INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Animals
Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate
Blood and tissue sampling
Nitric oxide (NO) assay
Malondialdehyde (MDA) assay
Glutathione (GSH) assay
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Changes in body weight
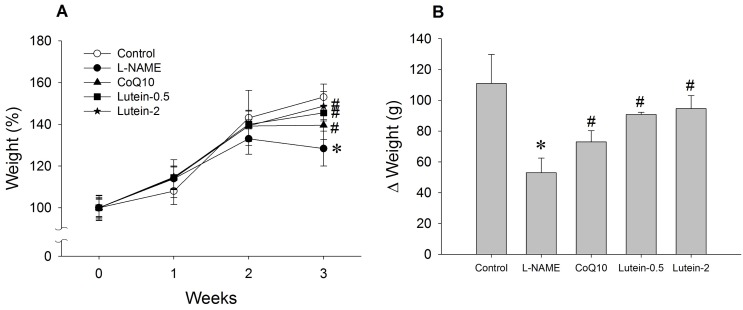 | Fig. 1Effect of lutein on the body weight in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. (A) Weight (%), weight/initial weight. (B) Δ Weight (g), body weight on third week minus body weight on initial week. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
Effect of lutein on blood pressure in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats
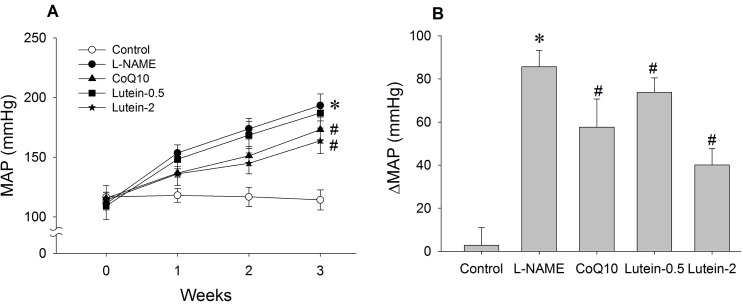 | Fig. 2Effect of lutein on mean arterial pressure (MAP) in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. (A) Time-course effect of lutein on MAP over 3 weeks. (B) Change in MAP from initial to final week. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
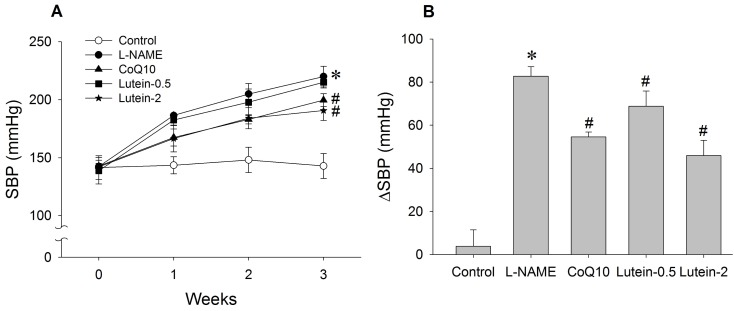 | Fig. 3Effect of lutein on systolic blood pressure (SBP) in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. (A) Time-course effect of lutein on SBP for 3 weeks. (B) Change in SBP from initial week to final week. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
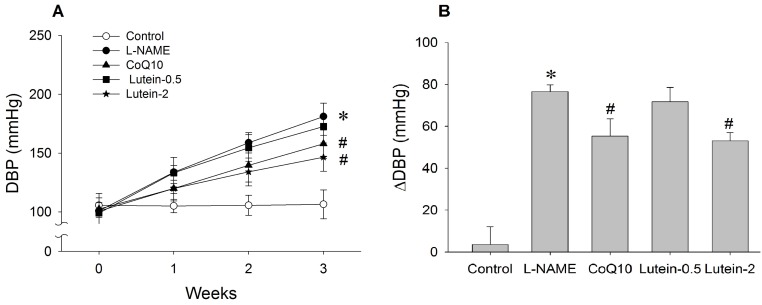 | Fig. 4Effect of lutein on diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. (A) Time-course effect of lutein on DBP for 3 weeks. (B) Change in DBP from initial week to final week. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
