INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Cell culture and viability assay
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme assay
Measurements of mineralization and calcium content
Western blot
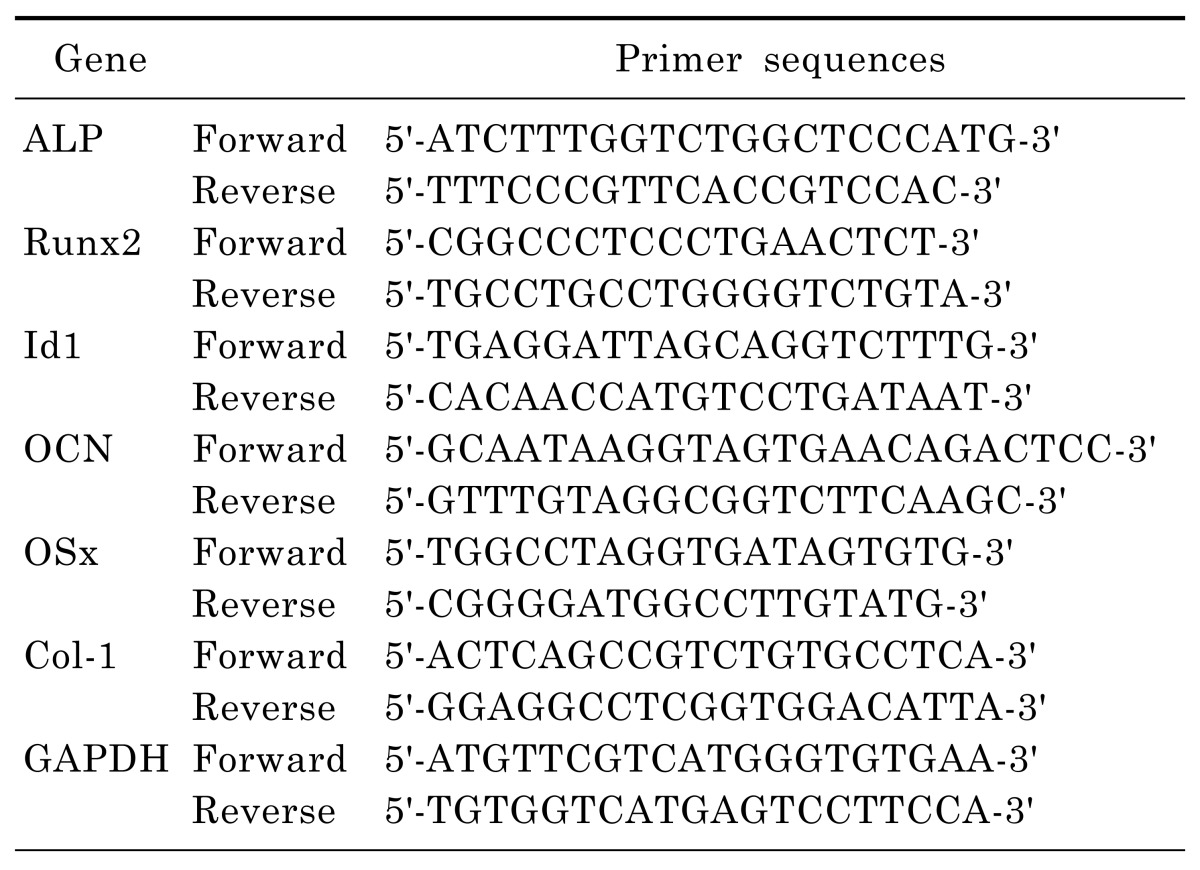
RNA extraction and real-time PCR
Transient transfection and luciferase reporter assay
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Nectandrin A enhances the BMP-2 induced osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization
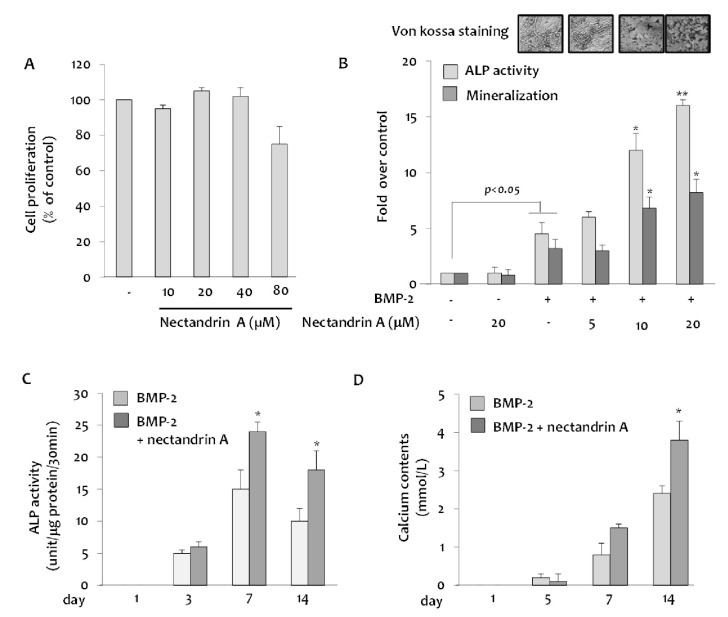 | Fig. 1Effects of nectandrin A on BMP-2-inudced osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in C2C12 cells. (A) Cells were cultured in a 96-well plate for 24 h and then the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 5% FBS and rhBMP-2 (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of nectandrin A (differentiation day 0). Cell viability assay was then performed on the differentiation day 3. Medium was changed every third day. (B) ALP enzyme activity and Alizarin Red staining were performed on the differentiation day 7 and 14, respectively. (C, D) ALP activity and calcium contents were measured at different time points after the induction of C2C12 differentiation in the presence or absence of nectandrin A. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared to rhBMP-2 treated group. |
