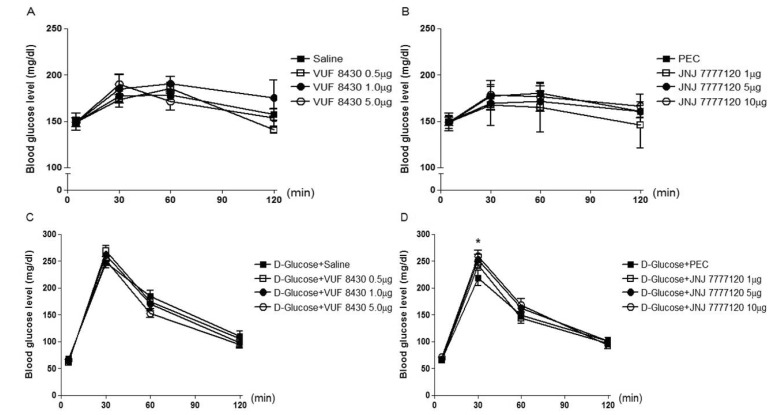 | Fig. 4Effect of VUF 8430 or JNJ 7777120 administered i.t. on the blood glucose level. Mice were intrathecally (i.t.) administered with VUF 8430 (from 0.5 to 5 µg) (A) or JNJ 7777120 (from 1 to 10 µg) (B). The 16 h fasted mice were pretreated i.t. with VUF 8430 (C) or JNJ 7777120 (D) for 10 min and then, D-glucose (2 g/kg body weight) administered orally once. The blood glucose level was measured at 30, 60 and 120 min after i.t. or oral administration. The blood was collected from tail-vein. The vertical bars indicate the standard error of mean. Each quantified result was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc test (D: *p<0.05; compared to D-Glucose +PEC group). The number of animals used for each group was 8~10. |
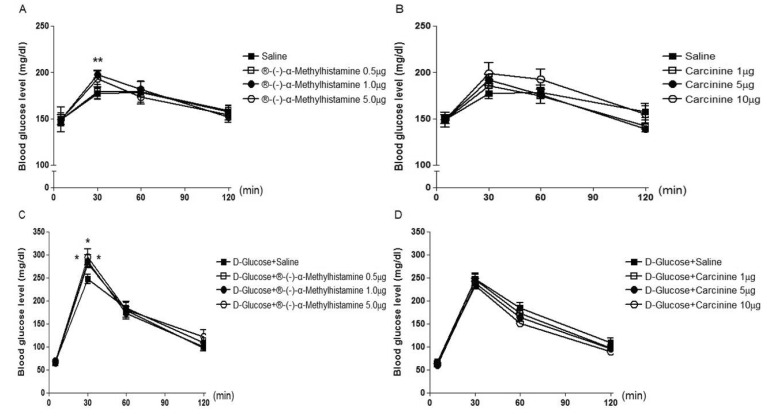 | Fig. 3Effect of α-methylhistamine or carcinine administered i.t. on the blood glucose level. Mice were intrathecally (i.t.) administered with α-methylhistamine (0.5 to 5 µg) (A) or carcinine (from 1 to 10 µg) (B). The 16 h fasted mice were pretreated i.t. with α-methylhistamine (C) or carcinine (D) for 10 min and then, D-glucose (2 g/kg body weight) administered orally once. The blood glucose level was measured at 30, 60 and 120 min after i.t. or oral administration. The blood was collected from tail-vein. The vertical bars indicate the standard error of mean. Each quantified result was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc test (A: **p<0.01; compared to saline group, C and D: *p<0.05; compared to D-Glucose+Saline group). The number of animals used for each group was 8~10. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download