Effect of lutein on heart rate
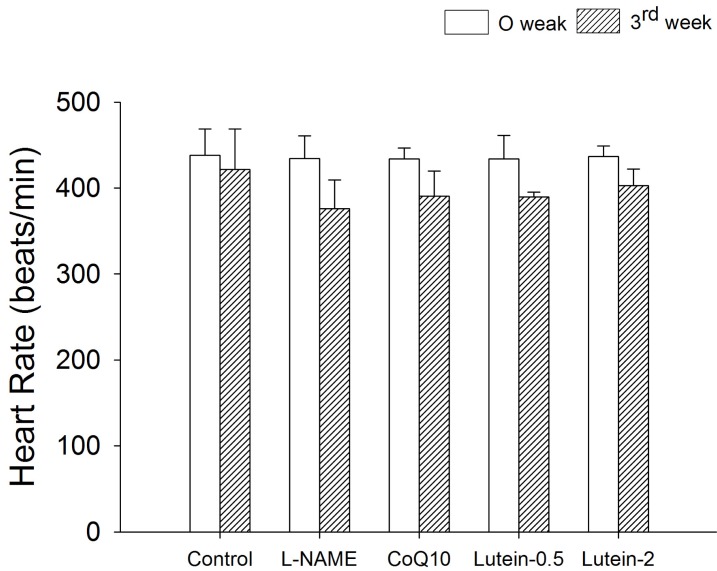 | Fig. 5Effect of lutein on heart rate in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. 0 week in the same group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME group at 3rd week. |
Effect of lutein on the organ weight
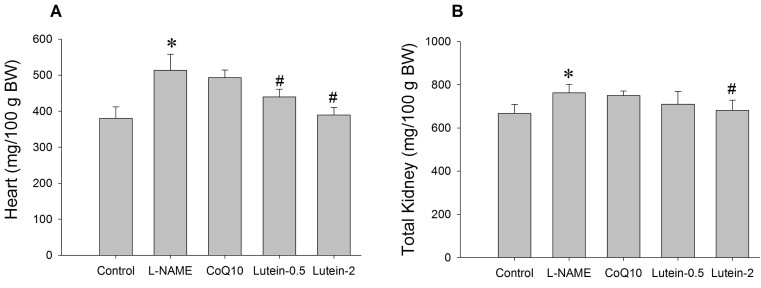 | Fig. 6Effect of lutein on the cardiac (A) and renal (B) hypertrophy in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
Effect of lutein on NO, lipid peroxidation, and GSH levels in plasma
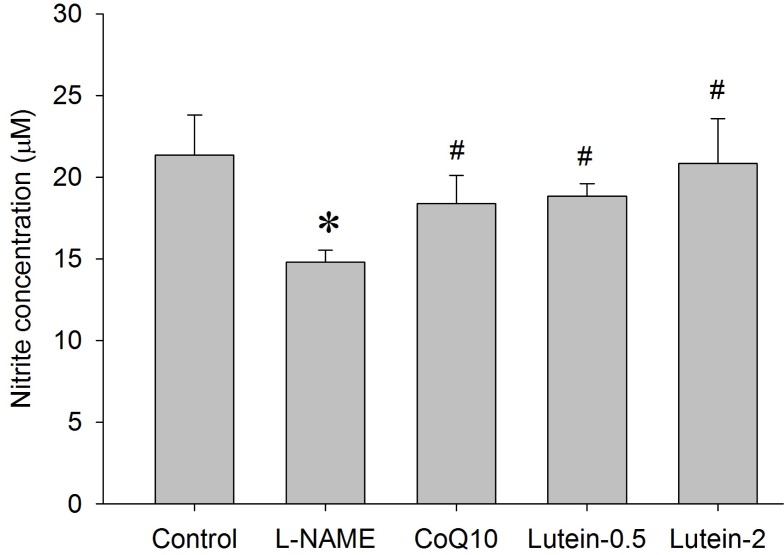 | Fig. 7Effects of lutein on plasma nitrite concentration in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
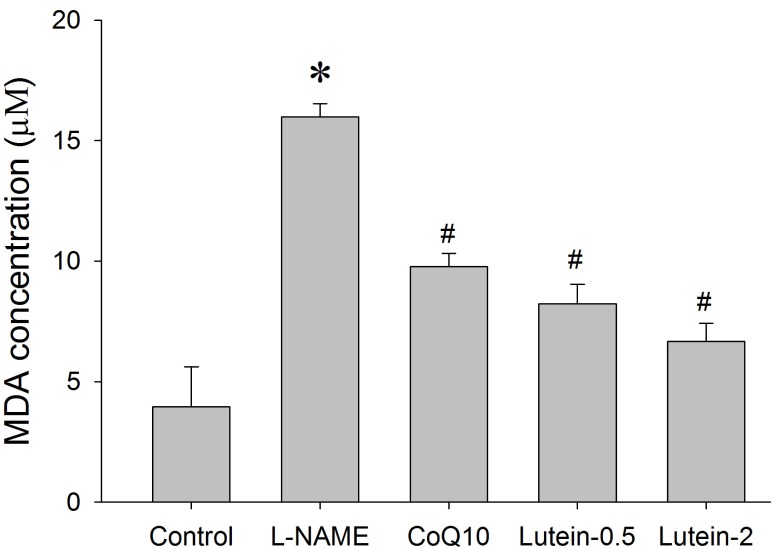 | Fig. 8Effect of lutein on the plasma malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |
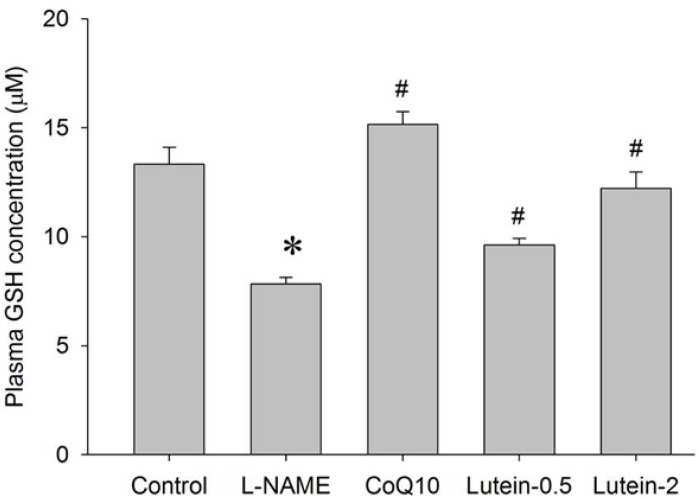 | Fig. 9Effect of lutein on the plasma glutathione (GSH) concentration in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive rats. L-NAME rats fed 40 mg/kg L-NAME. L-NAME+CoQ10 rats fed L-NAME with 10 mg/kg coenzyme Q10. L-NAME+Lutein-0.5 rats fed L-NAME with 0.5 mg/kg lutein. L-NAME+Lutein-2 rats fed L-NAME with 2 mg/kg lutein. Results are expressed as mean±standard deviation of seven animals. *p<0.05 vs. normal control group, #p<0.05 vs. L-NAME control group. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download