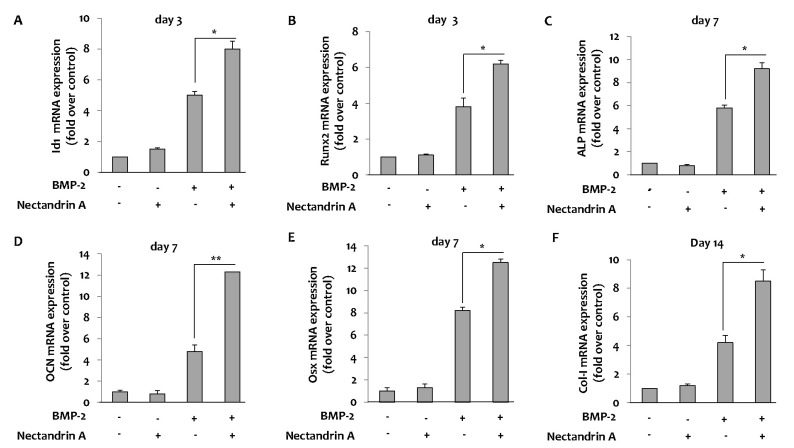 | Fig. 2Effects of nectandrin A on BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation markers and transcription factors. C2C12 cells were cultured in a 6-well plate for 1 day and then the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 5% FBS and rhBMP-2 (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of nectandrin A (differentiation day 0). Medium was changed every third day. Total RNA was prepared and mRNA expression levels of Id1, Runx2, ALP, OCN, Osx and Col-I were analyzed by real-time PCR. The mRNA expression levels of Id1 (A) and Runx2 (B) were analyzed on day 3 and mRNA expression levels of ALP (C), OCN (D) and Osx (E) were analyzed on day 7. mRNA expression level of Col-I was analyzed on day 14 (F). Each value represents the mean±SEM of three independent experiments. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared to rhBMP-2 treated group. |
Nectandrin A enhances the BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation via p38 MAPK-Smad signaling pathway
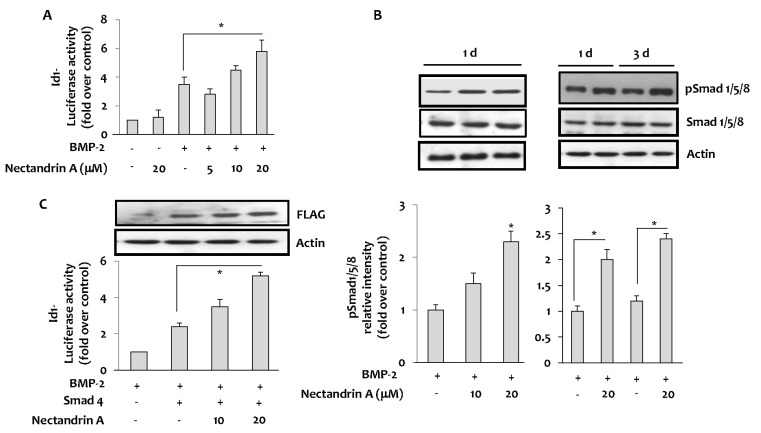 | Fig. 3Effects of nectandrin A on Id1 and Smad activation. (A) Id1 activation was measured by luciferase reporter assay using Id1-promoter-driven luciferase plasmid (Id1-Luc)-transfected C2C12 cells. Cells was cultured in a 6-well plate for 1 day and then incubated with DMEM containing 5% FBS in the presence or absence of rhBMP-2 with/without nectandrin A for 1 day. (B) The effect of nectandrin A on the activation of Smad was evaluated by Western blot analysis. Cells were cultured in a 6-well plate for 1 day and then incubated with DMEM containing 5% FBS in the presence or absence of rhBMP-2 (100 ng/ml) with/without nectandrin A for indicated time periods. (C) Cells were transfected with pCMV-Smad4-Flag with or without Id1-Luc reporter and then cells were incubated with DMEM containing 5% FBS and 100 ng/ml rhBMP-2 in the presence or absence of nectandrin A for 4 h. *p<0.05 compared to rhBMP-2 treated group. |
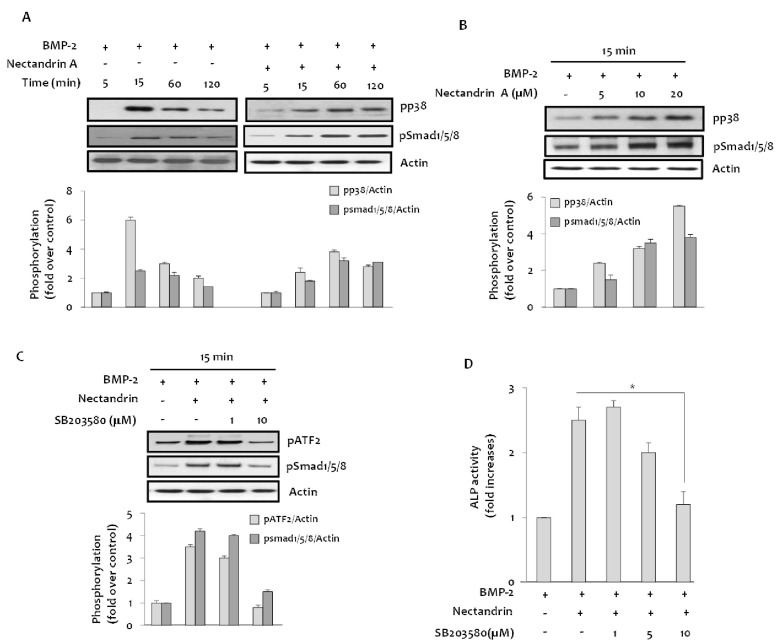 | Fig. 4Involvement of p38 MAPK in the nectandrin A-enhanced osteoblastic differentiation. (A) Cells were cultured in a 6-well plate for 1 day and then incubated with DMEM containing 5% FBS in the presence or absence of BMP-2 and/or nectandrin A for up to 120 min. (B) Phosphorylated levels of p38 and Smad1/5/8 were determined after C2C12 cells were treated with nectantrin A as indicated in the presence of BMP-2. (C) Cells in a 6-well plate were treated with indicated concentrations of SB203580 for 1 h, followed by 15 min treatment with 100 ng/ml rhBMP-2 with/without 20 µM nectandrin A. (D) On differentiation day 6, ALP enzyme activity was determined as described in 'Methods'. *p<0.05 compared to rhBMP-2 plus nectandrin A treated group. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download